Top Related Projects
Quickly switch windows in Emacs
Emacs package that displays available keybindings in popup
Emacs incremental completion and selection narrowing framework
Quick Overview
Avy is a GNU Emacs package that provides a quick and efficient way to move the point (cursor) to any visible location in the current window. It works by assigning a short sequence of characters to each possible target location, allowing users to jump to their desired position by typing the corresponding sequence.
Pros
- Fast and efficient cursor movement without using the mouse
- Highly customizable, allowing users to tailor the behavior to their preferences
- Works seamlessly with various Emacs modes and configurations
- Improves productivity by reducing the time spent navigating through text
Cons
- Requires a learning curve to become proficient with the key sequences
- May feel unintuitive for users accustomed to traditional cursor movement methods
- Can be visually distracting when the overlay characters appear on screen
- Limited usefulness in very small buffers or when the target is already nearby
Code Examples
- Basic usage to jump to a character:
(avy-goto-char ?a)
This command will highlight all visible 'a' characters and allow you to jump to one by typing its assigned sequence.
- Jumping to a line:
(avy-goto-line)
This command assigns sequences to each visible line, allowing you to quickly navigate to any line in the buffer.
- Using Avy to select a region:
(avy-mark-region)
This command lets you select a region by jumping to its start and end points using Avy.
Getting Started
To start using Avy in your Emacs configuration:
- Install Avy using your preferred package manager (e.g.,
package.eloruse-package). - Add the following to your Emacs configuration file:
(require 'avy)
(global-set-key (kbd "C-:") 'avy-goto-char)
(global-set-key (kbd "C-'") 'avy-goto-char-2)
(global-set-key (kbd "M-g f") 'avy-goto-line)
(global-set-key (kbd "M-g w") 'avy-goto-word-1)
This sets up some basic keybindings for common Avy commands. Adjust the key combinations as desired.
Competitor Comparisons
Quickly switch windows in Emacs
Pros of ace-window
- Specifically designed for window management and navigation
- Provides a visual overlay for easy window selection
- Offers additional window manipulation commands (e.g., swap, delete)
Cons of ace-window
- Limited to window operations, less versatile than avy
- May have a steeper learning curve for new users
- Requires more screen space for displaying window labels
Code Comparison
ace-window:
(defun aw-select (mode-line &optional action)
(let ((start-window (selected-window))
(next-window-scope (cl-case aw-scope
('global 'visible)
('frame 'frame)
('visible 'visible))))
(setq aw-mode-line-string mode-line)
(aw-update)
(aw-set-mode-line)))
avy:
(defun avy-goto-char (char &optional arg)
"Jump to the currently visible CHAR.
The window scope is determined by `avy-all-windows' (ARG negates it)."
(interactive (list (read-char "char: " t)
current-prefix-arg))
(avy-with avy-goto-char
(avy-process
(avy--regex-candidates
(regexp-quote (string char))))))
Emacs package that displays available keybindings in popup
Pros of which-key
- Provides a comprehensive key binding discovery system
- Offers customizable display options for key bindings
- Integrates well with various Emacs modes and packages
Cons of which-key
- May introduce a slight delay when displaying key bindings
- Requires more setup and configuration compared to avy
- Can be overwhelming for new users due to the amount of information displayed
Code Comparison
which-key:
(which-key-mode)
(setq which-key-idle-delay 0.5)
(setq which-key-side-window-location 'bottom)
avy:
(global-set-key (kbd "C-:") 'avy-goto-char)
(avy-setup-default)
(setq avy-background t)
which-key focuses on displaying available key bindings, while avy provides quick navigation within visible text. which-key is more about discoverability and learning, whereas avy emphasizes efficient movement and selection. Both packages enhance the Emacs experience in different ways, with which-key being more suited for exploration and avy for rapid navigation.
Emacs incremental completion and selection narrowing framework
Pros of Helm
- Comprehensive framework for incremental narrowing and selection
- Extensive customization options and plugins ecosystem
- Powerful integration with various Emacs features and external tools
Cons of Helm
- Steeper learning curve due to its complexity
- Can be resource-intensive, especially on larger projects
- May feel overwhelming for users who prefer simpler, focused tools
Code Comparison
Helm configuration example:
(require 'helm)
(require 'helm-config)
(helm-mode 1)
(global-set-key (kbd "M-x") #'helm-M-x)
(global-set-key (kbd "C-x C-f") #'helm-find-files)
Avy usage example:
(require 'avy)
(global-set-key (kbd "C-:") 'avy-goto-char)
(global-set-key (kbd "C-'") 'avy-goto-char-2)
(global-set-key (kbd "M-g f") 'avy-goto-line)
Summary
Helm is a powerful, feature-rich framework for Emacs that provides extensive functionality for narrowing and selection tasks. It offers deep integration with various Emacs features and external tools, making it a comprehensive solution for many users. However, its complexity can be overwhelming for some, and it may have a performance impact on larger projects.
Avy, on the other hand, is a more focused tool that excels at quick navigation within buffers. It's lightweight, easy to learn, and provides efficient movement without the overhead of a full framework. While it lacks the breadth of features found in Helm, Avy's simplicity and speed make it an attractive option for users who prioritize fast, targeted navigation.
Convert  designs to code with AI
designs to code with AI

Introducing Visual Copilot: A new AI model to turn Figma designs to high quality code using your components.
Try Visual CopilotREADME
Introduction
avy is a GNU Emacs package for jumping to visible text using a char-based decision tree. See also ace-jump-mode and vim-easymotion - avy uses the same idea.
![]()
Command overview
You can bind some of these useful commands in your config.
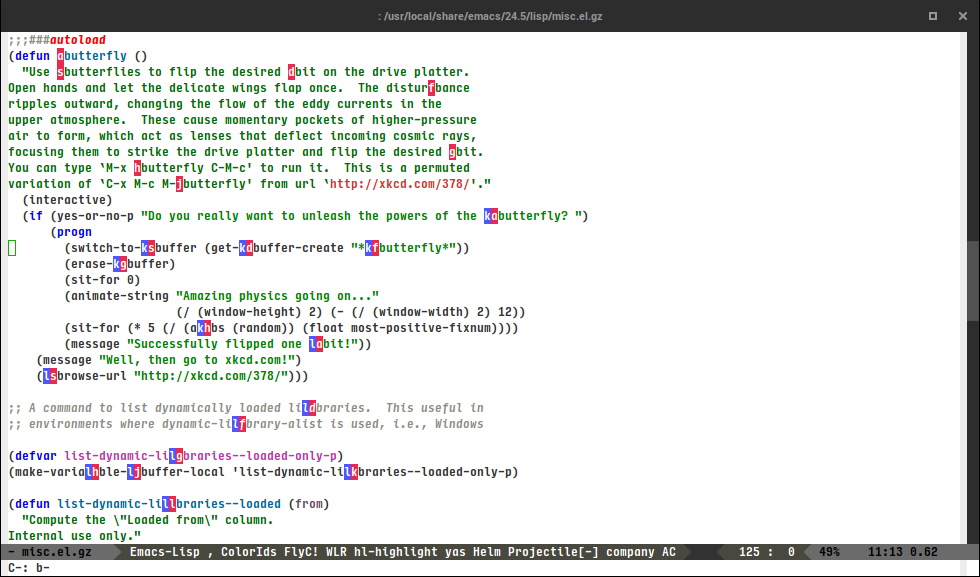
avy-goto-char
Input one char, jump to it with a tree.
(global-set-key (kbd "C-:") 'avy-goto-char)
After C-: b:
avy-goto-char-2
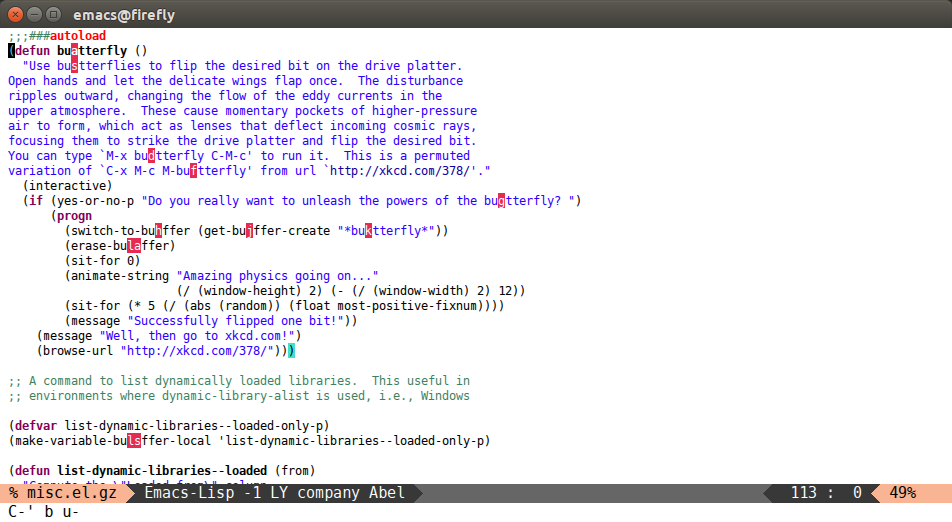
Input two consecutive chars, jump to the first one with a tree.
The advantage over the previous one is less candidates for the tree search. And it's not too inconvenient to enter two consecutive chars instead of one.
(global-set-key (kbd "C-'") 'avy-goto-char-2)
After C-' bu:
avy-goto-char-timer
Input an arbitrary amount of consecutive chars, jump to the first one with a tree.
This is a more flexible version of avy-goto-char-2. First part works similarly to isearch: you type a query and it's highlighted dynamically on the screen. When you stop typing for avy-timeout-seconds (0.5s by default), you'll be able to select one of the candidates with avy. As you're inputting characters, you can use C-h (backspace) or DEL (delete) to
forget the last typed character and RET to end the input sequence immediately and select a candidate.
avy-goto-line
Input zero chars, jump to a line start with a tree.
(global-set-key (kbd "M-g f") 'avy-goto-line)
After M-g f:
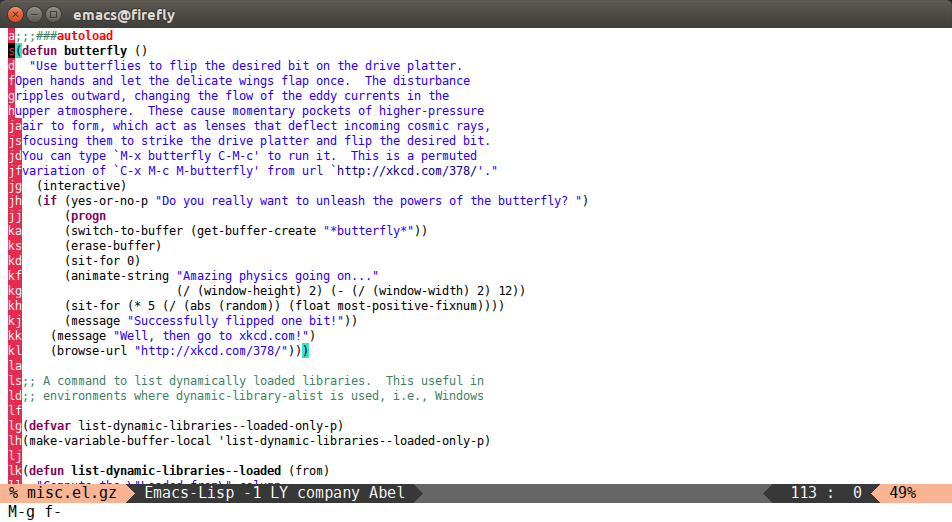
You can actually replace the M-g g binding of goto-line, since if you enter a digit for avy-goto-line, it will switch to goto-line with that digit already entered.
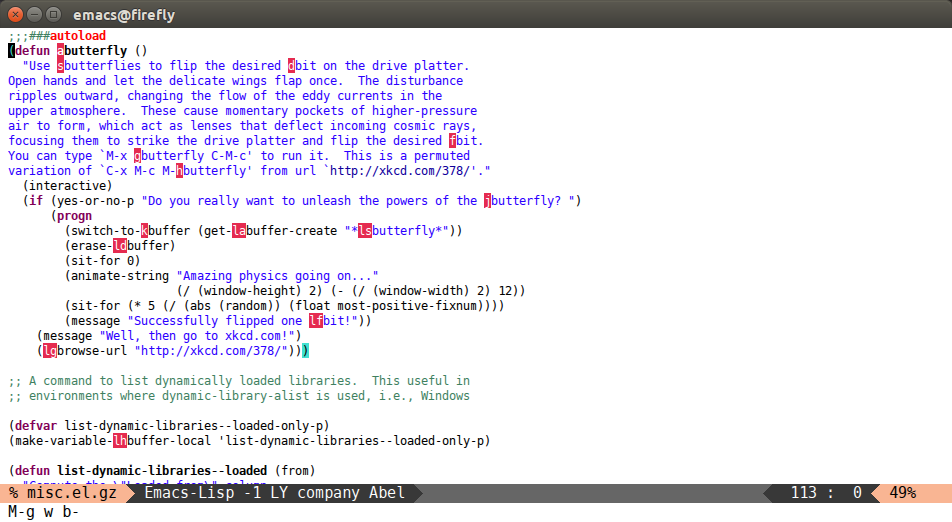
avy-goto-word-1
Input one char at word start, jump to a word start with a tree.
(global-set-key (kbd "M-g w") 'avy-goto-word-1)
After M-g wb:
avy-goto-word-0
Input zero chars, jump to a word start with a tree.
Compared to avy-goto-word-1, there are a lot more candidates. But at a least there's not need to input the initial char.
(global-set-key (kbd "M-g e") 'avy-goto-word-0)
After M-g e:
Org-mode commands
avy-org-goto-heading-timer: Type part of an Org heading. When you stop typing, if only one heading on the screen matches, it will be jumped to; if more than one matches, you can jump to a heading with Avy. This is likeavy-goto-char-timerbut for Org headings.avy-org-refile-as-child: With point in an entry you want to refile, run this command, select a heading with Avy, and the entry will be refiled as its first child heading. This makes it quick and easy to refile to headings that are visible on-screen, even to other windows or buffers.
Other commands
There are some more commands which you can explore yourself by looking at the code.
Bindings
You add this to your config to bind some stuff:
(avy-setup-default)
(global-set-key (kbd "C-c C-j") 'avy-resume)
It will bind, for example, avy-isearch to C-' in isearch-mode-map, so that you can select one of the currently visible isearch candidates using avy.
Customization
See the comprehensive custom variable list on the defcustom wiki page.
See how to write your own avy commands on the custom-commands wiki page.
Contributing
Copyright Assignment
Avy is subject to the same copyright assignment policy as Emacs itself, org-mode, CEDET and other packages in GNU ELPA. Any legally significant contributions can only be accepted after the author has completed their paperwork. Please see the request form if you want to proceed.
The copyright assignment isn't a big deal, it just says that the copyright for your submitted changes to Emacs belongs to the FSF. This assignment works for all projects related to Emacs. To obtain it, you need to send one email, then send one letter (if you live in the US, it's digital), and wait for some time (in my case, I had to wait for one month).
Style
The basic code style guide is to use (setq indent-tabs-mode nil). It is provided for you in .dir-locals.el, please obey it.
Before submitting the change, run make compile and make test to make sure that it doesn't introduce new compile warnings or test failures. Also run make checkdoc to see that your changes obey the documentation guidelines.
Use your own judgment for the commit messages, I recommend a verbose style using magit-commit-add-log.
Top Related Projects
Quickly switch windows in Emacs
Emacs package that displays available keybindings in popup
Emacs incremental completion and selection narrowing framework
Convert  designs to code with AI
designs to code with AI

Introducing Visual Copilot: A new AI model to turn Figma designs to high quality code using your components.
Try Visual Copilot