 AidLearning-FrameWork
AidLearning-FrameWork
🔥🔥🔥AidLearning is a powerful AIOT development platform, AidLearning builds a linux env supporting GUI, deep learning and visual IDE on Android...Now Aid supports CPU+GPU+NPU for inference with high performance acceleration...Linux on Android or HarmonyOS
Top Related Projects
Termux - a terminal emulator application for Android OS extendible by variety of packages.
Open source UI framework written in Python, running on Windows, Linux, macOS, Android and iOS
PyTorch android examples of usage in applications
TensorFlow examples
Kotlin/Native infrastructure
Quick Overview
AidLearning-FrameWork is an AI development platform for mobile devices, particularly Android phones and tablets. It provides a complete Linux environment with pre-installed deep learning frameworks, allowing users to develop and run AI applications directly on their mobile devices without the need for cloud services or powerful desktop computers.
Pros
- Enables AI development and deployment on mobile devices
- Includes pre-installed popular deep learning frameworks (TensorFlow, PyTorch, Keras)
- Provides a full Linux environment with GUI support
- Offers easy installation and setup process
Cons
- May have performance limitations compared to desktop or cloud-based AI development
- Requires significant storage space on the mobile device
- Limited to Android devices, not available for iOS
- May drain battery faster due to intensive computations
Getting Started
- Download the AidLearning app from the Google Play Store or the project's GitHub releases page.
- Install the app on your Android device (Android 6.0 or higher required).
- Launch the app and follow the on-screen instructions to set up the Linux environment.
- Once setup is complete, you can access the Linux terminal, use pre-installed AI frameworks, and develop your AI applications.
Example commands to get started:
# Update the system
apt update && apt upgrade
# Launch Python and import TensorFlow
python3
>>> import tensorflow as tf
>>> print(tf.__version__)
# Clone a sample AI project
git clone https://github.com/aidlearning/AidLearning-FrameWork.git
cd AidLearning-FrameWork/examples
# Run a sample AI script
python3 mnist_example.py
Note: Specific code examples are not provided as this is not a traditional code library, but rather a development environment for running various AI frameworks and applications on mobile devices.
Competitor Comparisons
Termux - a terminal emulator application for Android OS extendible by variety of packages.
Pros of Termux
- Lightweight and efficient, focusing on providing a Linux terminal environment
- Extensive package repository with a wide range of tools and utilities
- Active community and regular updates
Cons of Termux
- Limited GUI support, primarily focused on command-line interface
- Requires more technical knowledge to set up and use effectively
- May not provide as comprehensive an AI development environment out-of-the-box
Code Comparison
Termux (package installation):
pkg install python
pip install numpy scipy matplotlib
AidLearning-FrameWork (AI-related code):
import torch
import torchvision
model = torchvision.models.resnet18(pretrained=True)
The code snippets highlight the different focus areas of the two projects. Termux emphasizes package management and system-level operations, while AidLearning-FrameWork provides pre-configured AI development tools and libraries.
AidLearning-FrameWork offers a more comprehensive AI development environment with pre-installed libraries and GUI support, making it easier for beginners to start with AI projects. However, Termux provides a more flexible and customizable Linux environment, allowing users to install and configure their preferred tools and libraries.
Both projects have their strengths, with Termux being more suitable for general-purpose Linux usage on Android, and AidLearning-FrameWork catering specifically to AI developers looking for a ready-to-use environment on mobile devices.
Open source UI framework written in Python, running on Windows, Linux, macOS, Android and iOS
Pros of Kivy
- Cross-platform compatibility (desktop and mobile)
- Large and active community with extensive documentation
- Flexible and customizable UI design with Python
Cons of Kivy
- Steeper learning curve for beginners
- Limited native look and feel on some platforms
- Performance can be slower compared to native solutions
Code Comparison
Kivy:
from kivy.app import App
from kivy.uix.button import Button
class MyApp(App):
def build(self):
return Button(text='Hello World')
MyApp().run()
AidLearning-FrameWork:
import cv2
import numpy as np
from cvs import *
def main():
img = np.zeros((300, 300, 3), np.uint8)
cv2.putText(img, "Hello World", (50, 150), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, (255, 255, 255), 2)
imshow(img)
main()
The Kivy example demonstrates a simple GUI application with a button, while the AidLearning-FrameWork example shows image processing and display capabilities. Kivy focuses on cross-platform GUI development, whereas AidLearning-FrameWork is tailored for AI and computer vision tasks on mobile devices.
PyTorch android examples of usage in applications
Pros of android-demo-app
- Focused specifically on Android development with PyTorch
- Provides ready-to-use demo applications for common ML tasks
- Easier integration for developers already familiar with Android ecosystem
Cons of android-demo-app
- Limited to Android platform, less versatile than AidLearning-FrameWork
- May require more setup and configuration for complex ML projects
- Less comprehensive in terms of overall AI development environment
Code Comparison
AidLearning-FrameWork:
import cv2
import numpy as np
from cvs import *
def process_frame(frame):
# AI processing logic here
return processed_frame
cvs = CVS()
cvs.run(process_frame)
android-demo-app:
import org.pytorch.IValue;
import org.pytorch.Module;
import org.pytorch.Tensor;
Module module = Module.load(assetFilePath(this, "model.pt"));
Tensor inputTensor = Tensor.fromBlob(inputArray, inputShape);
Tensor outputTensor = module.forward(IValue.from(inputTensor)).toTensor();
The AidLearning-FrameWork code snippet shows a more Python-centric approach with OpenCV integration, while the android-demo-app example demonstrates Java-based PyTorch model loading and inference on Android.
TensorFlow examples
Pros of TensorFlow Examples
- Comprehensive collection of TensorFlow examples covering various ML tasks
- Well-maintained and regularly updated by the TensorFlow team
- Extensive documentation and explanations for each example
Cons of TensorFlow Examples
- Focused solely on TensorFlow, lacking support for other AI frameworks
- Requires separate setup and configuration of development environment
- May be overwhelming for beginners due to the large number of examples
Code Comparison
AidLearning-FrameWork:
import cv2
import numpy as np
from cvs import *
def process_image(image):
# Image processing code here
return processed_image
show_img(process_image(read_img("input.jpg")))
TensorFlow Examples:
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
model = keras.Sequential([
keras.layers.Dense(64, activation='relu'),
keras.layers.Dense(10, activation='softmax')
])
model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='categorical_crossentropy')
The AidLearning-FrameWork example focuses on image processing with OpenCV, while the TensorFlow Examples code demonstrates building a simple neural network model. AidLearning-FrameWork provides a more integrated environment for AI development on mobile devices, whereas TensorFlow Examples offers a wider range of machine learning examples across various domains.
Kotlin/Native infrastructure
Pros of kotlin-native
- Allows Kotlin code to be compiled to native binaries without a VM
- Supports cross-platform development for iOS, macOS, Android, Windows, Linux
- Integrates well with existing Kotlin and Java codebases
Cons of kotlin-native
- Steeper learning curve compared to AidLearning-FrameWork
- More complex setup and configuration required
- Limited support for some Kotlin features in native code
Code Comparison
kotlin-native example:
fun main() {
println("Hello, Kotlin/Native!")
}
AidLearning-FrameWork example:
import cv2
img = cv2.imread("image.jpg")
cv2.imshow("Image", img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
The kotlin-native example shows a simple "Hello World" program, while the AidLearning-FrameWork example demonstrates basic image processing using OpenCV. This highlights the different focus areas of the two projects - kotlin-native for native compilation of Kotlin code, and AidLearning-FrameWork for AI and computer vision tasks on mobile devices.
Convert  designs to code with AI
designs to code with AI

Introducing Visual Copilot: A new AI model to turn Figma designs to high quality code using your components.
Try Visual CopilotREADME
AidLux 1.3 æ£å¼åå¸ï¼(è§çè§é¢â¬ï¸ðº)
AIï¼Androidï¼Linuxï¼ARMï¼åºäºAndroid+LinuxèåçæçAIåºç¨å¼åå¹³å°ã [English]
[AidLux](https://docs.aidlux.com) æ¯ä¸ä¸ªåºäºARMæ建ï¼åæ¶æ¯æå¤çæèåï¼Android+Linuxï¼ç¯å¢çAIåºç¨å¼ååé¨ç½²å¹³å°ï¼ä¸ºå¼åè 带æ¥å¼ºå¤§ãç®åãæ éåæå¯è½çå¥å¦ä½éªï¼
AidLuxèåæ¶æï¼å®ç°å¤çæè¶ çº§å å
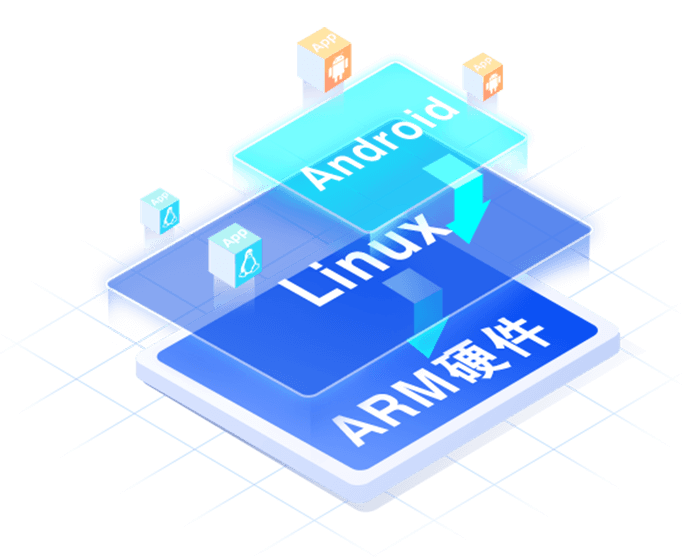
éè¿å
±äº«Android Linux kernelæ建äºå®æ´çLinuxç³»ç»ç¯å¢ï¼å¹¶ä¸ä¸Androidç³»ç»ç¯å¢åæ¶æä¾ç¨æ·è®¿é®ãå¨ä¸ºç¨æ·æä¾ååçLinuxç³»ç»ç±»ä¼¼çå½ä»¤è¡ä½¿ç¨ä½éªï¼å¦éè¿ apt å½ä»¤è¿è¡å
管çï¼çåæ¶ï¼åºäºWebæ建äºå¾å½¢åæ¡é¢ç¯å¢ï¼ç¨æ·å¯ä»¥ç´æ¥éè¿è§¦æ¸å±ææµè§å¨è®¿é®ã
AidLuxè¡¥å ¨äºAIè¿è¡æéçææåºç¡ç§å¦è®¡ç®å /åºï¼æ¯æäºä¸ç主æµæ·±åº¦å¦ä¹ æ¡æ¶ï¼å¹¶å ç½®èªä¸»ç åçAIæºè½å éææ¯ï¼ä¸ºå¼åè æä¾äºä¸ä¸ªâAI 就绪âçåºç¨å¼åå¹³å°ã
Android+Linux å ±ç, 1+1>2
-
ä¸é¨è®¾å¤åæ¶è¿è¡ä¸¤ä¸ªç³»ç»ç¯å¢ï¼æ¢æ¯ä¸é¨Android设å¤ï¼åæ¶ä¹æ¯ä¸é¨Linux设å¤ã两个çæçèµæºä¼å¿å¯åæ¶è¢«å 以å©ç¨ã
-
跨系ç»æ ç¼äº¤äºï¼é«æï¼å®å ¨ï¼ç¨³å®ãAndroidåºç¨ä¸Linuxåºç¨å®ç°æ¬å°é«æç´æ¥è®¿é®ï¼æ éå¤é¨æ¥å£ï¼å¦ç½ç»ï¼ï¼å åéæ¾ç¡¬ä»¶æè½ã Androidè´è´£ç¨æ·äº¤äºï¼Linuxè´è´£æå¡æ¯æçæ°ååºç¨å½¢æçå¾ ä½ çå¥æå¦æ³ã
-
é对已æåºç¨ï¼AndroidæLinuxï¼ï¼å¯è½»æ¾è·å¾è·¨ç³»ç»åè½æ¯æï¼ä½¿åºç¨åè½æ´å 强大ï¼å åä¿æ¤å·²æå¼åæå ¥ã
-
ä¸é®å®è£ ãèªå¨é¨ç½²ãAppå¼å¯å¨ï¼è¿ç¨å¿«éãç®åã
ä½AIå¼åé¨æ§, å¿«éãç®åãæè´æ§è½
-
éæä¸ç主æµAI深度å¦ä¹ æ¡æ¶ï¼æ éé ç½®ï¼å®è£ å³ç¨ï¼æ大çéä½äºAIå¼åååºç¨é¨ç½²çç¯å¢é ç½®å¤æ度ï¼å¤§å¹ åå°äºç¸å ³çæ¶é´æå ¥ã æ¡æ¶æ¯æå¦ä¸ï¼
TensorFlow PyTorch Caffe MXNet Keras MindSpore PandlePandle TNN MNN SNPE â â â â â â â â â â -
å ç½®åæ°æ§çCPU+GPU+NPUæºè½å éææ¯ï¼éè¿â硬件+æ¡æ¶+Op"å¤å±ä¼åï¼èµäºæ·±åº¦å¦ä¹ è¿ç®æ§è½çå¤§å¹ åº¦æåã并ä¸æä¾ç»ä¸APIæ¥å£ï¼å¨æ¹ä¾¿å¼åè è°ç¨çåæ¶ï¼è¿æ¯æä¸åAIæ¡æ¶æ¨¡åèªå¨è½¬æ¢ã以ä¸æµè¯ä¸ºåºäºç¸åARM设å¤ï¼å¨LinuxãAidLuxä¸æµè¯è·å¾ãå项æµè¯è¿è¡20次åèæ¶ï¼çºµè½´ï¼å¹³åå¼ã
-
å¨Wizardä¸è¿è¡ææ½å¼AIåºç¨å¼åï¼AIç»ä»¶å¿«éèµè½ï¼1åéçæä½ ç第ä¸ä¸ªAIåºç¨ï¼
-
å 置丰å¯AIåºç¨æ¡ä¾å对åºä»£ç ï¼æ¹ä¾¿å¼åè è½å¿«éå ¥é¨ã
便æºãå¼æ¾ãä¸ç«å¼
-
AidLux äºæ¡é¢ç³»ç»ï¼æ¯æä»PC, å¹³æ¿, ææºçå¤ç§å±å¹éæ¶éå°åæ¶è®¿é®ï¼å®ç°ä½ çè¶ çº§ç§»å¨å¼åå¹³å°ã å¿«éè¿PCä¸çæµè§å¨ï¼è¾å ¥äºæ¡é¢å°åï¼è®¿é®ä½ ææºä¸çAidLuxæ¡é¢å§ï¼
-
æµ·éå¤è®¾è½»æ¾æ¯æ(ç½ç»ãUSBã串å£ã...)ï¼åæ空é´æ éæ©å±ã
-
æ¯æVSCode, Jupyter notebook çå¤ç§å¼æºå¼åå·¥å ·åPython, C/C++, Java, JavaScriptçå¼åè¯è¨ã
-
ä¸ç«å¼å¼åãæµè¯ãé¨ç½²å ¨æµç¨æ¯æï¼AidLuxå ³æ³¨æçï¼æ¨å ³æ³¨åæï¼
ApkBuildåºç¨ï¼å¯ä»¥å¿«éå°åºäºPythonå¼åç项ç®æå æAPKè¿è¡åå¸ï¼æ¹ä¾¿ç¨æ·å¨å ¶å®Androidç³»ç»è¿è¡é¨ç½²ã
ç®åï¼AidLuxå·²å¨å大Appåºç¨ä¸å¿ä¸çº¿ï¼ä¸è½½å¯å¨æ¬¡æ°200ä¸+ã
å¼å§ä½¿ç¨
ç¹å»ä»¥ä¸é¾æ¥å³å¯ä¸è½½ææ°çå®è£ å ãAidLux v1.3.0ã
è´¡ç®ä¸åä¸
QQ交æµç¾¤
License
è´è°¢
AidLuxåä¸äººåï¼billãflayãgondonãwillamãguguãyoline777ãqidisoãyugeãmuzi_ysçã
ä¸å项ç®ï¼
- VTE (libvte): Terminal emulator widget for GTK+, mainly used in gnome-terminal. Source, Open Issues, and All (including closed) issues.
- iTerm 2: OS X terminal application. Source, Issues and Documentation (which includes iTerm2 proprietary escape codes).
- Konsole: KDE terminal application. Source, in particular tests, Bugs and Wishes.
- hterm: JavaScript terminal implementation from Chromium. Source, including tests, and Google group.
- xterm: The grandfather of terminal emulators. Source.
- Connectbot: Android SSH client. Source
- Android Terminal Emulator: Android terminal app which Termux terminal handling is based on. Inactive. Source.
- Termux: Android terminal and Linux environment - app repository. Source.
- remi:Python REMote Interface library. Platform independent. In about 100 Kbytes, perfect for your diet.Source.
- Caffe
- Tensorflow
- Mxnet
- Keras
- ncnn
- pytorch
- opencv
- macUI
Top Related Projects
Termux - a terminal emulator application for Android OS extendible by variety of packages.
Open source UI framework written in Python, running on Windows, Linux, macOS, Android and iOS
PyTorch android examples of usage in applications
TensorFlow examples
Kotlin/Native infrastructure
Convert  designs to code with AI
designs to code with AI

Introducing Visual Copilot: A new AI model to turn Figma designs to high quality code using your components.
Try Visual Copilot





