 shardingsphere
shardingsphere
Empowering Data Intelligence with Distributed SQL for Sharding, Scalability, and Security Across All Databases.
Top Related Projects
Free and Open Source, Distributed, RESTful Search Engine
Vitess is a database clustering system for horizontal scaling of MySQL.
CockroachDB — the cloud native, distributed SQL database designed for high availability, effortless scale, and control over data placement.
YugabyteDB - the cloud native distributed SQL database for mission-critical applications.
TiDB - the open-source, cloud-native, distributed SQL database designed for modern applications.
Quick Overview
Apache ShardingSphere is an open-source ecosystem for distributed database solutions. It provides a sharding-scaling, distributed transaction, and database governance platform, aiming to transform any database into a distributed database system while enhancing it with sharding, elastic scaling, encryption features, and more.
Pros
- Flexible and powerful sharding strategies for horizontal scaling
- Supports multiple databases (MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, SQLServer)
- Provides distributed transaction capabilities
- Offers database governance features like dynamic configuration, monitoring, and security
Cons
- Steep learning curve for complex configurations
- Performance overhead for certain operations due to additional abstraction layer
- Limited support for NoSQL databases
- May require significant changes to existing applications for full utilization
Code Examples
- Basic sharding configuration:
ShardingRuleConfiguration shardingRuleConfig = new ShardingRuleConfiguration();
shardingRuleConfig.getTableRuleConfigs().add(getOrderTableRuleConfiguration());
shardingRuleConfig.getTableRuleConfigs().add(getOrderItemTableRuleConfiguration());
shardingRuleConfig.getBindingTableGroups().add("t_order, t_order_item");
- Distributed transaction usage:
TransactionTypeHolder.set(TransactionType.XA);
try (Connection conn = dataSource.getConnection()) {
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
// Execute SQL statements
conn.commit();
} catch (SQLException ex) {
conn.rollback();
}
- Encryption configuration:
EncryptRuleConfiguration encryptRuleConfig = new EncryptRuleConfiguration();
encryptRuleConfig.getEncryptors().put("aes_encryptor", new EncryptorRuleConfiguration("AES", new Properties()));
EncryptColumnRuleConfiguration columnConfig = new EncryptColumnRuleConfiguration("", "user_encrypt", "", "aes_encryptor");
encryptRuleConfig.getTables().put("t_user", new EncryptTableRuleConfiguration(Collections.singletonMap("user_id", columnConfig)));
Getting Started
- Add ShardingSphere dependency to your project:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shardingsphere</groupId>
<artifactId>shardingsphere-jdbc-core</artifactId>
<version>5.1.1</version>
</dependency>
- Configure sharding rule in your application:
DataSource dataSource = ShardingSphereDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(
createDataSourceMap(), Collections.singleton(createShardingRuleConfiguration()), new Properties());
- Use the configured DataSource in your application:
String sql = "SELECT * FROM t_order WHERE user_id = ?";
try (
Connection conn = dataSource.getConnection();
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql)) {
ps.setInt(1, 10);
try (ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery()) {
while (rs.next()) {
// Process result set
}
}
}
Competitor Comparisons
Free and Open Source, Distributed, RESTful Search Engine
Pros of Elasticsearch
- Powerful full-text search capabilities with advanced querying and analytics
- Distributed architecture for high scalability and fault tolerance
- Rich ecosystem with extensive plugins and integrations
Cons of Elasticsearch
- Higher resource consumption, especially for large-scale deployments
- Steeper learning curve for complex configurations and optimizations
- Limited support for ACID transactions compared to traditional databases
Code Comparison
Elasticsearch query example:
GET /my_index/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"title": "elasticsearch"
}
}
}
ShardingSphere SQL example:
SELECT * FROM t_order WHERE order_id = 1
Key Differences
- Elasticsearch is primarily a search and analytics engine, while ShardingSphere focuses on database sharding and scaling
- ShardingSphere provides a SQL-based interface, whereas Elasticsearch uses a REST API with JSON-based queries
- Elasticsearch excels in full-text search and log analysis, while ShardingSphere is better suited for distributed relational database management
Both projects serve different primary purposes but can be complementary in certain scenarios. Elasticsearch is ideal for search-heavy applications, while ShardingSphere is better for scaling traditional relational databases across multiple nodes.
Vitess is a database clustering system for horizontal scaling of MySQL.
Pros of Vitess
- More mature project with longer history and wider adoption in production environments
- Better support for large-scale horizontal sharding and multi-datacenter replication
- Native integration with Kubernetes for easier deployment and scaling
Cons of Vitess
- Steeper learning curve and more complex setup compared to ShardingSphere
- Limited support for databases other than MySQL
- Less flexibility in terms of customization and extensibility
Code Comparison
Vitess (VTGate query routing):
func (vtg *VTGate) ExecuteKeyspaceIds(ctx context.Context, sql string, bindVariables map[string]*querypb.BindVariable, keyspace string, keyspaceIds [][]byte, tabletType topodatapb.TabletType, session *vtgatepb.Session, notInTransaction bool, options *querypb.ExecuteOptions) (*sqltypes.Result, error) {
// Implementation details
}
ShardingSphere (ShardingRule):
public final class ShardingRule implements BaseRule {
private final ShardingRuleConfiguration ruleConfiguration;
private final ShardingDataSourceNames shardingDataSourceNames;
// More fields and methods
}
Both projects aim to solve database scaling challenges, but Vitess focuses more on horizontal sharding for MySQL, while ShardingSphere provides a more general-purpose sharding solution with support for multiple databases. Vitess excels in large-scale deployments, while ShardingSphere offers more flexibility and easier integration for smaller to medium-sized applications.
CockroachDB — the cloud native, distributed SQL database designed for high availability, effortless scale, and control over data placement.
Pros of CockroachDB
- Fully distributed SQL database with strong consistency and high availability
- Built-in support for geo-partitioning and multi-region deployments
- Automatic sharding and rebalancing without manual intervention
Cons of CockroachDB
- Higher resource requirements and potentially higher operational costs
- Steeper learning curve for administrators unfamiliar with distributed systems
- Limited support for certain SQL features and stored procedures
Code Comparison
CockroachDB (Go):
func (n *Node) startGossip(ctx context.Context, stopper *stop.Stopper) {
n.gossip.Start(n.grpcServer.Addr())
n.gossip.EnableSimulationCycles()
n.storePool.Start(stopper, n.gossip)
}
ShardingSphere (Java):
public final class ShardingDataSource extends AbstractDataSourceAdapter {
public ShardingDataSource(final Map<String, DataSource> dataSourceMap,
final ShardingRule shardingRule,
final Properties props) throws SQLException {
super(dataSourceMap);
this.shardingContext = new ShardingContext(dataSourceMap, shardingRule, props);
}
}
ShardingSphere focuses on database sharding and distributed transaction management, while CockroachDB is a complete distributed SQL database solution. ShardingSphere offers more flexibility in integrating with existing databases, whereas CockroachDB provides a more comprehensive out-of-the-box distributed database experience.
YugabyteDB - the cloud native distributed SQL database for mission-critical applications.
Pros of YugabyteDB
- Fully distributed SQL database with high availability and horizontal scalability
- Native multi-region and multi-cloud support
- ACID-compliant transactions with strong consistency
Cons of YugabyteDB
- Steeper learning curve for deployment and management
- Limited ecosystem compared to more established databases
- Higher resource requirements for small-scale deployments
Code Comparison
YugabyteDB (C++):
Status YBClient::CreateTable(const string& table_name,
const Schema& schema,
const CreateTableOptions& opts) {
return impl_->CreateTable(table_name, schema, opts);
}
ShardingSphere (Java):
public final class ShardingRule implements BaseRule {
private final ShardingRuleConfiguration ruleConfiguration;
private final ShardingDataSourceNames shardingDataSourceNames;
private final Collection<TableRule> tableRules;
}
YugabyteDB focuses on distributed SQL implementation, while ShardingSphere provides a sharding layer for existing databases. YugabyteDB's code deals with table creation in a distributed environment, whereas ShardingSphere's code defines sharding rules and configurations. Both projects aim to improve database scalability and performance, but with different approaches and architectures.
TiDB - the open-source, cloud-native, distributed SQL database designed for modern applications.
Pros of TiDB
- Designed as a distributed NewSQL database, offering strong consistency and horizontal scalability
- Built-in support for HTAP (Hybrid Transactional/Analytical Processing) workloads
- Native compatibility with MySQL protocol, making migration easier
Cons of TiDB
- Higher resource requirements and complexity for deployment
- Steeper learning curve due to its distributed nature and unique architecture
- Limited support for certain advanced MySQL features
Code Comparison
TiDB (SQL parser example):
func (p *Parser) parseSelectStmt(ctx context.Context) (ast.StmtNode, error) {
lexer := p.lexer
if err := lexer.NextTokenAfterWhitespace(); err != nil {
return nil, errors.Trace(err)
}
// ... (additional parsing logic)
}
ShardingSphere (SQL parser example):
public final class SQLParserEngine {
public SQLStatement parse(final String sql, final boolean useCache) {
ParsingHook parsingHook = new ParsingHook();
parsingHook.start(sql);
try {
// ... (parsing logic)
} finally {
parsingHook.finishSuccess();
}
}
}
Both projects implement SQL parsing, but TiDB uses Go while ShardingSphere uses Java. TiDB's parser is more tightly integrated with its distributed architecture, while ShardingSphere's parser is designed for flexibility across different database systems.
Convert  designs to code with AI
designs to code with AI

Introducing Visual Copilot: A new AI model to turn Figma designs to high quality code using your components.
Try Visual CopilotREADME
Distributed SQL transaction & query engine for data sharding, scaling, encryption, and more - on any database.
Official Website: https://shardingsphere.apache.org/

|

|

|
|---|
OVERVIEW
Apache ShardingSphere is a distributed SQL transaction & query engine that allows for data sharding, scaling, encryption, and more - on any database. Our community's guiding development concept is Database Plus for creating a complete ecosystem that allows you to transform any database into a distributed database system.
It focuses on repurposing existing databases, by placing a standardized upper layer above existing and fragmented databases, rather than creating a new database.
The goal is to provide unified database services and minimize or eliminate the challenges caused by underlying databases' fragmentation. This results in applications only needing to communicate with a single standardized service.
The concepts at the core of the project are Connect, Enhance and Pluggable.
Connect:Flexible adaptation of database protocol, SQL dialect and database storage. It can quickly connect applications and heterogeneous databases.Enhance:Capture database access entry to provide additional features transparently, such as: redirect (sharding, readwrite-splitting and shadow), transform (data encrypt and mask), authentication (security, audit and authority), governance (circuit breaker and access limitation and analyze, QoS and observability).Pluggable:Leveraging the micro kernel and 3 layers pluggable mode, features and database ecosystem can be embedded flexibly. Developers can customize their ShardingSphere just like building with LEGO blocks.
ShardingSphere became an Apache Top-Level Project on April 16, 2020.
So far, ShardingSphere has been used by over 15,000 projects on GitHub.
AI ABSTRACTION
ShardingSphere wiki which is generated by DeepWiki automatically.
DOCUMENTATIONð
For full documentation & more details, visit: Docs
CONTRIBUTIONðð§ð»
For guides on how to get started and setup your environment, contributor & committer guides, visit: Contribution Guidelines
Team
We deeply appreciate community contributors for their dedication to Apache ShardingSphere.
COMMUNITY & SUPPORTðð¤
:link: Mailing List. Best for: Apache community updates, releases, changes.
:link: GitHub Issues. Best for: larger systemic questions/bug reports or anything development related.
:link: GitHub Discussions. Best for: technical questions & support, requesting new features, proposing new features.
:link: Slack channel. Best for: instant communications and online meetings, sharing your applications.
:link: Twitter. Best for: keeping up to date on everything ShardingSphere.
:link: LinkedIn. Best for: professional networking and career development with other ShardingSphere contributors.
STATUSð
:white_check_mark: Version 5.5.2: released :tada:
ð For the release notes, follow this link to the relevant GitHub page.
:soon: Version 5.5.3
We are currently working towards our 5.5.3 milestone. Keep an eye on the milestones page of this repo to stay up to date.
How it Works
Apache ShardingSphere includes 2 independent products: JDBC & Proxy. They all provide functions of data scale-out, distributed transaction and distributed governance, applicable in a variety of situations such as Java-based isomorphism, heterogeneous language and Cloud-Native.
ShardingSphere-JDBC
A lightweight Java framework providing extra services at the Java JDBC layer. With the client end connecting directly to the database, it provides services in the form of a jar and requires no extra deployment and dependence.
:link: For more details, follow this link to the official website.
ShardingSphere-Proxy
A transparent database proxy, providing a database server that encapsulates the database binary protocol to support heterogeneous languages. Friendlier to DBAs, the MariaDB, MySQL and PostgreSQL version now provided can use any kind of terminal.
:link: For more details, follow this link to the official website.
Hybrid Architecture
ShardingSphere-JDBC adopts a decentralized architecture, applicable to high-performance light-weight OLTP applications developed with Java. ShardingSphere-Proxy provides static entry and all languages support, suitable for an OLAP application and sharding databases management and operation.
Through the combination of ShardingSphere-JDBC & ShardingSphere-Proxy together with a unified sharding strategy by the same registry center, the ShardingSphere ecosystem can build an application system suitable to all kinds of scenarios.
:link: More details can be found following this link to the official website.
Solution
| Solutions/Features | Distributed Database | Data Security | Database Gateway | Stress Testing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data Sharding | Data Encryption | Heterogeneous Databases Supported | Shadow Database | |
| Read/write Splitting | Row Authority (TODO) | SQL Dialect Translate (TODO) | Observability | |
| Distributed Transaction | SQL Audit (TODO) | |||
| Elastic Scale-out | SQL Firewall (TODO) | |||
| High Availability |
Roadmap
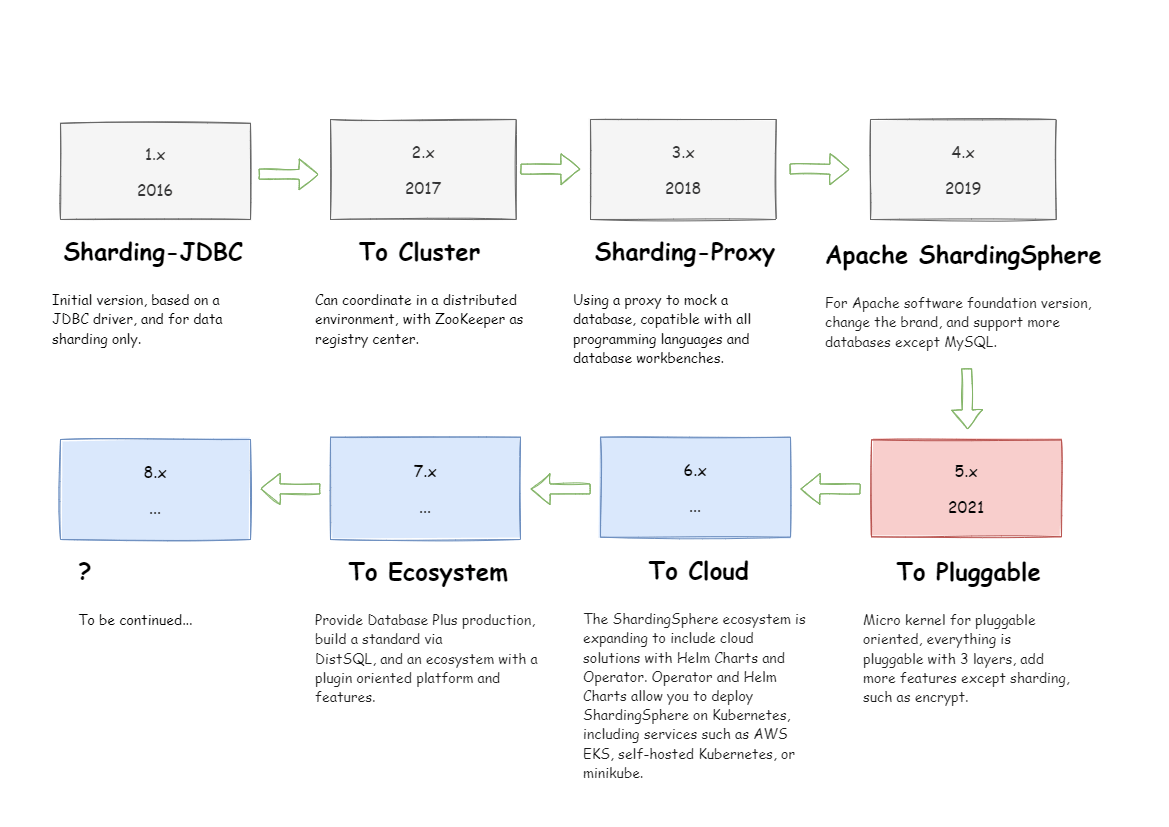
How to Build Apache ShardingSphere
Check out Wiki section for details on how to build Apache ShardingSphere and a full guide on how to get started and setup your local dev environment.
Landscapes

Apache ShardingSphere enriches the CNCF CLOUD NATIVE Landscape.
Top Related Projects
Free and Open Source, Distributed, RESTful Search Engine
Vitess is a database clustering system for horizontal scaling of MySQL.
CockroachDB — the cloud native, distributed SQL database designed for high availability, effortless scale, and control over data placement.
YugabyteDB - the cloud native distributed SQL database for mission-critical applications.
TiDB - the open-source, cloud-native, distributed SQL database designed for modern applications.
Convert  designs to code with AI
designs to code with AI

Introducing Visual Copilot: A new AI model to turn Figma designs to high quality code using your components.
Try Visual Copilot







