Top Related Projects
OpenStreetMap-Tools for Android
Vector map library and writer - running on Android and Desktop.
MapLibre Native - Interactive vector tile maps for iOS, Android and other platforms.
Quick Overview
The Android Maps Utils library is an open-source project by Google that provides utility functions for working with Google Maps on Android. It offers a set of tools and features to enhance map functionality, including clustering, heatmaps, and custom marker management.
Pros
- Simplifies complex map operations like marker clustering and heatmap generation
- Provides efficient algorithms for handling large datasets on maps
- Integrates seamlessly with the Google Maps Android API
- Regularly updated and maintained by Google
Cons
- Limited documentation for some advanced features
- May require additional setup and configuration for certain functionalities
- Some features may have performance impacts on older devices
- Learning curve for developers new to map-related operations
Code Examples
- Marker Clustering:
// Initialize the ClusterManager
val clusterManager = ClusterManager<MyClusterItem>(context, map)
// Set up the custom renderer
clusterManager.renderer = CustomClusterRenderer(context, map, clusterManager)
// Add cluster items
clusterManager.addItems(myClusterItems)
// Set the cluster click listener
clusterManager.setOnClusterClickListener { cluster ->
// Handle cluster click
true
}
- Heatmap Generation:
// Create a HeatmapTileProvider
val provider = HeatmapTileProvider.Builder()
.data(latLngList)
.build()
// Add the heatmap layer to the map
val overlay = map.addTileOverlay(TileOverlayOptions().tileProvider(provider))
- Polygon Utils:
// Check if a point is inside a polygon
val isInside = PolygonUtil.containsLocation(point, polygonPoints, geodesic)
// Simplify a polygon
val simplifiedPolygon = PolygonUtil.simplify(polygonPoints, tolerance)
Getting Started
To use the Android Maps Utils library in your project:
- Add the dependency to your app's
build.gradlefile:
dependencies {
implementation 'com.google.maps.android:android-maps-utils:2.3.0'
}
-
Initialize the Google Maps SDK in your project if you haven't already.
-
Import the necessary classes from the library:
import com.google.maps.android.clustering.ClusterManager
import com.google.maps.android.heatmaps.HeatmapTileProvider
import com.google.maps.android.PolyUtil
- Start using the utility functions in your code as shown in the examples above.
Competitor Comparisons
OpenStreetMap-Tools for Android
Pros of osmdroid
- Open-source and free to use without API key requirements
- Supports offline map rendering and caching
- More customizable with various map sources and tile providers
Cons of osmdroid
- Less extensive documentation and community support
- May require more setup and configuration compared to Google Maps
- Limited integration with other Google services
Code Comparison
osmdroid:
MapView map = new MapView(context);
map.setTileSource(TileSourceFactory.MAPNIK);
map.setBuiltInZoomControls(true);
map.setMultiTouchControls(true);
android-maps-utils:
GoogleMap map = ((MapFragment) getFragmentManager()
.findFragmentById(R.id.map)).getMap();
map.setMapType(GoogleMap.MAP_TYPE_NORMAL);
map.getUiSettings().setZoomControlsEnabled(true);
map.setMyLocationEnabled(true);
Both libraries offer similar basic functionality for displaying maps, but osmdroid requires more manual setup while android-maps-utils integrates seamlessly with Google Maps API. osmdroid provides more flexibility in terms of map sources and offline capabilities, while android-maps-utils benefits from Google's extensive ecosystem and services integration.
Vector map library and writer - running on Android and Desktop.
Pros of mapsforge
- Supports offline maps, allowing for use without an internet connection
- Open-source and customizable, providing more flexibility for developers
- Lighter weight and potentially faster performance for basic mapping needs
Cons of mapsforge
- Less extensive documentation and community support compared to Google Maps
- Fewer built-in features and tools for advanced mapping functionality
- May require more manual implementation for certain map interactions
Code Comparison
mapsforge:
MapView mapView = new MapView(context);
mapView.setLayerType(View.LAYER_TYPE_SOFTWARE, null);
mapView.setClickable(true);
mapView.getMapScaleBar().setVisible(true);
mapView.setBuiltInZoomControls(true);
android-maps-utils:
GoogleMap map = ((SupportMapFragment) getSupportFragmentManager()
.findFragmentById(R.id.map)).getMap();
ClusterManager<MyItem> clusterManager = new ClusterManager<>(this, map);
map.setOnCameraIdleListener(clusterManager);
map.setOnMarkerClickListener(clusterManager);
clusterManager.addItems(items);
Both libraries offer mapping solutions for Android, but mapsforge focuses on offline capabilities and customization, while android-maps-utils provides additional utilities for Google Maps integration. The choice between them depends on specific project requirements and the desired level of Google Maps integration.
MapLibre Native - Interactive vector tile maps for iOS, Android and other platforms.
Pros of maplibre-native
- Open-source and community-driven, allowing for greater customization and flexibility
- Cross-platform support for multiple operating systems and devices
- Designed for offline use and supports vector tiles
Cons of maplibre-native
- Smaller ecosystem and community compared to Google Maps
- May require more setup and configuration for basic use cases
- Limited integration with Google services and APIs
Code Comparison
maplibre-native:
#include <mbgl/map/map.hpp>
#include <mbgl/style/style.hpp>
auto map = std::make_unique<mbgl::Map>(view, resourceOptions);
map->getStyle().loadJSON(jsonStyle);
map->setZoom(12.0);
android-maps-utils:
import com.google.maps.android.clustering.ClusterManager;
GoogleMap map = // ... obtain map instance
ClusterManager<MyItem> clusterManager = new ClusterManager<>(this, map);
map.setOnCameraIdleListener(clusterManager);
clusterManager.addItems(items);
The code snippets demonstrate basic setup and usage for each library. maplibre-native focuses on map creation and style loading, while android-maps-utils showcases clustering functionality specific to Google Maps.
Convert  designs to code with AI
designs to code with AI

Introducing Visual Copilot: A new AI model to turn Figma designs to high quality code using your components.
Try Visual CopilotREADME
Maps SDK for Android Utility Library
Description
This open-source library contains utilities that are useful for a wide range of applications using the Google Maps SDK for Android.
- Marker animation - animates a marker from one position to another
- Marker clustering â handles the display of a large number of points
- Marker icons â display text on your Markers
- Heatmaps â display a large number of points as a heat map
- Import KML â displays KML data on the map
- Import GeoJSON â displays and styles GeoJSON data on the map
- Polyline encoding and decoding â compact encoding for paths, interoperability with Maps API web services
- Spherical geometry â for example: computeDistance, computeHeading, computeArea
- Street View metadata â checks if a Street View panorama exists at a given location
You can also find Kotlin extensions for this library in Maps Android KTX.

Requirements
- Android API level 21+
- Sign up with Google Maps Platform
- A Google Maps Platform project with the Maps SDK for Android enabled
- An API key associated with the project above ... follow the API key instructions if you're new to the process
Installation
dependencies {
// Utilities for Maps SDK for Android (requires Google Play Services)
// You do not need to add a separate dependency for the Maps SDK for Android
// since this library builds in the compatible version of the Maps SDK.
implementation 'com.google.maps.android:android-maps-utils:3.14.0'
// Optionally add the Kotlin Extensions (KTX) for full Kotlin language support
// See latest version at https://github.com/googlemaps/android-maps-ktx
// implementation 'com.google.maps.android:maps-utils-ktx:<latest-version>'
}
Sample App
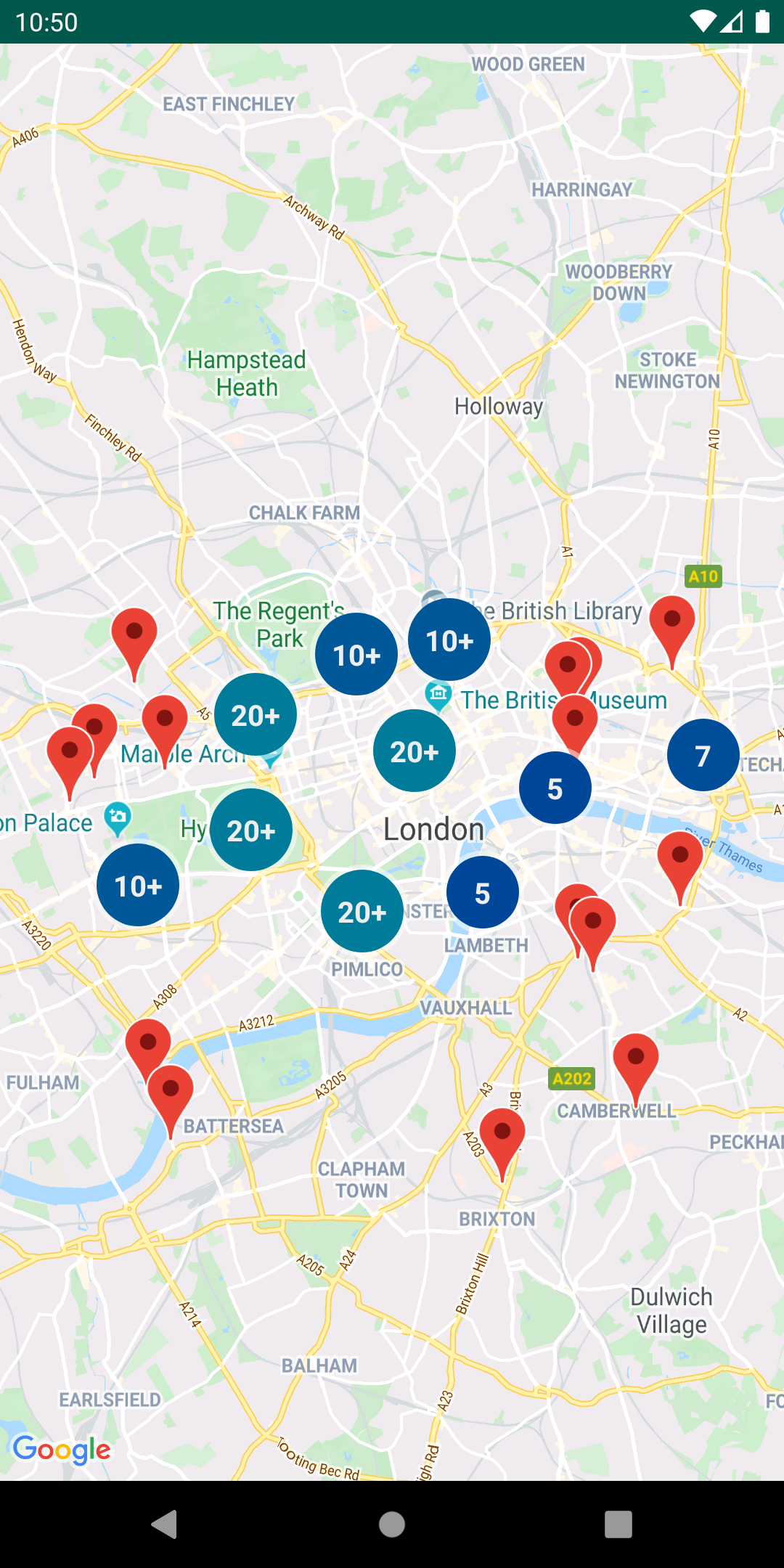
This repository includes a sample app that illustrates the use of this library.
To run the demo app, ensure you've met the requirements above then:
- Clone the repository
- Add a file
local.propertiesin the root project (this file should NOT be under version control to protect your API key) - Add a single line to
local.propertiesthat looks likeMAPS_API_KEY=YOUR_API_KEY, whereYOUR_API_KEYis the API key you obtained earlier - Build and run the
debugvariant for the Maps SDK for Android version
Documentation
See the documentation for a full list of classes and their methods.
Full guides for using the utilities are published in Google Maps Platform documentation.
Usage
Marker utilities
- Marker animation source, sample code
- Marker clustering source, guide
- Advanced Markers clustering source, sample code
- Marker icons source, sample code
Data visualization utilities
Data visualization utilities
Polyline and spherical geometry utilities
Additional utilities
- Polyline encoding and decoding source, encoding sample, decoding sample
- Spherical geometry source, compute distance sample
Street View metadata utility
Street View metadata utility
The StreetViewUtil class provides functionality to check whether a location is supported in StreetView. You can avoid errors when adding a Street View panorama to an Android app by calling this metadata utility and only adding a Street View panorama if the response is OK.
StreetViewUtils.fetchStreetViewData(LatLng(8.1425918, 11.5386121), BuildConfig.MAPS_API_KEY,Source.DEFAULT)
fetchStreetViewData will return NOT_FOUND, OK, ZERO_RESULTS or REQUEST_DENIED, depending on the response.
By default, the Source is set to Source.DEFAULT, but you can also specify Source.OUTDOOR to request outdoor Street View panoramas.
Contributing
Contributions are welcome and encouraged! If you'd like to contribute, send us a pull request and refer to our code of conduct and contributing guide.
Terms of Service
This library uses Google Maps Platform services. Use of Google Maps Platform services through this library is subject to the Google Maps Platform Terms of Service.
This library is not a Google Maps Platform Core Service. Therefore, the Google Maps Platform Terms of Service (e.g. Technical Support Services, Service Level Agreements, and Deprecation Policy) do not apply to the code in this library.
Support
This library is offered via an open source license. It is not governed by the Google Maps Platform Support [Technical Support Services Guidelines, the SLA, or the Deprecation Policy. However, any Google Maps Platform services used by the library remain subject to the Google Maps Platform Terms of Service.
This library adheres to semantic versioning to indicate when backwards-incompatible changes are introduced. Accordingly, while the library is in version 0.x, backwards-incompatible changes may be introduced at any time.
If you find a bug, or have a feature request, please file an issue on GitHub. If you would like to get answers to technical questions from other Google Maps Platform developers, ask through one of our developer community channels. If you'd like to contribute, please check the contributing guide.
You can also discuss this library on our Discord server.
Top Related Projects
OpenStreetMap-Tools for Android
Vector map library and writer - running on Android and Desktop.
MapLibre Native - Interactive vector tile maps for iOS, Android and other platforms.
Convert  designs to code with AI
designs to code with AI

Introducing Visual Copilot: A new AI model to turn Figma designs to high quality code using your components.
Try Visual Copilot




