 graffle
graffle
Simple GraphQL Client for JavaScript. Minimal. Extensible. Type Safe. Runs everywhere.
Top Related Projects
Generation of diagrams like flowcharts or sequence diagrams from text in a similar manner as markdown
Generate diagrams from textual description
Creates diagrams from textual descriptions!
D2 is a modern diagram scripting language that turns text to diagrams.
Virtual whiteboard for sketching hand-drawn like diagrams
draw.io is a JavaScript, client-side editor for general diagramming.
Quick Overview
Graffle is a TypeScript library for building GraphQL servers. It provides a type-safe and declarative approach to defining GraphQL schemas and resolvers, with a focus on developer experience and code maintainability.
Pros
- Strong type safety with TypeScript integration
- Declarative schema definition using a code-first approach
- Automatic generation of GraphQL SDL from TypeScript types
- Built-in support for common GraphQL features like pagination and filtering
Cons
- Limited documentation and examples available
- Relatively new project with a smaller community compared to established GraphQL libraries
- May have a steeper learning curve for developers new to GraphQL or TypeScript
Code Examples
- Defining a simple GraphQL schema:
import { createSchema, t } from 'graffle'
const schema = createSchema({
types: {
User: t.object({
id: t.id(),
name: t.string(),
email: t.string(),
}),
},
query: {
user: t.field({
type: 'User',
args: {
id: t.id(),
},
resolve: (_, { id }, ctx) => ctx.db.findUser(id),
}),
},
})
- Adding a mutation:
const schema = createSchema({
// ... other schema definitions
mutation: {
createUser: t.field({
type: 'User',
args: {
name: t.string(),
email: t.string(),
},
resolve: (_, { name, email }, ctx) => ctx.db.createUser({ name, email }),
}),
},
})
- Using pagination:
const schema = createSchema({
// ... other schema definitions
query: {
users: t.connection({
type: 'User',
resolve: (_, args, ctx) => ctx.db.findUsers(args),
}),
},
})
Getting Started
To start using Graffle, follow these steps:
-
Install the library:
npm install graffle -
Create a new TypeScript file and import Graffle:
import { createSchema, t } from 'graffle' -
Define your schema and resolvers:
const schema = createSchema({ types: { // Define your types here }, query: { // Define your queries here }, mutation: { // Define your mutations here }, }) -
Create a GraphQL server using your preferred framework (e.g., Express) and use the generated schema.
Competitor Comparisons
Generation of diagrams like flowcharts or sequence diagrams from text in a similar manner as markdown
Pros of Mermaid
- More mature and widely adopted project with a larger community
- Supports a broader range of diagram types (flowcharts, sequence diagrams, Gantt charts, etc.)
- Extensive documentation and examples available
Cons of Mermaid
- Steeper learning curve due to more complex syntax
- Larger file size and potentially slower rendering for complex diagrams
Code Comparison
Mermaid example:
graph TD
A[Start] --> B{Is it?}
B -->|Yes| C[OK]
B -->|No| D[End]
Graffle example:
const g = graffle`
(Start) -> [Is it?]
[Is it?] -> (OK) {label: Yes}
[Is it?] -> (End) {label: No}
`
Summary
Mermaid is a more established and feature-rich diagramming tool, offering support for various diagram types and extensive documentation. However, it may have a steeper learning curve and potentially slower rendering for complex diagrams. Graffle, on the other hand, appears to have a simpler syntax and potentially faster rendering, but with fewer diagram types and a smaller community. The choice between the two depends on the specific needs of the project and the user's preference for syntax complexity versus simplicity.
Generate diagrams from textual description
Pros of PlantUML
- Widely adopted and supported in various tools and platforms
- Extensive documentation and large community for support
- Supports a wide range of diagram types beyond just UML
Cons of PlantUML
- Syntax can be verbose and less intuitive for beginners
- Limited customization options for diagram styling
- Slower rendering performance for complex diagrams
Code Comparison
PlantUML:
@startuml
Alice -> Bob: Hello
Bob --> Alice: Hi there
@enduml
Graffle:
graph(`
Alice -> Bob: Hello
Bob -> Alice: Hi there
`)
Summary
PlantUML is a mature and widely-used tool for creating various types of diagrams, including UML. It offers extensive documentation and community support. However, its syntax can be verbose, and customization options are limited.
Graffle, on the other hand, is a newer project that aims to provide a simpler and more intuitive syntax for creating diagrams. It focuses on graph-based diagrams and offers a JavaScript-based approach. While it may not have the same level of adoption or feature set as PlantUML, it provides a more streamlined experience for certain types of diagrams.
The choice between the two depends on specific requirements, such as the types of diagrams needed, integration with existing tools, and the preferred syntax style.
Creates diagrams from textual descriptions!
Pros of Kroki
- Supports a wide range of diagram types (20+), including PlantUML, Mermaid, and GraphViz
- Offers multiple deployment options: Docker, CLI, and web service
- Actively maintained with regular updates and contributions
Cons of Kroki
- Requires external dependencies for each diagram type
- May have a steeper learning curve due to the variety of supported formats
- Potentially higher resource usage when running as a service
Code Comparison
Kroki (Docker usage):
docker run -d -p 8000:8000 yuzutech/kroki
curl -X POST --data-raw 'digraph G {Hello->World}' http://localhost:8000/graphviz/svg
Graffle (JavaScript usage):
import { graffle } from 'graffle'
const svg = graffle`
graph TD
A-->B
`
Summary
Kroki offers a comprehensive solution for generating various types of diagrams, with multiple deployment options and broad format support. However, it may require more setup and resources compared to Graffle. Graffle, on the other hand, provides a simpler JavaScript-based approach but with more limited diagram types. The choice between the two depends on the specific needs of the project, such as the variety of diagrams required and the preferred integration method.
D2 is a modern diagram scripting language that turns text to diagrams.
Pros of d2
- More active development with frequent updates and contributions
- Broader range of diagram types and features
- Better documentation and examples
Cons of d2
- Steeper learning curve due to more complex syntax
- Larger codebase, potentially harder to customize or extend
Code Comparison
d2:
shape: sequence_diagram
alice -> bob: Hello
bob -> alice: Hi
graffle:
const diagram = graffle.new()
diagram.add(graffle.box('Alice'))
diagram.add(graffle.box('Bob'))
diagram.add(graffle.arrow('Alice', 'Bob', 'Hello'))
Summary
d2 offers a more comprehensive diagramming solution with a wider range of features and diagram types. It has a more active community and better documentation. However, this comes at the cost of a steeper learning curve and a more complex codebase.
graffle, on the other hand, provides a simpler, JavaScript-based approach to creating diagrams. It may be easier to integrate into existing JavaScript projects but offers fewer features and diagram types compared to d2.
The choice between the two depends on the specific needs of the project, the desired level of complexity, and the preferred programming language or environment.
Virtual whiteboard for sketching hand-drawn like diagrams
Pros of Excalidraw
- More feature-rich and mature project with a larger community
- Offers a complete drawing application with a user interface
- Supports collaborative editing and real-time collaboration
Cons of Excalidraw
- Larger codebase and potentially more complex to contribute to
- May have more dependencies and a steeper learning curve
- Focused on a specific use case (whiteboard-style drawings)
Code Comparison
Excalidraw (React component usage):
import { Excalidraw } from "@excalidraw/excalidraw";
<Excalidraw
initialData={initialData}
onChange={(elements, state) => console.log("Elements :", elements, "State : ", state)}
/>
Graffle (Node.js usage):
const graffle = require('graffle')
const diagram = graffle.create()
diagram.addNode('A')
diagram.addNode('B')
diagram.addEdge('A', 'B')
Excalidraw is a full-featured drawing application with a web-based interface, while Graffle appears to be a simpler library for creating diagrams programmatically. Excalidraw offers a more comprehensive solution for collaborative drawing, but Graffle might be easier to integrate into existing Node.js projects for generating diagrams.
draw.io is a JavaScript, client-side editor for general diagramming.
Pros of draw.io
- More comprehensive and feature-rich diagramming tool
- Supports a wide range of diagram types and export formats
- Active development with frequent updates and improvements
Cons of draw.io
- Larger codebase and more complex architecture
- Steeper learning curve for new users
- Heavier resource usage due to its extensive feature set
Code Comparison
draw.io (JavaScript):
mxGraph.prototype.insertVertex = function(parent, id, value, x, y, width, height, style, relative)
{
var vertex = this.createVertex(parent, id, value, x, y, width, height, style, relative);
return this.addCell(vertex, parent);
};
Graffle (TypeScript):
export function createNode(
graph: Graph,
options: CreateNodeOptions
): Node {
const node = new Node(options);
graph.addNode(node);
return node;
}
Summary
draw.io is a more comprehensive diagramming tool with a wider range of features, while Graffle appears to be a simpler, more focused library. draw.io's extensive capabilities come at the cost of increased complexity and resource usage, whereas Graffle likely offers a more streamlined experience for specific use cases.
Convert  designs to code with AI
designs to code with AI

Introducing Visual Copilot: A new AI model to turn Figma designs to high quality code using your components.
Try Visual CopilotREADME
[!IMPORTANT] The next version (
8) ofgraphql-requestis being renamed tograffle. It has the same base simplicity but with many fixes, enhancements, and major new type safe features. It is not released yet but will be in the coming weeks/months and is already usable. Learn more about it here. You can see the in progress website at https://graffle.js.org.The following README is still for
graphql-request@7.x.x
graphql-request
Minimal GraphQL client supporting Node and browsers for scripts or simple apps.
Highlights
- Most simple & lightweight GraphQL client
- Promise-based API (works with
async/await) - Pure ESM package
- First class TypeScript support
- Including
TypedDocumentNode
- Including
- Isomorphic (works in both Node and Browsers)
Install
npm add graffle graphql
TypeScript Setup
This package uses package.exports. Therefore if you are a TypeScript user you must:
- have your
tsconfig.jsonmoduleResolutionset to"bundler"or"node16"/"nodenext". - Have your
package.jsontypeset to"module".
Quick Start
Send a GraphQL document using a static request function:
import { gql, request } from 'graffle'
const document = gql`
{
company {
ceo
}
}
`
await request('https://api.spacex.land/graphql/', document)
The function can be passed a configuration object for more complex cases:
await request({
url,
document,
variables,
requestHeaders,
})
A class is available for constructing your own instances:
import { gql, GraphQLClient } from 'graffle'
const document = gql`
{
company {
ceo
}
}
`
const endpoint = 'https://api.spacex.land/graphql/'
const client = new GraphQLClient(endpoint)
await client.request(document)
Examples
- Request:
- GraphQL:
- Configuration:
- TypeScript:
- Other:
Node Version Support
We only (officially) support versions of Nodejs of the following status:
- Current
- LTS
- Maintenance and end of life not yet reached
So for example on Oct 24 2023 that would mean these versions: 18, 20, 21.
Any issue that exists solely for an unsupported version of Nodejs will be rejected (not worked on).
Reference
â ï¸ This reference is incomplete. Check out the examples for more reference material.
Configuration
ErrorPolicy
By default GraphQLClient will throw when an error is received. However, sometimes you still want to resolve the (partial) data you received.
You can define errorPolicy in the GraphQLClient constructor.
const client = new GraphQLClient(endpoint, { errorPolicy: 'all' })
None (default)
Allow no errors at all. If you receive a GraphQL error the client will throw.
Ignore
Ignore incoming errors and resolve like no errors occurred
All
Return both the errors and data, only works with rawRequest.
IgnoreOperationName
OperationName has been introduced to address issues reported here Support operation name, However, on certain occasions this information may not be needed in requests. In such cases, you might consider ignoring operationName to avoid the extraction steps currently performed by a parsing operation when the document is provided in string format.
By default the GraphQLClient tries to extract the operationName from the document.
You can define excludeOperationName in the constructor of GraphQLClient to avoid the extraction process if it is not needed. This can be useful if you don't use operationName and want to optimise queries by reducing the amount of computation as much as possible, especially if we are in a context where we are using documents in string format to reduce bundle size.
// example where the operation name is not ignored
const client = new GraphQLClient(endpoint, {
method: 'POST',
})
// example in which the operation name is ignored
const client = new GraphQLClient(endpoint, {
method: 'POST',
excludeOperationName: true,
})
Knowledge Base
Why was the file upload feature taken away? Will it return?
In this issue we decided to make this library more stable and maintainable. In principal the feature is still in scope of this library and will make a return when we find time to do the feature right.
Why do I have to install graphql?
graffle uses methods exposed by the graphql package to handle some internal logic. On top of that, for TypeScript users, some types are used from the graphql package to provide better typings.
Do I need to wrap my GraphQL documents inside the gql template exported by graffle?
No. It is there for convenience so that you can get the tooling support like automatic formatting and syntax highlighting. You can use gql from graphql-tag if you need it for some reason too.
What sets graffle apart from other clients like Apollo, Relay, etc.?
graffle is the most minimal and simplest to use GraphQL client. It's perfect for small scripts or simple apps.
Compared to GraphQL clients like Apollo or Relay, graffle doesn't have a built-in cache and has no integrations for frontend frameworks. The goal is to keep the package and API as minimal as possible.
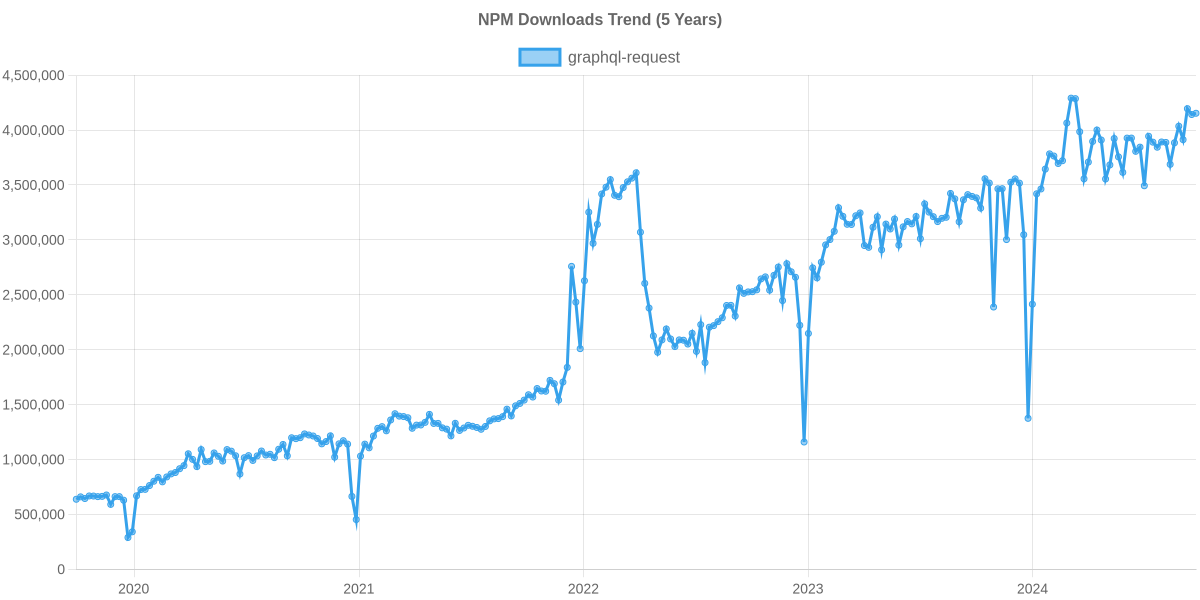
Project Stats
Package Installs
Repo Beats
Top Related Projects
Generation of diagrams like flowcharts or sequence diagrams from text in a similar manner as markdown
Generate diagrams from textual description
Creates diagrams from textual descriptions!
D2 is a modern diagram scripting language that turns text to diagrams.
Virtual whiteboard for sketching hand-drawn like diagrams
draw.io is a JavaScript, client-side editor for general diagramming.
Convert  designs to code with AI
designs to code with AI

Introducing Visual Copilot: A new AI model to turn Figma designs to high quality code using your components.
Try Visual Copilot