 awesome-system-design
awesome-system-design
A curated list of awesome System Design (A.K.A. Distributed Systems) resources.
Top Related Projects
Learn how to design large-scale systems. Prep for the system design interview. Includes Anki flashcards.
The Patterns of Scalable, Reliable, and Performant Large-Scale Systems
System design interview for IT companies
Preparation links and resources for system design questions
A curated list of engineering blogs
💯 Curated coding interview preparation materials for busy software engineers
Quick Overview
The "awesome-system-design" repository is a curated list of system design resources, including articles, videos, and tools. It serves as a comprehensive guide for software engineers and architects to learn about and implement large-scale distributed systems. The repository covers various aspects of system design, from basic concepts to advanced topics.
Pros
- Extensive collection of high-quality resources on system design
- Well-organized structure with clear categories for easy navigation
- Regularly updated with new and relevant content
- Includes both theoretical concepts and practical implementation guides
Cons
- May be overwhelming for beginners due to the vast amount of information
- Some links may become outdated over time
- Lacks a structured learning path for newcomers to system design
- Limited coverage of certain niche or emerging technologies
Note: As this is not a code library, the code example and quick start sections have been omitted.
Competitor Comparisons
Learn how to design large-scale systems. Prep for the system design interview. Includes Anki flashcards.
Pros of system-design-primer
- More comprehensive and structured learning approach
- Includes detailed explanations and visual aids
- Offers practice problems and solutions
Cons of system-design-primer
- Less frequently updated compared to awesome-system-design
- Focuses primarily on theoretical concepts rather than real-world examples
- May be overwhelming for beginners due to its depth
Code Comparison
While both repositories primarily focus on system design concepts rather than code, system-design-primer does include some code snippets for illustration. Here's an example of a simple cache implementation from system-design-primer:
class Cache(object):
def __init__(self, limit=10):
self.limit = limit
self.size = 0
self.map = {}
self.list = DoublyLinkedList()
awesome-system-design doesn't typically include code snippets, as it's more of a curated list of resources.
Both repositories serve as valuable resources for learning about system design, with system-design-primer offering a more structured approach and awesome-system-design providing a broader collection of external resources. The choice between them depends on individual learning preferences and goals.
The Patterns of Scalable, Reliable, and Performant Large-Scale Systems
Pros of awesome-scalability
- More comprehensive coverage of scalability topics, including databases, caching, and message queues
- Includes practical examples and case studies from real-world companies
- Offers a dedicated section on management and soft skills for system designers
Cons of awesome-scalability
- Less focus on system design patterns and principles compared to awesome-system-design
- May be overwhelming for beginners due to its extensive content
- Lacks a clear structure for progressive learning
Code Comparison
While both repositories primarily contain curated lists of resources rather than code, awesome-scalability does include some code snippets in its examples. Here's a brief comparison:
awesome-scalability:
def get_user(user_id):
user = cache.get(user_id)
if user is None:
user = database.query(user_id)
cache.set(user_id, user)
return user
awesome-system-design: No direct code examples provided.
Both repositories serve as excellent resources for learning about system design and scalability, with awesome-scalability offering a more comprehensive but potentially overwhelming experience, while awesome-system-design provides a more focused approach to system design principles.
System design interview for IT companies
Pros of system-design-interview
- More focused on interview preparation with specific examples and scenarios
- Includes a section on system design basics, helpful for beginners
- Provides links to external resources for further learning
Cons of system-design-interview
- Less comprehensive coverage of system design topics compared to awesome-system-design
- Not as frequently updated, potentially containing outdated information
- Lacks organization into clear categories, making navigation more challenging
Code Comparison
While both repositories primarily consist of curated lists and resources rather than code, system-design-interview does include some code snippets in its examples. Here's a brief comparison:
system-design-interview:
def consistent_hashing(key):
hash_value = hash(key)
return hash_value % num_nodes
awesome-system-design: No direct code examples are provided in the main README.
Summary
system-design-interview is more tailored for interview preparation, offering specific examples and scenarios. However, awesome-system-design provides a more comprehensive and up-to-date collection of system design resources, organized into clear categories. The choice between the two depends on whether the user is specifically preparing for interviews or seeking a broader understanding of system design concepts.
Preparation links and resources for system design questions
Pros of system_design
- More focused on practical system design interview preparation
- Includes specific interview questions and their solutions
- Provides code snippets and examples for some design problems
Cons of system_design
- Less comprehensive in terms of overall system design resources
- Not as frequently updated as awesome-system-design
- Lacks organization into distinct categories or topics
Code Comparison
system_design:
def consistent_hashing(self, key):
hash_key = self.hash_function(key)
for node in self.sorted_nodes:
if hash_key <= node:
return self.nodes[node]
return self.nodes[self.sorted_nodes[0]]
awesome-system-design does not provide specific code examples, as it is primarily a curated list of resources.
Summary
system_design is more tailored for system design interview preparation, offering specific questions and solutions. However, awesome-system-design provides a more comprehensive and regularly updated collection of system design resources. The choice between the two depends on whether you're specifically preparing for interviews or seeking a broader understanding of system design concepts.
A curated list of engineering blogs
Pros of engineering-blogs
- Focuses specifically on engineering blogs, providing a curated list of valuable resources for developers
- Regularly updated with new blog entries, ensuring fresh content
- Organized by company, making it easy to find blogs from specific organizations
Cons of engineering-blogs
- Limited scope compared to awesome-system-design, which covers a broader range of system design topics
- Lacks categorization beyond company names, making it harder to find content on specific topics
- Does not include additional resources like books, courses, or articles on system design
Code Comparison
engineering-blogs:
* [Airbnb Engineering](https://medium.com/airbnb-engineering)
* [Amazon](https://developer.amazon.com/blogs)
* [Atlassian Developers](https://blog.developer.atlassian.com/)
awesome-system-design:
## Videos
* [System Design Interview](https://www.youtube.com/c/SystemDesignInterview)
* [Gaurav Sen](https://www.youtube.com/c/GauravSensei)
* [sudoCODE](https://www.youtube.com/c/sudoCODE)
While engineering-blogs provides a straightforward list of engineering blogs, awesome-system-design offers a more comprehensive collection of resources, including videos, articles, and tools for system design. The code structure in engineering-blogs is simpler, focusing on listing blog URLs, while awesome-system-design organizes content into categories with more detailed descriptions.
💯 Curated coding interview preparation materials for busy software engineers
Pros of tech-interview-handbook
- Comprehensive coverage of various technical interview topics, including algorithms, system design, and behavioral questions
- Includes practical advice on interview preparation, resume writing, and negotiation strategies
- Regularly updated with contributions from the community
Cons of tech-interview-handbook
- Primarily focused on interview preparation, rather than in-depth system design concepts
- May not provide as extensive resources for advanced system design topics
- Less curated list of external resources compared to awesome-system-design
Code comparison
While both repositories are primarily resource collections, tech-interview-handbook includes some code snippets for algorithm problems. Here's an example from tech-interview-handbook:
def binary_search(arr, target):
left, right = 0, len(arr) - 1
while left <= right:
mid = (left + right) // 2
if arr[mid] == target:
return mid
elif arr[mid] < target:
left = mid + 1
else:
right = mid - 1
return -1
awesome-system-design doesn't typically include code snippets, as it focuses on system design concepts and resources rather than implementation details.
Convert  designs to code with AI
designs to code with AI

Introducing Visual Copilot: A new AI model to turn Figma designs to high quality code using your components.
Try Visual CopilotREADME
 If you appreciate the content ð, support projects visibility, give ð| â| ð
If you appreciate the content ð, support projects visibility, give ð| â| ð
A curated list of awesome System Designing articles, videos and resources for distributed computing, AKA Big Data.
Whether you're preparing for an interview or you want to design a distributed/microservice oriented application, this list will definitely help you achieve that.
Attention: Stars on GitHub does not reflect usage or popularity for every item here listed.
Inspired By Awesome-BigData
Started By Gabriel Leon de Mattos
Contents
- Relational Database
- NoSQL
- Distributed File Systems
- Resource Management
- Stream Processing
- Message Broker
- Load Balancers
- Hadoop Ecosystem
- REST Framework
Articles
Introduction / Interviews
-
System Design Primer - [109k â] - Awesome compilation of resources, including Anki flashcard decks.
-
System Design Interview Questions - Concepts you should know - A curated list of topics to introduce you to system design.
-
Grokking the System Design Interview - [Paid ðµ] - Grokking System Design preparation is one of the most talked about course. The best thing about it is the design of applications it suggests rather than explanations of what each tool is supposed to do.
-
System Design in Software Development - Basic article on the topics of system design and architecture.
-
System Design - Introductory interview preparation resources.
-
Design Pattern for Distributed Systems - Article talking about some patterns as well as some technologies to be considered.
-
Practice system design problems using AI on Codemia.io - A tool which allows you to practice system design problems interactively like an interview with AI. There's iterative feedback and final evaluation which scores your performance
Advanced
-
Distributed Computing - Wikipedia article broadening the view of distributed system design.
-
Fallacies of Distributed Computing - Wikipedia article introducing the topic of fallacies of distributed computing and its effects.
-
Fallacies of Distributed Computing Explained - In depth explanation of the fallacies mentioned above.
-
CAP Theorem - IBM Article about CAP Theorem, Microservices and NoSQL DBs.
-
Pattern: Microservice Architecture - Good article talking about Microservice architecture as well as its drawbacks.
-
Taxonomy of Distributed Systems - 11 Page lecture classifying distributed systems and specifically why we need them.
-
Top 10 Secure Coding Practices - Brief article talking about good practices for code securities.
-
Scalable Web Architecture and Distributed Systems - Good article about distributed systems as well as some of the potential tools.
Books
-
Designing Distributed Systems: Patterns and Paradigms for Scalable, Reliable Services - [Paid ðµ] - Book that talks about disitributed systems as well as lightly demonstrating some code of what it looks like.
-
Designing Data Intensive Applications - [Paid ðµ] - Goes in depth to explain various resources we use when working with distributed systems, as well as how it came to be and what problems it aims to solve.
-
The System Design Manual - [Paid ðµ] - Covers the core aspects of distributed systems, like: network fundamentals, the theory underpinning distributed systems, architectural patterns of scalable systems, stability patterns that harden systems against failures and operational best-practices on how to maintain large-scale systems with a small team.
-
Building Microservices - [Free ð] - Awesome book that talks about designing sytem architecture with microservices in depth, includes most relevant topics in this regard.
-
Monolith to Microservices - [Free ð] - Written by the same author as the one above, this book will cover the migration from Monolith to Microservices, it's recommended you start by the previous book.
-
Distributed Systems (3rd Edition) - [Free ð] - Great overview of and in-depth introduction to distributed systems. Recommended for intermediate level readers.
Videos
A collection of videos based on distributed systems.
Introduction / Interviews
-
Gaurav Sen - System Design Series - Good resource for people who want to learn more about system design, introduces the topic in a very easy to understand way.
-
Tech Dummies - System Design Series - Another introduction to system design.
-
Mock System Design Interview at Google - Overview of what an interview on system design would look like from the perspective of a flawed but close fulfilling of the requirements. Key thing here is how the interaction with the interviewer goes.
-
Google Preparation Guide - A quick video explaining how they interview.
-
System Design Interview - YouTube channel focussed on content specific to system design interviews, with detailed explanation of a variety of problems.
-
Intro to Architecture and System Design Interviews - A youtube video with Jackson Gabbard with good info about system design interviews.
-
System Design Introduction for Interview - Tushar's intro to System Design.
-
Distributed Systems - This is an introductory course in Distributed Systems made by Chris Colohan. He got PhD from Carnegie Mellon, then spent 10 years working at Google building distributed systems.
-
The Easy Way - Up and coming channel with easy to understand videos about Distributed Systems.
-
System Design by SDE Skills - Good resource for people who are preparing for System Design interviews, there are multiple system design mock interviews and deep dives.
-
System Design by CodeKarle - Another great free resource, a list of commonly asked interview questions.
Advanced
- The evolution of Reddit Architecture - Overview of how Reddit system design scaled.
- 6.824 Distributed Systems by MIT - Graduate level course on distributed systems from MIT (2020).
- CSE138 Distributed Systems by UCSC - Undergraduate course on distributed systems from UCSC (2020).
Tools
- A collection of most commonly used tools for distributed systems
Relational Database Management System
-
MariaDB - MariaDB is a fork of MySQL server.
-
MySQL - Widely used relational database.
-
PostgresSQL - Relational database that has been gaining popularity.
-
SQLite - Another widely used database that is built into all mobile phones and most computers.
-
Sql Server - Widely used relational database.
NoSQL
Cache (Key-Value)
-
Apache Ignite - [3.3k â] - In memory caching with ACID properties.
-
Couchbase - Inspired by memcached, adding features such as replication and persistance.
-
Oracle Coherence - [126 â] - High scaling, low latency in-memory caching.
-
Memcached - [10.2k â] - One of the first in-memory caching database, high performing and multi-threaded.
-
Redis - [44k â] - Widely used in-memory caching database with many added features such as persistent storage and supporting strings, lists, sets, hashses, streams, bitmaps, etc.
Store (Key-Value)
-
Apple FoundationDB - [10k â] - Multi-model (many data types in a single database), ACID key-value store. Easily scalable and fault tolerant.
-
Cosmos DB - Microsoft's globally distributed, multi-model database service. Eastically and independently scale throughput and storage. SQL, MongoDB, Cassandra, Tables, Gremlin, and Spark APIs.
Document Store
-
CouchDB - [4.6k â] - ACID compliant NoSQL document-store DB, provides a RESTful HTTP API for reading and updating database documents.
-
MongoDB - One of the most popular 'NoSQL' database for general purpose.
-
RethinkDB - [23.8k â] - Document-store DB.
-
ElasticSearch - [49.9k â] - Widely popular 'NoSQL' database for fast and scalable search engines.
-
Cosmos DB - Microsoft's globally distributed, multi-model database service. Eastically and independently scale throughput and storage. SQL, MongoDB, Cassandra, Tables, Gremlin, and Spark APIs.
Wide Column Store
-
Amazon DynamoDB - Key-Value and Document database, highly performant, scalable and secure.
-
Google Bigtable - Scalable and performant 'NoSQL' database for large analytical and operational workload.
-
Cassandra - Facebook-born project very fast, easily scalable, with option to include consistency with each operation.
-
Scylla - [4.9k â] - 'NoSQL' data store using seastar framework, compatible with Cassandra.
-
HBase - [3.6k â] - Modeled after Google's Bigtable and written in Java. Developed as a part of Apache Hadoop project and runs on top of HDFS or Alluxio. (See Hadoop Related)
-
Cosmos DB - Microsoft's globally distributed, multi-model database service. Eastically and independently scale throughput and storage. SQL, MongoDB, Cassandra, Tables, Gremlin, and Spark APIs.
Graph
-
Amazon Neptune - Fast, reliable and fully managed graph database service.
-
ArangoDB - [10k â] - Flexible database for documents, key-value, graphs. Uses its own query language, AQL.
-
Neo4j - [7.9k â] - Good support for a graph db, ACID compliant and flexible.
-
Cosmos DB - Microsoft's globally distributed, multi-model database service. Eastically and independently scale throughput and storage. SQL, MongoDB, Cassandra, Tables, Gremlin, and Spark APIs.
Distributed File Systems
-
HDFS - Hadoop File System is a a widely popular choice among its big data competitors, providing high throughput access.
-
Lustre - File system for computer clusters.
-
CephFS - Unified, distributed storage system.
-
GlusterFS - Scale-out NAS file system.
-
MooseFS - POSIX-compliant distributed file system.
-
XtreemFS - Fault tolerant file system.
Resource Management
- Kubernetes - Highly popular way to deploy, manage and automatically scale a cluster of containers on bare-metal or virtual servers.
Stream Processing
-
Apache Samza - Build stateful applications that process data in real time from multiple sources, including Kafka. Easy and inexpensive multi-subscriber model, can eliminate backpressure and has reliable persistency with low latency.
-
Apache Flink - Based on the concept of streams and transofrmations. Uses maven, handles batch tasks as data streams with finite boundaries. Low latency, high throughput.
-
Amazon Kinesis Streams - Durable, scalable, real-tme service. Collects gigabytes of data per second from hundreds of thousands of sources, including database event streams, website clickstreams, financial transactions, etc.
-
Azure Stream Analytics - Real-time analytics service that is designed for mission-critical workloads.
Message Broker
-
Amazon MQ - Open source message broker from Amazon.
-
Apache ActiveMQ - It's a multi-protocol, java based messaging server.
-
Apache Kafka - Widely popular message broker with low latency for data streaming.
-
RabbitMQ - Widely popular lightweight message broker written in erlang that also supports multiple messaging protocols.
-
IronMQ - Very fast and highly scalable messaging broker. (not open source)
-
Apache Pulsar - Created by yahoo, also highly scalable, low latency, geo-replication and multi-tenacy.
-
Kestrel - Written in Scala and speaks the memcached protocol. It works much like Kafka.
-
Azure Service Bus - A fully managed enterprise integration message broker.
Load Balancers
Open Source Software
-
SeeSaw - [5.1k â] - Used by Google, developed in Go, linux-based virtual load balancer server.
-
HAProxy - Widely popular option, provides high-availability, proxy, TCP/HTTP load balancing. Used by Reddit, Imgur, MaxCDN, GitHub, AirBNB.
-
Zevenet - Supports L3, L4 and L7. Easy install with a docker repo. Supports advanced health-check monitorining.
-
Neutrino - Used by eBay, built with Scala and Netty. Supports round-robin and least-connection algorithms.
-
Nginx - Wait, isn't Nginx a web server? Yes, the open source does support basic level of content switching and request routing. Plus edition supports load balancing, WAF, monitoring, etc.
-
Openresty - Nginx + Lua, perfect combination.
Hardware
-
F5 - Robust hardware load balancer option, supporting multiple protocols (IP, TCP, FTP, UDP, HTTP).
-
TP-Link - Cheaper alternative that works as a load balancer.
-
Barracuda - One of the top choices for load balancing when it comes to in-house servers. Top security measures built in, comprehensive reports and monitoring outbound traffic for data loss prevention.
Cloud
-
Amazon Elastic Load Balancing - Popular choice for amazon customers, supports lambda functions, highly scalable.
-
Google Load Balancing - Popular choice for google customers, comes with auto-scaling feature, very fast, has intergrated CDN.
-
Cloudflare Load Balancing - Scalable load balancing by Cloudflare, feature fast failover and a dashboard.
-
DigitalOcean Load Balancing - If you're a digitalocean customer, this is a good option, very cheap, regional availability, scalable, easy to deploy among your other droplets.
-
Azure Load Balancing - Popular choice for Microsoft's Azure customers. Supports internal and external traffics, ipv6, monitorining and the standard load balancing set of features.
Hadoop Ecosystem
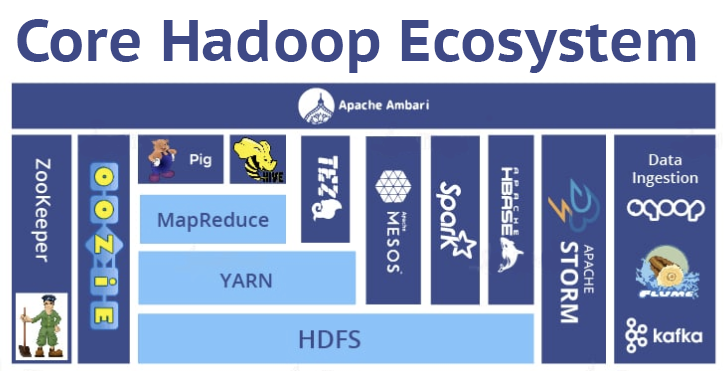
Dashboard
- Ambari - Dashboard that integrates most of hadoop related technologies for easy management and executions.
Data Ingestion
-
Sqoop - Efficiently transfer data between Hadoop and structured datastores such as relational databases.
-
Flume - Distributed, highly available and efficient in collecting, aggregating and moving large amounts of log data.
-
Apache Kafka - Widely popular message broker with low latency for data streaming.
Workflow Scheduler
- Oozie - Create workflows in xml to execute jobs (from other hadoop-ecosystem applications) in steps, allows for parallel execution as well.
Query
- Hive - Query hadoop stored data in SQL.
- Pig - Scriping language that looks like SQL to query hadoop data.
Processing
- Tez - Solves a similar problem to Spark and MapReduce, it's more efficient than MapReduce because it calculates the most efficient way of doing it.
- Map Reduce - MapReduce, as the name implies, maps data and reduce the results.
- Spark - Powerful data processing to not only process data like Tez (and MapReduce), it can process streams of data in real time, apply regression analysis algorithms in ML and much more.
- Apex - *Retired project, it's a YARN-native platform that unifies stream and batch processing.
DB
- HBase - [3.6k â] - Modeled after Google's Bigtable and written in Java. Developed as a part of Apache Hadoop project.
Resource Management
- YARN - 'Yet Another Resource Negotiator', works like a kernel to manage computer resources across the clusters.
- MESOS - Works like a Linux Kernel by managing CPU, memory, storage and other resources across the cluster.
REST Framework
-
Gin - [40.6k â] - Blazingly fast microservice framework using Golang, high throughput capacity.
-
Phoenix - [15.5k â] - Distributed processing, easily scalable, support for channels and live chat. This framework - written in Elixir, uses BEAM and Erlang, very efficient for large scale systems and supports high throughput.
-
Express.js - [49.6k â] - Fast node.js rest api that can perform well under many scenarios.
-
Rails - [46.2k â] - Written in Ruby, Rails delivers quick apis from prototype to production in an efficient manner.
-
Play Framework - [11.6k â] - Very fast, high throughput framework written in Scala/Java that is RESTful by default.
-
Flask - [51.6k â] - A lightweight Python Microframework for fast prototyping and production.
-
FastAPI - [22.7k â] - A lightweight Python Microframework inspired in Flask but more modern, using Python async.
-
Django REST - [18.4k â] - Written in Python, Django Rest is a powerful and flexible REST API. The efficiency and time to market resembles Rails.
-
ASP.NET Core MVC - A rich framework for building web apps and APIs using the Model-View-Controller design pattern in C# or F#. Number 6 on TechEmpower Composite Benchmarks for web frameworks.
-
Fastify - [15.4k â] - A Node.js web framework highly focused on providing the best developer experience with the least overhead and a powerful plugin architecture.
Top Related Projects
Learn how to design large-scale systems. Prep for the system design interview. Includes Anki flashcards.
The Patterns of Scalable, Reliable, and Performant Large-Scale Systems
System design interview for IT companies
Preparation links and resources for system design questions
A curated list of engineering blogs
💯 Curated coding interview preparation materials for busy software engineers
Convert  designs to code with AI
designs to code with AI

Introducing Visual Copilot: A new AI model to turn Figma designs to high quality code using your components.
Try Visual Copilot