MixedRealityToolkit-Unity
MixedRealityToolkit-Unity
This repository is for the legacy Mixed Reality Toolkit (MRTK) v2. For the latest version of the MRTK please visit https://github.com/MixedRealityToolkit/MixedRealityToolkit-Unity
Top Related Projects
This repository contains various examples to use with the XR Interaction Toolkit
Samples to demonstrate use of the WebXR Device API
Quick Overview
The Microsoft Mixed Reality Toolkit (MRTK) is an open-source project that provides a set of components and features to accelerate the development of mixed reality applications for Microsoft HoloLens, Windows Mixed Reality, and other virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) platforms. It is designed to be cross-platform and highly extensible, making it a popular choice for developers working on mixed reality projects.
Pros
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: MRTK supports a wide range of mixed reality platforms, including Microsoft HoloLens, Windows Mixed Reality, and other VR/AR devices, allowing developers to create applications that can run on multiple platforms.
- Extensive Feature Set: The toolkit provides a comprehensive set of features, including input handling, spatial awareness, user interface components, and more, which can significantly reduce development time and effort.
- Active Community and Documentation: MRTK has a large and active community of developers, and the project is well-documented, with extensive guides and tutorials available.
- Customization and Extensibility: The toolkit is highly customizable and extensible, allowing developers to build upon the existing functionality and create custom solutions to meet their specific needs.
Cons
- Learning Curve: The toolkit can have a steep learning curve, especially for developers who are new to mixed reality development or the Unity game engine, which is the primary development platform for MRTK.
- Performance Considerations: Depending on the complexity of the application and the target hardware, MRTK-based applications may face performance challenges, requiring careful optimization and optimization.
- Dependency on Unity: MRTK is tightly integrated with the Unity game engine, which means that developers who prefer other development platforms or frameworks may not be able to fully utilize the toolkit.
- Potential Compatibility Issues: As the mixed reality landscape continues to evolve, there may be compatibility issues between MRTK and newer hardware or software releases, requiring developers to stay up-to-date with the latest updates and changes.
Code Examples
Here are a few examples of how to use the MRTK in your Unity-based mixed reality projects:
- Instantiating a Holographic Button:
// Create a new GameObject for the button
GameObject buttonObject = new GameObject("Holographic Button");
// Add the NearInteractionTouchable component to the button
NearInteractionTouchable touchable = buttonObject.AddComponent<NearInteractionTouchable>();
// Add the PressableButton component to the button
PressableButton button = buttonObject.AddComponent<PressableButton>();
// Configure the button's properties
button.ButtonPressed.AddListener(() => Debug.Log("Button pressed!"));
button.StartPushDistance = 0.01f;
button.MaxPushDistance = 0.02f;
This code creates a new holographic button in the scene, configures its properties, and adds a listener to the ButtonPressed event.
- Handling Gaze Input:
// Get the GazeProvider component from the MRTK
GazeProvider gazeProvider = MixedRealityToolkit.Instance.GetService<IGazeProvider>() as GazeProvider;
// Add a listener to the GazeProvider's OnPointerSpecificEvent
gazeProvider.OnPointerSpecificEvent.AddListener((PointerEventData eventData) =>
{
// Handle the gaze input event
Debug.Log("Gaze input detected on: " + eventData.pointerCurrentRaycast.gameObject.name);
});
This code retrieves the GazeProvider component from the MRTK and adds a listener to its OnPointerSpecificEvent, which is triggered whenever the user's gaze is detected.
- Placing Holograms in the World:
// Get the SpatialAwarenessMeshObserver component from the MRTK
SpatialAwarenessMeshObserver meshObserver = MixedRealityToolkit.Instance.GetService<IMixedRealitySpatialAwarenessSystem>()
.GetObservers<SpatialAwarenessMeshObserver>()
.FirstOrDefault();
// Raycast from the
Competitor Comparisons
This repository contains various examples to use with the XR Interaction Toolkit
Pros of XR-Interaction-Toolkit-Examples
- Focused on providing a comprehensive set of examples for the XR Interaction Toolkit, making it easier to learn and implement the toolkit.
- Includes a variety of interaction scenarios, such as locomotion, object manipulation, and UI interactions, which can serve as a reference for developers.
- Provides a clear and well-documented structure, making it easier to navigate and understand the examples.
Cons of XR-Interaction-Toolkit-Examples
- Narrower in scope compared to the MixedRealityToolkit-Unity, which covers a broader range of mixed reality features and functionality.
- May not provide the same level of customization and extensibility as the MixedRealityToolkit-Unity.
- Relies more heavily on the XR Interaction Toolkit, which may not be suitable for all mixed reality projects.
Code Comparison
Here's a brief code comparison between the two repositories:
MixedRealityToolkit-Unity (Teleportation Example):
public class TeleportPointer : BaseControllerPointer
{
protected override void OnPostSceneQuery()
{
base.OnPostSceneQuery();
if (IsSelectPressed)
{
TeleportRequestEventData eventData = GetEventData<TeleportRequestEventData>();
eventData.Initialize(this, TeleportHotSpot);
CoreServices.InputSystem?.RaiseEvent(eventData);
}
}
}
XR-Interaction-Toolkit-Examples (Teleportation Example):
public class TeleportationProvider : MonoBehaviour, ITeleportationProvider
{
public void QueueTeleportRequest(TeleportRequest teleportRequest)
{
if (teleportRequest.Destination != null)
{
transform.position = teleportRequest.Destination.position;
transform.rotation = teleportRequest.Destination.rotation;
}
}
}
Samples to demonstrate use of the WebXR Device API
Pros of webxr-samples
- Web-based, allowing for cross-platform compatibility without the need for separate builds
- Lightweight and focused specifically on WebXR implementations
- Easier to get started with for web developers familiar with JavaScript and HTML
Cons of webxr-samples
- Limited functionality compared to the more comprehensive MixedRealityToolkit-Unity
- Less robust community support and fewer resources available
- May not offer the same level of performance optimization for high-end XR experiences
Code Comparison
MixedRealityToolkit-Unity (C#):
public class ExampleBehavior : MonoBehaviour
{
private IMixedRealityInputSystem inputSystem = null;
protected override void OnEnable()
{
inputSystem = CoreServices.InputSystem;
}
}
webxr-samples (JavaScript):
function onXRFrame(t, frame) {
const pose = frame.getViewerPose(xrRefSpace);
if (pose) {
for (const view of pose.views) {
const viewport = xrGLLayer.getViewport(view);
gl.viewport(viewport.x, viewport.y, viewport.width, viewport.height);
}
}
}
The code snippets demonstrate the different approaches: MixedRealityToolkit-Unity uses C# and Unity's MonoBehaviour system, while webxr-samples utilizes JavaScript and WebXR APIs for handling XR experiences in web browsers.
Convert  designs to code with AI
designs to code with AI

Introducing Visual Copilot: A new AI model to turn Figma designs to high quality code using your components.
Try Visual CopilotREADME
[!IMPORTANT]
With the creation of the new Mixed Reality Toolkit organization, there now exists two MRTK repositories, one repository for version 3+ and a legacy one for version 2.
MRTK v3+
New versions of the Mixed Reality Toolkit will be released by the Mixed Reality Toolkit organization using a repository at https://github.com/MixedRealityToolkit/MixedRealityToolkit-Unity. Visit this repository for the latest version of the MRTK project, and when creating new issues or discussion topics for MRTK version 3 or later.
MRTK v2 (Legacy)
The old MRTK2 repository, https://github.com/microsoft/MixedRealityToolkit-Unity, is remaining under Microsoft's management and will stay on version 2. Microsoft is committed to the next version of MRTK, and recommends applications move to MRTK version 3 or later. However, Microsoft will continue to support and address critical MRTK2 issues, until MRTK2 is deprecated. Please open MRTK2 issues and discussion topics using the old repository.

What is the Mixed Reality Toolkit
MRTK-Unity is a Microsoft-driven project that provides a set of components and features, used to accelerate cross-platform MR app development in Unity. Here are some of its functions:
- Provides the cross-platform input system and building blocks for spatial interactions and UI.
- Enables rapid prototyping via in-editor simulation that allows you to see changes immediately.
- Operates as an extensible framework that provides developers the ability to swap out core components.
- Supports a wide range of devices:
| XR SDK Plugin (Unity XR Plugin Management Providers) | Supported Devices |
|---|---|
| Unity OpenXR Plugin (Unity 2020 or 2021 LTS) (Mixed Reality OpenXR Plugin required for certain features on certain devices) | Microsoft HoloLens 2 Windows Mixed Reality headsets Meta Quest Device running on SteamVR via OpenXR |
| Windows XR Plugin | Microsoft HoloLens Microsoft HoloLens 2 Windows Mixed Reality headsets |
| Oculus XR Plugin (Unity 2019 or newer LTS) | Meta Quest (via Oculus Integration Package) |
| ARCore XR Plug-in | Android (via AR Foundation) |
| ARKit XR Plug-in | iOS (via AR Foundation) |
Additional devices supported:
- Ultraleap Leap Motion controller for hand tracking (via Ultraleap's OpenXR API layer (recommended) or via Ultraleap's Plugin for Unity)
| NOTE: We have introduced the public preview of MRTK3, the next chapter of MRTK. For documentation, please go to the MRTK3 documentation. For code, please go to the mrtk3 branch. |
|---|
Getting started with MRTK
If you're new to MRTK or Mixed Reality development in Unity, we recommend you start at the beginning of our Unity development journey in the Microsoft Docs. The Unity development journey is specifically tailored to walk new developers through the installation, core concepts, and usage of MRTK.
| IMPORTANT: The Unity development journey currently uses MRTK version 2.8.2, Mixed Reality OpenXR plugin version 1.6.0 and Unity 2020.3.42+. |
|---|
If you're an experienced Mixed Reality or MRTK developer, check the links in the next section for the newest packages and release notes.
Documentation
Starting from MRTK 2.6, we are publishing both conceptual docs and API references on docs.microsoft.com. For conceptual docs, please visit our new landing page. For API references, please visit the MRTK-Unity section of the dot net API explorer. Existing content will remain here but will not be updated further.
Release Notes | MRTK Overview | Feature Guides | API Reference |
|---|
Build status
| Branch | CI Status | Docs Status |
|---|---|---|
main |
Required software
 Windows SDK Windows SDK |  Unity 2018/2019/2020 LTS Unity 2018/2019/2020 LTS |  Visual Studio 2019 Visual Studio 2019 |  Emulators (optional) Emulators (optional) |
|---|
Please refer to the Install the tools page for more detailed information.
Feature areas
UX building blocks
 Button Button | 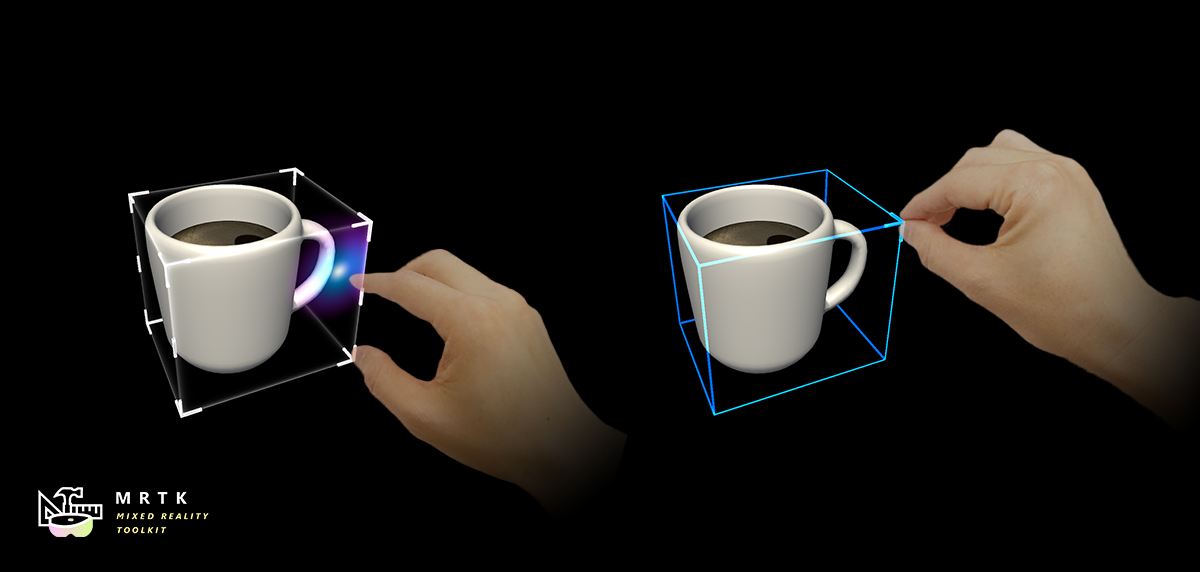 Bounds Control Bounds Control | 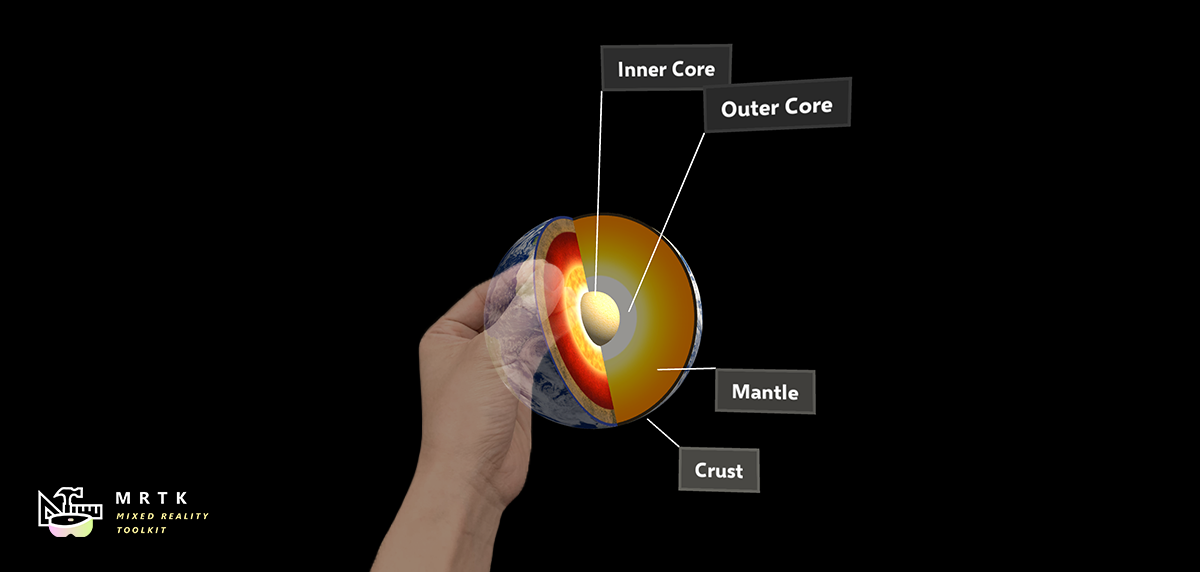 Object Manipulator Object Manipulator |
|---|---|---|
| A button control which supports various input methods, including HoloLens 2's articulated hand | Standard UI for manipulating objects in 3D space | Script for manipulating objects with one or two hands |
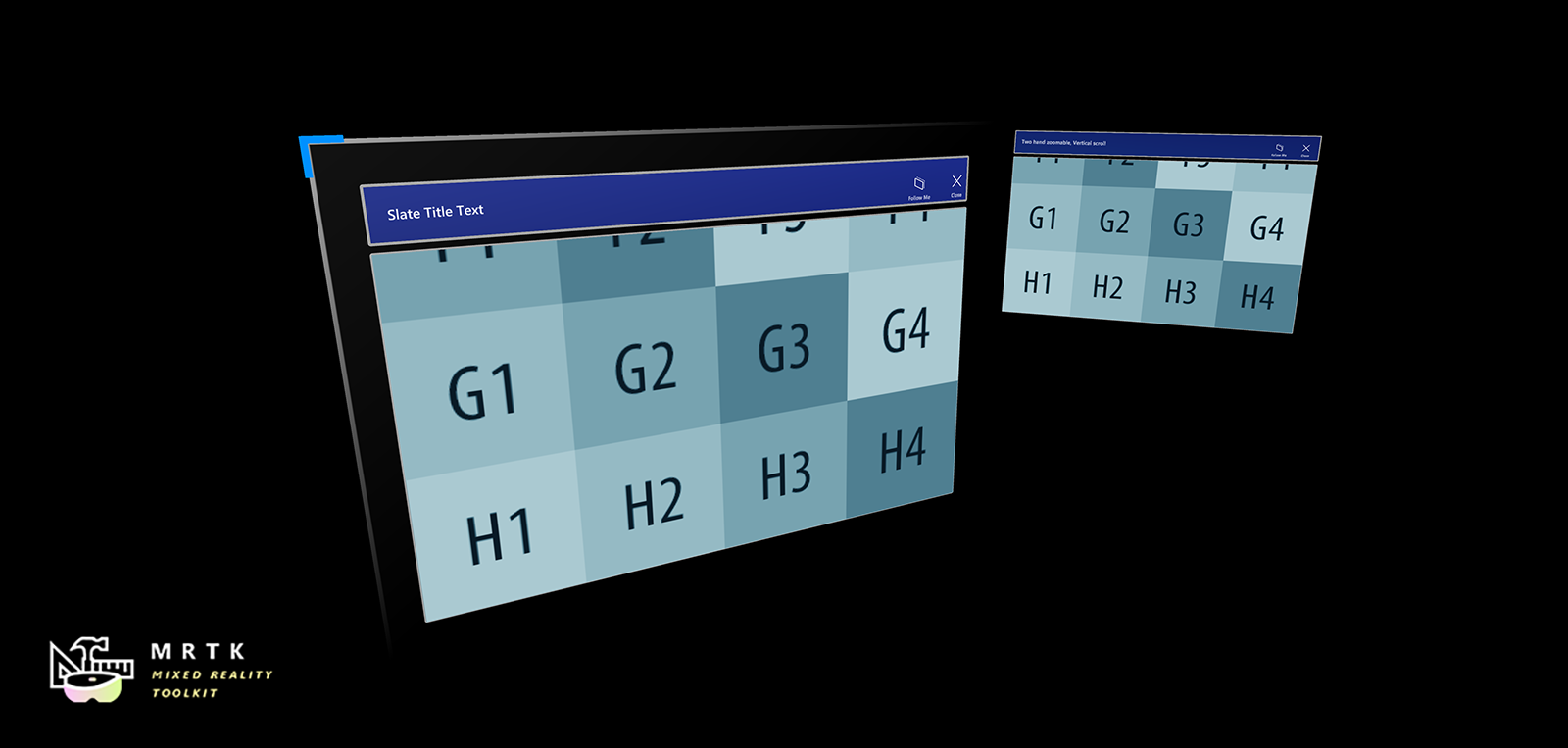 Slate Slate |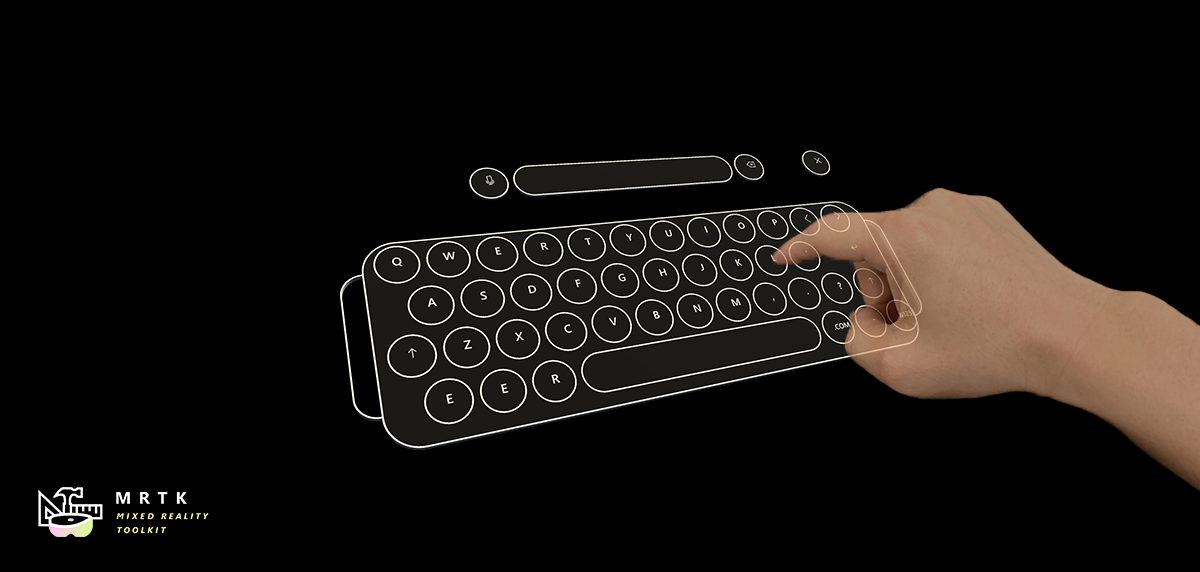  System Keyboard System Keyboard | 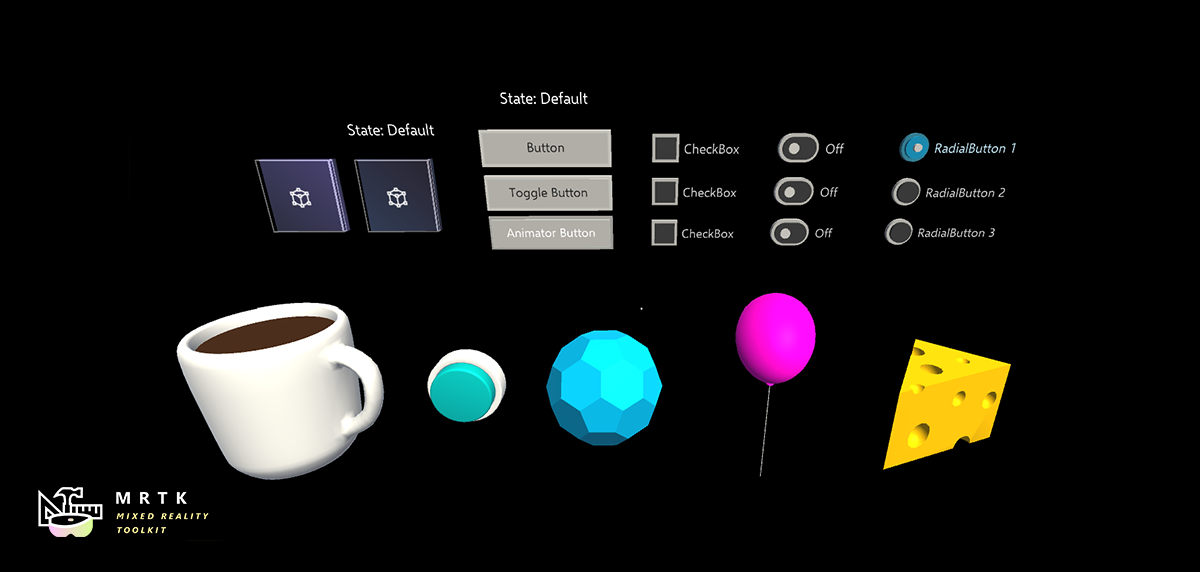 Interactable Interactable |
| 2D style plane which supports scrolling with articulated hand input | Example script of using the system keyboard in Unity | A script for making objects interactable with visual states and theme support |
 Solver Solver |  Object Collection Object Collection | 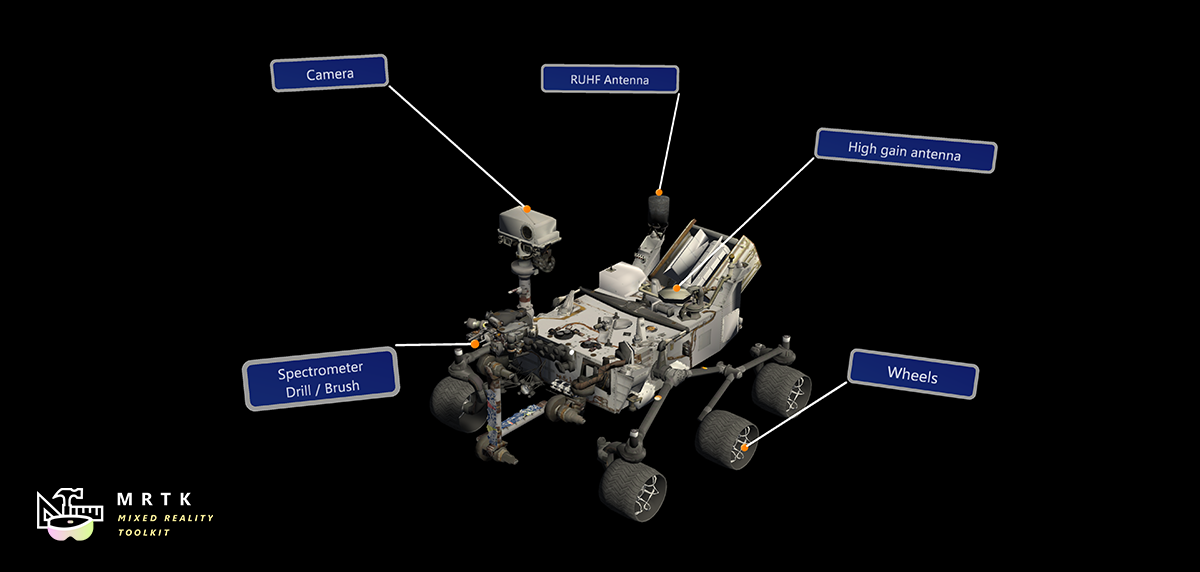 Tooltip Tooltip |
| Various object positioning behaviors such as tag-along, body-lock, constant view size and surface magnetism | Script for laying out an array of objects in a three-dimensional shape | Annotation UI with a flexible anchor/pivot system, which can be used for labeling motion controllers and objects |
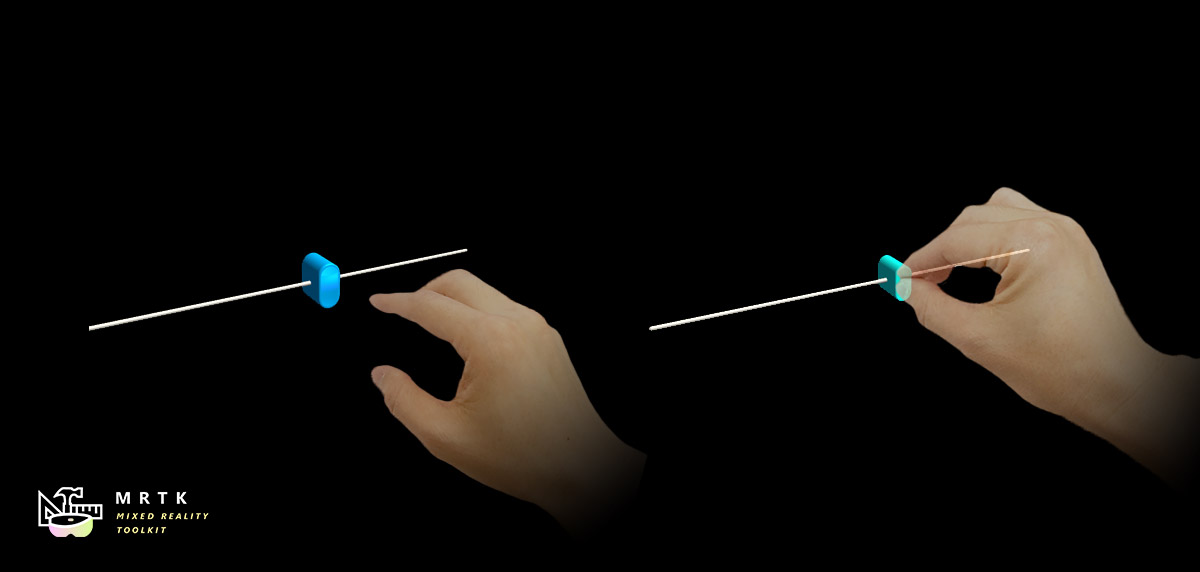 Slider Slider |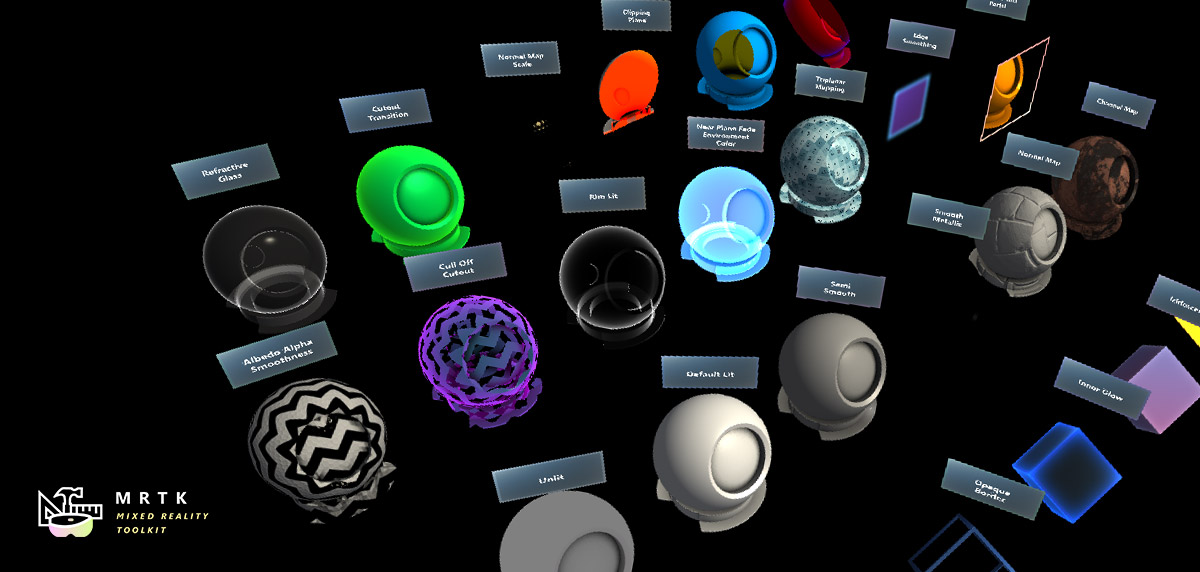  MRTK Standard Shader MRTK Standard Shader |  Hand Menu Hand Menu |
| Slider UI for adjusting values supporting direct hand tracking interaction | MRTK's Standard shader supports various Fluent design elements with performance | Hand-locked UI for quick access, using the Hand Constraint Solver |
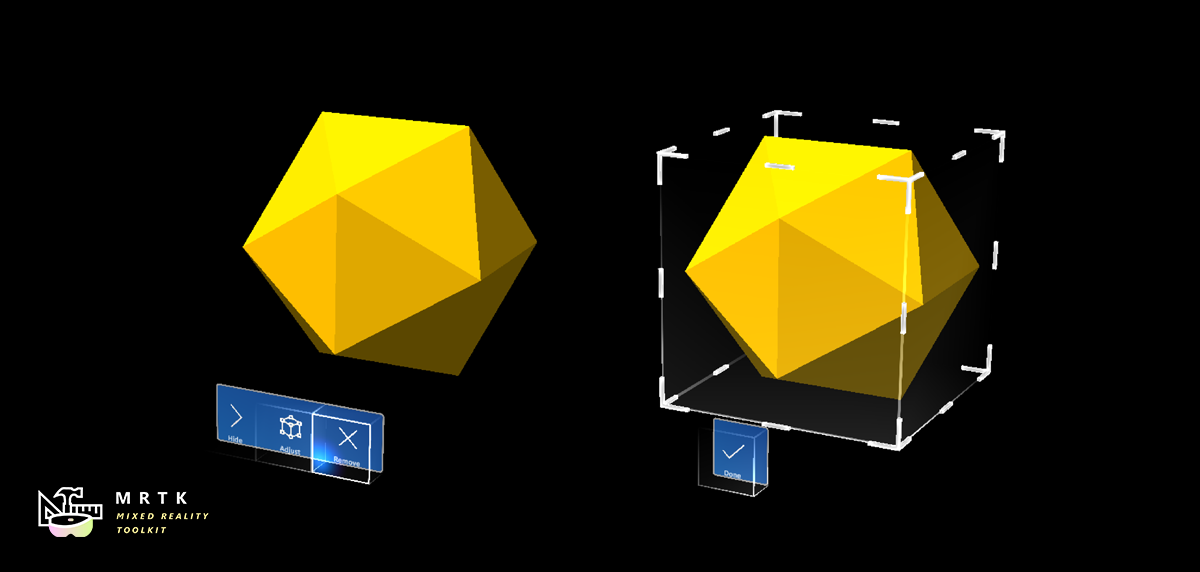 App Bar App Bar | 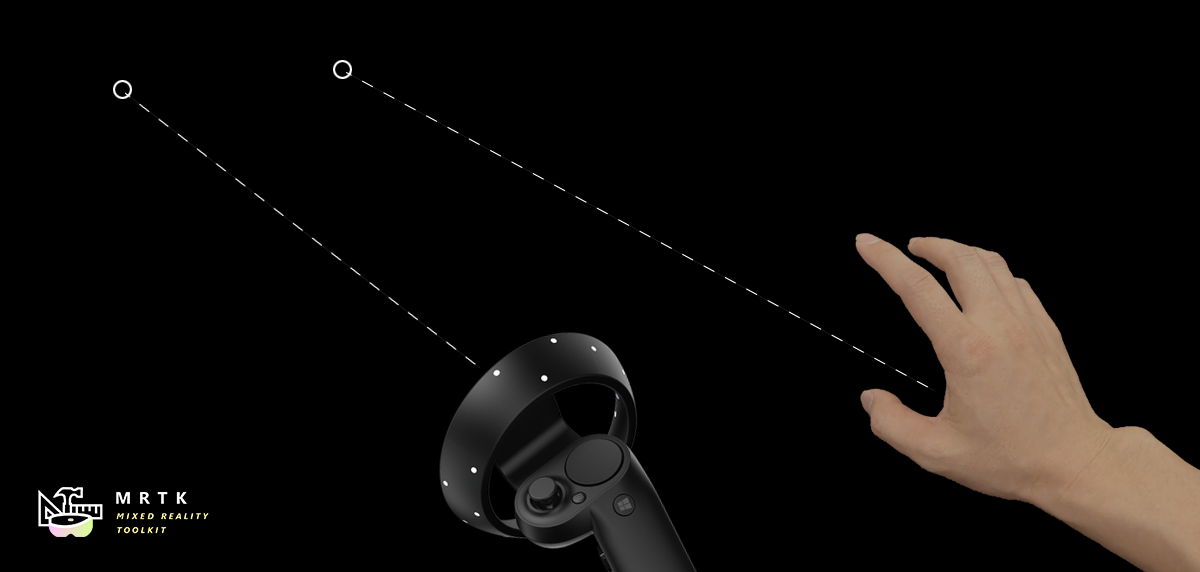 Pointers Pointers | 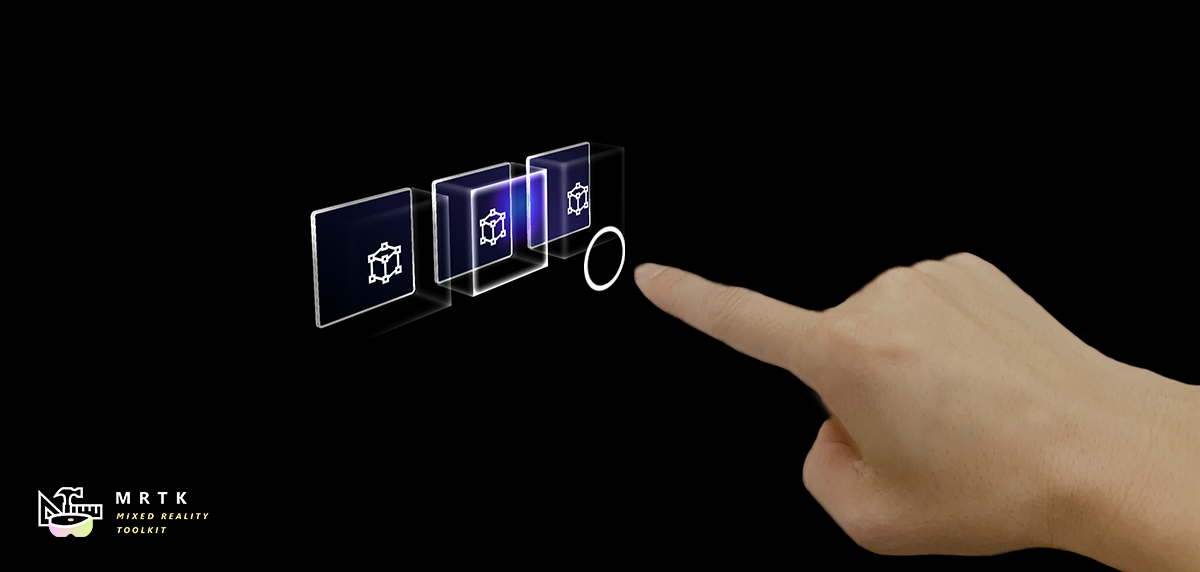 Fingertip Visualization Fingertip Visualization |
| UI for Bounds Control's manual activation | Learn about various types of pointers | Visual affordance on the fingertip which improves the confidence for the direct interaction |
 Near Menu Near Menu |  Spatial Awareness Spatial Awareness |  Voice Command / Dictation Voice Command / Dictation |
| Floating menu UI for the near interactions | Make your holographic objects interact with the physical environments | Scripts and examples for integrating speech input |
 Progress Indicator Progress Indicator |  Dialog [Experimental] Dialog [Experimental] |  Hand Coach Hand Coach |
| Visual indicator for communicating data process or operation | UI for asking for user's confirmation or acknowledgement | Component that helps guide the user when the gesture has not been taught |
 Hand Physics Service [Experimental] Hand Physics Service [Experimental] |  Scrolling Collection Scrolling Collection |  Dock [Experimental] Dock [Experimental] |
| The hand physics service enables rigid body collision events and interactions with articulated hands | An Object Collection that natively scrolls 3D objects | The Dock allows objects to be moved in and out of predetermined positions |
| Combine eyes, voice and hand input to quickly and effortlessly select holograms across your scene | Learn how to auto-scroll text or fluently zoom into focused content based on what you are looking at | Examples for logging, loading and visualizing what users have been looking at in your app |
Tools
| Automate configuration of Mixed Reality projects for performance optimizations | Analyze dependencies between assets and identify unused assets | Configure and execute an end-to-end build process for Mixed Reality applications | Record and playback head movement and hand tracking data in editor |
Example scenes
Explore MRTK's various types of interactions and UI controls through the example scenes. You can find example scenes under Assets/MRTK/Examples/Demos folder.
MRTK examples hub
With the MRTK Examples Hub, you can try various example scenes in MRTK. On HoloLens 2, you can download and install MRTK Examples Hub through the Microsoft Store app.
See Examples Hub README page to learn about the details on creating a multi-scene hub with MRTK's scene system and scene transition service.
Sample apps made with MRTK
 |  |  |
|---|---|---|
| Periodic Table of the Elements is an open-source sample app which demonstrates how to use MRTK's input system and building blocks to create an app experience for HoloLens and Immersive headsets. Read the porting story: Bringing the Periodic Table of the Elements app to HoloLens 2 with MRTK v2 | Galaxy Explorer is an open-source sample app that was originally developed in March 2016 as part of the HoloLens 'Share Your Idea' campaign. Galaxy Explorer has been updated with new features for HoloLens 2, using MRTK v2. Read the story: The Making of Galaxy Explorer for HoloLens 2 | Surfaces is an open-source sample app for HoloLens 2 which explores how we can create a tactile sensation with visual, audio, and fully articulated hand-tracking. Check out Microsoft MR Dev Days session Learnings from the Surfaces app for the detailed design and development story. |
Session videos from Mixed Reality Dev Days 2020
See Mixed Reality Dev Days to explore more session videos.
Engage with the community
-
Join the conversation around MRTK on Slack. You can join the Slack community via the automatic invitation sender.
-
Ask questions about using MRTK on Stack Overflow using the MRTK tag.
-
Search for known issues or file a new issue if you find something broken in MRTK code.
-
For questions about contributing to MRTK, go to the mixed-reality-toolkit channel on slack.
This project has adopted the Microsoft Open Source Code of Conduct. For more information, see the Code of Conduct FAQ or contact opencode@microsoft.com with any additional questions or comments.
Useful resources on the Mixed Reality Dev Center
| Learn to build mixed reality experiences for HoloLens and immersive headsets (VR). | Get design guides. Build user interface. Learn interactions and input. | Get development guides. Learn the technology. Understand the science. | Get your app ready for others and consider creating a 3D launcher. |
Useful resources on Azure
Spatial Anchors | Speech Services | Vision Services |
|---|---|---|
| Spatial Anchors is a cross-platform service that allows you to create Mixed Reality experiences using objects that persist their location across devices over time. | Discover and integrate Azure powered speech capabilities like speech to text, speaker recognition or speech translation into your application. | Identify and analyze your image or video content using Vision Services like computer vision, face detection, emotion recognition or video indexer. |
Learn more about the MRTK project
You can find our planning material on our wiki under the Project Management Section. You can always see the items the team is actively working on in the Iteration Plan issue.
How to contribute
Learn how you can contribute to MRTK at Contributing.
For details on the different branches used in the Mixed Reality Toolkit repositories, check this Branch Guide here.
Top Related Projects
This repository contains various examples to use with the XR Interaction Toolkit
Samples to demonstrate use of the WebXR Device API
Convert  designs to code with AI
designs to code with AI

Introducing Visual Copilot: A new AI model to turn Figma designs to high quality code using your components.
Try Visual Copilot