Top Related Projects
VST 3 Plug-In SDK
JUCE is an open-source cross-platform C++ application framework for desktop and mobile applications, including VST, VST3, AU, AUv3, LV2 and AAX audio plug-ins.
An audio server, programming language, and IDE for sound synthesis and algorithmic composition.
Mirror of Ardour Source Code
Quick Overview
Giada is an open-source, minimalistic, and cross-platform audio tool for DJs, live performers, and electronic musicians. It offers a compact interface for live audio production, featuring loop-based sequencing, live recording, and sample management capabilities.
Pros
- Cross-platform compatibility (Windows, macOS, Linux)
- Lightweight and minimalistic interface
- Real-time audio processing and live performance features
- Active development and community support
Cons
- Limited advanced features compared to more comprehensive DAWs
- Steeper learning curve for users accustomed to traditional DAW interfaces
- Documentation could be more extensive for new users
Getting Started
To get started with Giada:
- Download the latest release from the official GitHub repository.
- Install the application following the instructions for your operating system.
- Launch Giada and familiarize yourself with the interface.
- Load samples by clicking the "+" button in a channel.
- Use the sequencer to create patterns and loops.
- Experiment with live recording and real-time effects.
For more detailed instructions, refer to the official documentation.
Competitor Comparisons
VST 3 Plug-In SDK
Pros of vst3sdk
- Comprehensive SDK for developing VST3 plugins
- Extensive documentation and examples
- Widely adopted industry standard
Cons of vst3sdk
- Steeper learning curve for beginners
- More complex setup and configuration
- Limited to VST3 format
Code Comparison
vst3sdk:
#include "public.sdk/source/vst/vstaudioeffect.h"
class MyPlugin : public Steinberg::Vst::AudioEffect
{
public:
tresult PLUGIN_API process(Steinberg::Vst::ProcessData& data) override;
};
Giada:
#include "core/model/plugin.h"
class MyPlugin : public giada::m::Plugin
{
public:
void process(float* out, const float* in, int frames) override;
};
Summary
vst3sdk is a comprehensive toolkit for developing VST3 plugins, offering extensive documentation and industry-wide adoption. However, it has a steeper learning curve and is limited to the VST3 format. Giada, on the other hand, is a more focused project for loop-based live performance, with a simpler plugin architecture but less flexibility for third-party plugin development.
JUCE is an open-source cross-platform C++ application framework for desktop and mobile applications, including VST, VST3, AU, AUv3, LV2 and AAX audio plug-ins.
Pros of JUCE
- Comprehensive cross-platform framework for audio applications
- Extensive documentation and community support
- Wide range of audio-related features and tools
Cons of JUCE
- Steeper learning curve due to its extensive feature set
- Larger codebase and potential overhead for simpler projects
- Commercial licensing required for some use cases
Code Comparison
JUCE example (audio processing):
void processBlock (AudioBuffer<float>& buffer, MidiBuffer& midiMessages)
{
for (int channel = 0; channel < buffer.getNumChannels(); ++channel)
{
float* channelData = buffer.getWritePointer(channel);
for (int sample = 0; sample < buffer.getNumSamples(); ++sample)
{
channelData[sample] *= gain;
}
}
}
Giada example (audio processing):
void Wave::process(AudioBuffer& out, const AudioBuffer& in, int frameOffset)
{
for (int i = 0; i < out.countFrames(); i++)
out[i] += in[i + frameOffset] * volume;
}
While both projects deal with audio processing, JUCE provides a more comprehensive framework for building audio applications, whereas Giada is a more focused loop machine with a simpler codebase. JUCE offers greater flexibility but may be overkill for simpler projects, while Giada is more specialized but potentially easier to work with for its specific use case.
An audio server, programming language, and IDE for sound synthesis and algorithmic composition.
Pros of SuperCollider
- More powerful and flexible audio synthesis capabilities
- Extensive library of built-in UGens (unit generators) for sound processing
- Supports distributed computing for complex audio tasks
Cons of SuperCollider
- Steeper learning curve due to its text-based programming interface
- Less intuitive for beginners compared to Giada's GUI-based approach
- Requires more setup and configuration for basic audio production tasks
Code Comparison
SuperCollider:
SynthDef("sine", { |freq = 440, amp = 0.1, gate = 1|
var sig = SinOsc.ar(freq) * amp * EnvGen.kr(Env.asr, gate, doneAction: 2);
Out.ar(0, sig ! 2);
}).add;
Giada:
void giadaSampleChannel::onBar(int frame)
{
if (status == STATUS_PLAY)
trigger(frame);
}
SuperCollider uses a text-based approach for defining synthesizers and audio processes, while Giada employs a more traditional C++ structure for handling audio events. SuperCollider's code is more focused on sound synthesis, whereas Giada's example shows event handling within its audio engine.
Both projects serve different purposes in the audio software ecosystem. SuperCollider excels in complex sound design and algorithmic composition, while Giada offers a more straightforward approach to loop-based music production and live performance.
Mirror of Ardour Source Code
Pros of Ardour
- More comprehensive DAW with advanced features for recording, editing, and mixing
- Supports a wider range of audio plugins and formats
- Larger and more active community, resulting in frequent updates and extensive documentation
Cons of Ardour
- Steeper learning curve due to its complexity
- Heavier resource usage, potentially requiring more powerful hardware
- Less focused on live performance and loop-based music creation
Code Comparison
Ardour (C++):
void AudioRegion::set_position_internal (framepos_t pos, bool allow_bbt_recompute)
{
_position = pos;
maybe_update_bbt (allow_bbt_recompute);
PropertyChanged (Properties::position);
}
Giada (C++):
void Channel::setPosition(Frame f)
{
m_tracker.setPosition(f);
m_state->offset = f;
}
Both projects use C++ and handle audio positioning, but Ardour's implementation is more complex, reflecting its broader feature set. Giada's code is simpler, focusing on live performance and loop-based functionality.
Convert  designs to code with AI
designs to code with AI

Introducing Visual Copilot: A new AI model to turn Figma designs to high quality code using your components.
Try Visual CopilotREADME

Giada - Your Hardcore Loop Machine | Official website: giadamusic.com |
What is Giada?
Giada is an open source, minimalistic and hardcore music production tool. Designed for DJs, live performers and electronic musicians.
â¦â¦â¦ See Giada in action! â¦â¦â¦
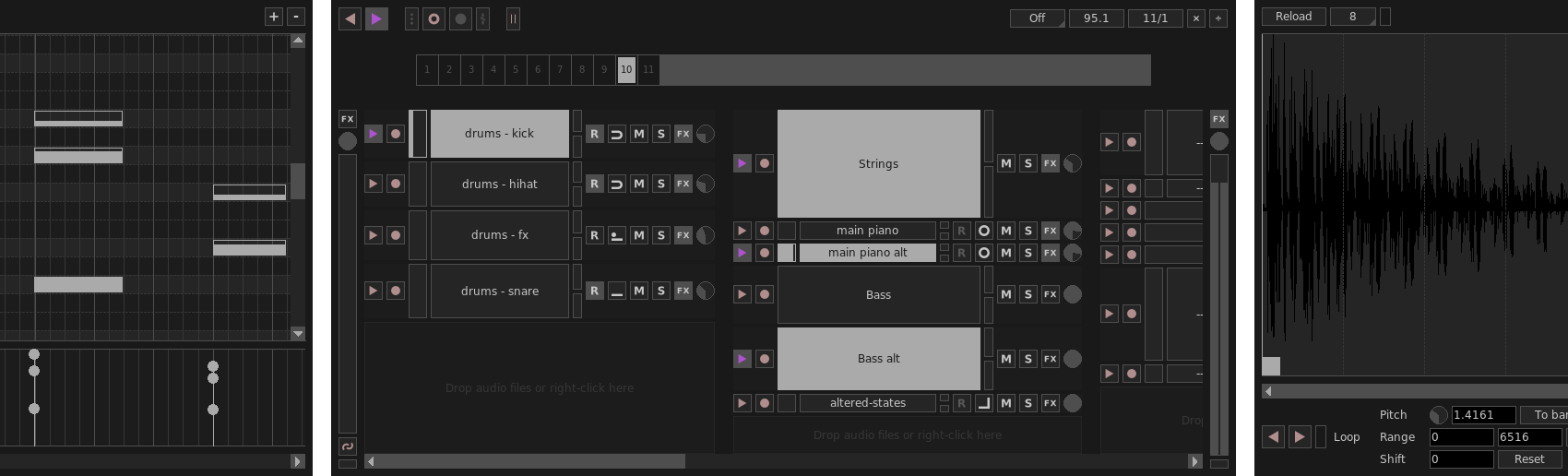
Main features
- Giada is a loop machine â build your performance in real time by layering audio tracks or MIDI events, driven by the main sequencer;
- Giada is a sample player â load samples from your crates and play them with a computer keyboard or a MIDI controller;
- Giada is a song editor â write songs from scratch or edit existing live recordings with the powerful Action Editor, for a fine-tuned control;
- Giada is a live recorder â record sounds from the real world and MIDI events coming from external devices or other apps;
- Giada is an FX processor â process samples or audio/MIDI input signals with VST instruments from your plug-ins collection;
- Giada is a MIDI controller â control other software or synchronize physical MIDI devices by using Giada as a MIDI master sequencer.
And more:
- Ultra-lightweight internal design;
- multi-thread/multi-core support;
- 32-bit floating point audio engine;
- ALSA, JACK + Transport, CoreAudio, ASIO and DirectSound full support;
- unlimited number of channels (optionally controllable via computer keyboard);
- BPM and beat sync with sample-accurate loop engine;
- MIDI input and output support, featuring custom MIDI lightning messages;
- super-sleek, built-in Wave Editor for audio samples and Piano Roll editor for MIDI messages;
- automatic quantizer;
- portable project storage system, based on super-hackable JSON files;
- support for all major uncompressed file formats;
- test-driven development style supported by GitHub Actions and Catch
- under a constant stage of development;
- 100% open-source GPL v3.
License
Giada is available under the terms of the GNU General Public License. Take a look at the COPYING file for further information.
Documentation
Documentation is available online in the user guide page.
An ever-growing collection of tutorials (both text and video) and live demos is available in the tutorials & media page.
Found a typo or a terrible mistake? Feel free to clone the website repository and send us your pull requests.
Build Giada from source
We do our best to make the compilation process as simple as possible. You can find all the information in the compiling from source chapter from the user guide.
Bugs, requests and questions for non-developers
Feel free to ask anything in the discussions area.
Copyright
Giada is Copyright (C) 2010-2025 by Giovanni A. Zuliani | Monocasual Laboratories
Giada - Your Hardcore Loopmachine is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
Giada - Your Hardcore Loopmachine is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along with Giada - Your Hardcore Loopmachine. If not, see http://www.gnu.org/licenses/.
Top Related Projects
VST 3 Plug-In SDK
JUCE is an open-source cross-platform C++ application framework for desktop and mobile applications, including VST, VST3, AU, AUv3, LV2 and AAX audio plug-ins.
An audio server, programming language, and IDE for sound synthesis and algorithmic composition.
Mirror of Ardour Source Code
Convert  designs to code with AI
designs to code with AI

Introducing Visual Copilot: A new AI model to turn Figma designs to high quality code using your components.
Try Visual Copilot