phan
phan
Phan is a static analyzer for PHP. Phan prefers to avoid false-positives and attempts to prove incorrectness rather than correctness.
Top Related Projects
PHP Static Analysis Tool - discover bugs in your code without running it!
A PHP static analysis tool for finding errors and security vulnerabilities in PHP applications
:bug: A tool that can speed up linting of php files by running several lint processes at once.
⚗️ Adds code analysis to Laravel improving developer productivity and code quality.
Quick Overview
Phan is a static code analysis tool for PHP that helps detect bugs, errors, and inconsistencies in your code. It uses a powerful type inference engine to analyze your codebase and provide detailed feedback on potential issues.
Pros
- Comprehensive Analysis: Phan can detect a wide range of issues, including type errors, undefined variables, unused variables, and more.
- Customizable Configuration: Phan allows you to configure various settings, including the types of issues to report, the severity of warnings, and the inclusion/exclusion of specific files or directories.
- Incremental Analysis: Phan can perform incremental analysis, which means it only analyzes the files that have changed since the last run, making it more efficient for large codebases.
- Integrations: Phan can be integrated with various development tools, such as IDEs, continuous integration (CI) systems, and code editors, making it easy to incorporate into your development workflow.
Cons
- Learning Curve: Phan has a relatively steep learning curve, especially for developers who are new to static code analysis tools.
- Performance: Phan can be resource-intensive, especially for large codebases, and may slow down the development process.
- Dependency Management: Phan relies on a specific version of the PHP parser, which can be challenging to manage, especially when working with different PHP versions.
- Limited Scope: Phan is primarily focused on static code analysis and may not provide the same level of functionality as other PHP tools, such as linters or code formatters.
Code Examples
Phan is a code analysis tool, so it doesn't have any code examples to provide. However, you can find examples of how to use Phan in the project's documentation.
Getting Started
To get started with Phan, follow these steps:
- Install Phan using Composer:
composer require --dev phan/phan
- Initialize Phan in your project:
./vendor/bin/phan --init
This will create a .phan/config.php file in your project, which you can customize to fit your needs.
- Run Phan:
./vendor/bin/phan
Phan will analyze your codebase and report any issues it finds.
You can also integrate Phan with your IDE or continuous integration system. For more information, refer to the Phan documentation.
Competitor Comparisons
PHP Static Analysis Tool - discover bugs in your code without running it!
Pros of phpstan/phpstan
- Supports a wider range of PHP versions, including the latest versions.
- Provides more detailed and accurate type inference, leading to more precise static analysis.
- Offers a more user-friendly configuration system, making it easier to customize and integrate into existing projects.
Cons of phpstan/phpstan
- May have a steeper learning curve for developers unfamiliar with its syntax and configuration.
- Can be more resource-intensive, especially on larger codebases, due to its more comprehensive analysis.
- Might not have as large of a community and ecosystem as Phan, with fewer available plugins and integrations.
Code Comparison
Phan:
/**
* @param int $a
* @param int $b
* @return int
*/
function add($a, $b) {
return $a + $b;
}
phpstan:
/**
* @param int $a
* @param int $b
* @return int
*/
function add(int $a, int $b): int {
return $a + $b;
}
The key differences are:
- phpstan uses stricter type annotations, specifying the parameter and return types as
int. - phpstan uses a return type declaration, while Phan relies on the PHPDoc.
A PHP static analysis tool for finding errors and security vulnerabilities in PHP applications
Pros of Psalm
- Psalm provides more detailed and comprehensive type analysis, including support for advanced type features like intersection and union types.
- Psalm has a more user-friendly interface, with clearer error messages and better integration with IDEs.
- Psalm has a larger and more active community, with more contributors and more third-party plugins and integrations.
Cons of Psalm
- Psalm has a steeper learning curve, with a more complex configuration and a larger codebase.
- Psalm may be slower than Phan, especially on larger codebases, due to its more comprehensive type analysis.
- Psalm has a more opinionated approach to code style and best practices, which may not align with all developers' preferences.
Code Comparison
Phan:
/**
* @param int $x
* @return int
*/
function add_one($x) {
return $x + 1;
}
Psalm:
/**
* @param int $x
* @return int
*/
function add_one(int $x): int {
return $x + 1;
}
The main difference in the code is the use of type annotations in Psalm, which provide more explicit type information and can help catch type-related errors more easily.
:bug: A tool that can speed up linting of php files by running several lint processes at once.
Pros of phplint
- Lightweight and fast, focusing solely on syntax checking
- Easy to integrate into CI/CD pipelines
- Simple configuration with minimal setup required
Cons of phplint
- Limited scope compared to Phan's comprehensive analysis
- Lacks advanced type checking and error detection capabilities
- Does not perform static analysis or identify potential runtime issues
Code Comparison
phplint example:
<?php
$linter = new Overtrue\PHPLint\Linter($path, $exclude);
$errors = $linter->lint();
if (!empty($errors)) {
foreach ($errors as $error) {
echo $error['file'] . ':' . $error['line'] . ' ' . $error['error'] . PHP_EOL;
}
}
Phan example:
<?php
$config = new Phan\Config();
$config->allow_missing_properties = false;
$config->null_casts_as_any_type = false;
$config->backward_compatibility_checks = true;
$result = Phan\Phan::analyzeFiles($files, $config);
While phplint focuses on quick syntax checking, Phan offers more comprehensive static analysis with configurable options for deeper code inspection and error detection.
⚗️ Adds code analysis to Laravel improving developer productivity and code quality.
Pros of Larastan
- Larastan is specifically designed for Laravel, providing deeper integration and understanding of the Laravel ecosystem.
- Larastan offers advanced features like support for Laravel-specific constructs, such as Facades, Contracts, and Eloquent models.
- Larastan's integration with PHPStan, a powerful static analysis tool, allows for more comprehensive code analysis within the Laravel context.
Cons of Larastan
- Larastan's focus on Laravel may limit its applicability to non-Laravel PHP projects.
- The learning curve for Larastan may be steeper for developers not familiar with PHPStan or the Laravel framework.
- Larastan's development and maintenance may be more closely tied to the evolution of the Laravel framework, potentially leading to compatibility issues.
Code Comparison
Phan:
/**
* @param int $x
* @return int
*/
function add_one($x) {
return $x + 1;
}
Larastan:
/**
* @param int $x
* @return int
*/
function add_one($x): int
{
return $x + 1;
}
The key differences are:
- Larastan enforces return type declarations, while Phan relies more on PHPDoc annotations.
- Larastan's code style follows the Laravel coding standards more closely.
Convert  designs to code with AI
designs to code with AI

Introducing Visual Copilot: A new AI model to turn Figma designs to high quality code using your components.
Try Visual CopilotREADME
Phan is a static analyzer for PHP that prefers to minimize false-positives. Phan attempts to prove incorrectness rather than correctness.
Phan looks for common issues and will verify type compatibility on various operations when type information is available or can be deduced. Phan has a good (but not comprehensive) understanding of flow control and can track values in a few use cases (e.g. arrays, integers, and strings).
Getting Started
The easiest way to use Phan is via Composer.
composer require phan/phan
With Phan installed, you'll want to create a .phan/config.php file in
your project to tell Phan how to analyze your source code. Once configured, you can run it via ./vendor/bin/phan.
Phan 5 depends on PHP 7.2+ with the php-ast extension (1.1.1+ is preferred) and supports analyzing PHP version 7.0-8.2 syntax.
Installation instructions for php-ast can be found here.
(Phan can be used without php-ast by using the CLI option --allow-polyfill-parser, but there are slight differences in the parsing of doc comments)
- Alternative Installation Methods
See Getting Started for alternative methods of using Phan and details on how to configure Phan for your project. - Incrementally Strengthening Analysis
Take a look at Incrementally Strengthening Analysis for some tips on how to slowly ramp up the strictness of the analysis as your code becomes better equipped to be analyzed. - Installing Dependencies
Take a look at Installing Phan Dependencies for help getting Phan's dependencies installed on your system.
The Wiki has more information about using Phan.
Features
Phan is able to perform the following kinds of analysis:
- Check that all methods, functions, classes, traits, interfaces, constants, properties and variables are defined and accessible.
- Check for type safety and arity issues on method/function/closure calls.
- Check for PHP8/PHP7/PHP5 backward compatibility.
- Check for features that weren't supported in older PHP 7.x minor releases (E.g.
object,void,iterable,?T,[$x] = ...;, negative string offsets, multiple exception catches, etc.) - Check for sanity with array accesses.
- Check for type safety on binary operations.
- Check for valid and type safe return values on methods, functions, and closures.
- Check for No-Ops on arrays, closures, constants, properties, variables, unary operators, and binary operators.
- Check for unused/dead/unreachable code. (Pass in
--dead-code-detection) - Check for unused variables and parameters. (Pass in
--unused-variable-detection) - Check for redundant or impossible conditions and pointless casts. (Pass in
--redundant-condition-detection) - Check for unused
usestatements. These and a few other issue types can be automatically fixed with--automatic-fix. - Check for classes, functions and methods being redefined.
- Check for sanity with class inheritance (e.g. checks method signature compatibility). Phan also checks for final classes/methods being overridden, that abstract methods are implemented, and that the implemented interface is really an interface (and so on).
- Supports namespaces, traits and variadics.
- Supports Union Types.
- Supports Generic Types (i.e.
@template). - Supports generic arrays such as
int[],UserObject[],array<int,UserObject>, etc.. - Supports array shapes such as
array{key:string,otherKey:?stdClass}, etc. (internally and in PHPDoc tags) This also supports indicating that fields of an array shape are optional viaarray{requiredKey:string,optionalKey?:string}(useful for@param) - Supports phpdoc type annotations.
- Supports inheriting phpdoc type annotations.
- Supports checking that phpdoc type annotations are a narrowed form (E.g. subclasses/subtypes) of the real type signatures
- Supports inferring types from assert() statements and conditionals in if elements/loops.
- Supports
@deprecatedannotation for deprecating classes, methods and functions - Supports
@internalannotation for elements (such as a constant, function, class, class constant, property or method) as internal to the package in which it's defined. - Supports
@suppress <ISSUE_TYPE>annotations for suppressing issues. - Supports magic @property annotations (
@property <union_type> <variable_name>) - Supports magic @method annotations (
@method <union_type> <method_name>(<union_type> <param1_name>)) - Supports
class_aliasannotations (experimental, off by default) - Supports indicating the class to which a closure will be bound, via
@phan-closure-scope(example) - Supports analysis of closures and return types passed to
array_map,array_filter, and other internal array functions. - Offers extensive configuration for weakening the analysis to make it useful on large sloppy code bases
- Can be run on many cores. (requires
pcntl) - Output is emitted in text, checkstyle, json, pylint, csv, codeclimate, html, or github formats.
- Can run user plugins on source for checks specific to your code. Phan includes various plugins you may wish to enable for your project.
See Phan Issue Types for descriptions and examples of all issues that can be detected by Phan. Take a look at the \Phan\Issue to see the definition of each error type.
Take a look at the Tutorial for Analyzing a Large Sloppy Code Base to get a sense of what the process of doing ongoing analysis might look like for you.
Phan can be used from various editors and IDEs for its error checking, "go to definition" support, etc. via the Language Server Protocol. Editors and tools can also request analysis of individual files in a project using the simpler Daemon Mode.
See the tests directory for some examples of the various checks.
Phan is imperfect and shouldn't be used to prove that your PHP-based rocket guidance system is free of defects.
Features provided by plugins
Additional analysis features have been provided by plugins.
- Checking for syntactically unreachable statements (E.g.
{ throw new Exception("Message"); return $value; }) - Checking
*printf()format strings against the provided arguments (as well as checking for common errors) - Checking that PCRE regexes passed to
preg_*()are valid - Checking for
@suppressannotations that are no longer needed. - Checking for duplicate or missing array keys.
- Checking coding style conventions
- Others
Example: Phan's plugins for self-analysis.
Usage
After installing Phan, Phan needs to be configured with details on where to find code to analyze and how to analyze it. The
easiest way to tell Phan where to find source code is to create a .phan/config.php file.
A simple .phan/config.php file might look something like the following.
<?php
/**
* This configuration will be read and overlaid on top of the
* default configuration. Command line arguments will be applied
* after this file is read.
*/
return [
// Supported values: `'5.6'`, `'7.0'`, `'7.1'`, `'7.2'`, `'7.3'`, `'7.4'`,
// `'8.0'`, `'8.1'`, `'8.2'`, `'8.3'`, `null`.
// If this is set to `null`,
// then Phan assumes the PHP version which is closest to the minor version
// of the php executable used to execute Phan.
"target_php_version" => null,
// A list of directories that should be parsed for class and
// method information. After excluding the directories
// defined in exclude_analysis_directory_list, the remaining
// files will be statically analyzed for errors.
//
// Thus, both first-party and third-party code being used by
// your application should be included in this list.
'directory_list' => [
'src',
'vendor/symfony/console',
],
// A directory list that defines files that will be excluded
// from static analysis, but whose class and method
// information should be included.
//
// Generally, you'll want to include the directories for
// third-party code (such as "vendor/") in this list.
//
// n.b.: If you'd like to parse but not analyze 3rd
// party code, directories containing that code
// should be added to the `directory_list` as
// to `exclude_analysis_directory_list`.
"exclude_analysis_directory_list" => [
'vendor/'
],
// A list of plugin files to execute.
// Plugins which are bundled with Phan can be added here by providing their name
// (e.g. 'AlwaysReturnPlugin')
//
// Documentation about available bundled plugins can be found
// at https://github.com/phan/phan/tree/v5/.phan/plugins
//
// Alternately, you can pass in the full path to a PHP file
// with the plugin's implementation.
// (e.g. 'vendor/phan/phan/.phan/plugins/AlwaysReturnPlugin.php')
'plugins' => [
// checks if a function, closure or method unconditionally returns.
// can also be written as 'vendor/phan/phan/.phan/plugins/AlwaysReturnPlugin.php'
'AlwaysReturnPlugin',
'DollarDollarPlugin',
'DuplicateArrayKeyPlugin',
'DuplicateExpressionPlugin',
'PregRegexCheckerPlugin',
'PrintfCheckerPlugin',
'SleepCheckerPlugin',
// Checks for syntactically unreachable statements in
// the global scope or function bodies.
'UnreachableCodePlugin',
'UseReturnValuePlugin',
'EmptyStatementListPlugin',
'LoopVariableReusePlugin',
],
];
Take a look at Creating a Config File and Incrementally Strengthening Analysis for more details.
Running phan --help will show usage information and command-line options.
Annotating Your Source Code
Phan reads and understands most PHPDoc
type annotations including Union Types
(like int|MyClass|string|null) and generic array types (like int[] or string[]|MyClass[] or array<int,MyClass>).
Take a look at Annotating Your Source Code and About Union Types for some help getting started with defining types in your code.
Phan supports (int|string)[] style annotations, and represents them internally as int[]|string[]
(Both annotations are treated like array which may have integers and/or strings).
When you have arrays of mixed types, just use array.
The following code shows off the various annotations that are supported.
/**
* @return void
*/
function f() {}
/** @deprecated */
class C {
/** @var int */
const C = 42;
/** @var string[]|null */
public $p = null;
/**
* @param int|null $p
* @return string[]|null
*/
public static function f($p) {
if (is_null($p)) {
return null;
}
return array_map(
/** @param int $i */
function($i) {
return "thing $i";
},
range(0, $p)
);
}
}
Just like in PHP, any type can be nulled in the function declaration which also means a null is allowed to be passed in for that parameter.
Phan checks the type of every single element of arrays (Including keys and values).
In practical terms, this means that [$int1=>$int2,$int3=>$int4,$int5=>$str6] is seen as array<int,int|string>,
which Phan represents as array<int,int>|array<int,string>.
[$strKey => new MyClass(), $strKey2 => $unknown] will be represented as
array<string,MyClass>|array<string,mixed>.
- Literals such as
[12,'myString']will be represented internally as array shapes such asarray{0:12,1:'myString'}
Generating a file list
This static analyzer does not track includes or try to figure out autoloader magic. It treats
all the files you throw at it as one big application. For code encapsulated in classes this
works well. For code running in the global scope it gets a bit tricky because order
matters. If you have an index.php including a file that sets a bunch of global variables and
you then try to access those after the include(...) in index.php the static analyzer won't
know anything about these.
In practical terms this simply means that you should put your entry points and any files
setting things in the global scope at the top of your file list. If you have a config.php
that sets global variables that everything else needs, then you should put that first in the list followed by your
various entry points, then all your library files containing your classes.
Development
Take a look at Developer's Guide to Phan for help getting started hacking on Phan.
When you find an issue, please take the time to create a tiny reproducing code snippet that illustrates
the bug. And once you have done that, fix it. Then turn your code snippet into a test and add it to
tests then ./test and send a PR with your fix and test. Alternatively, you can open an Issue with
details.
To run Phan's unit tests, just run ./test.
To run all of Phan's unit tests and integration tests, run ./tests/run_all_tests.sh
Code of Conduct
We are committed to fostering a welcoming community. Any participant and contributor is required to adhere to our Code of Conduct.
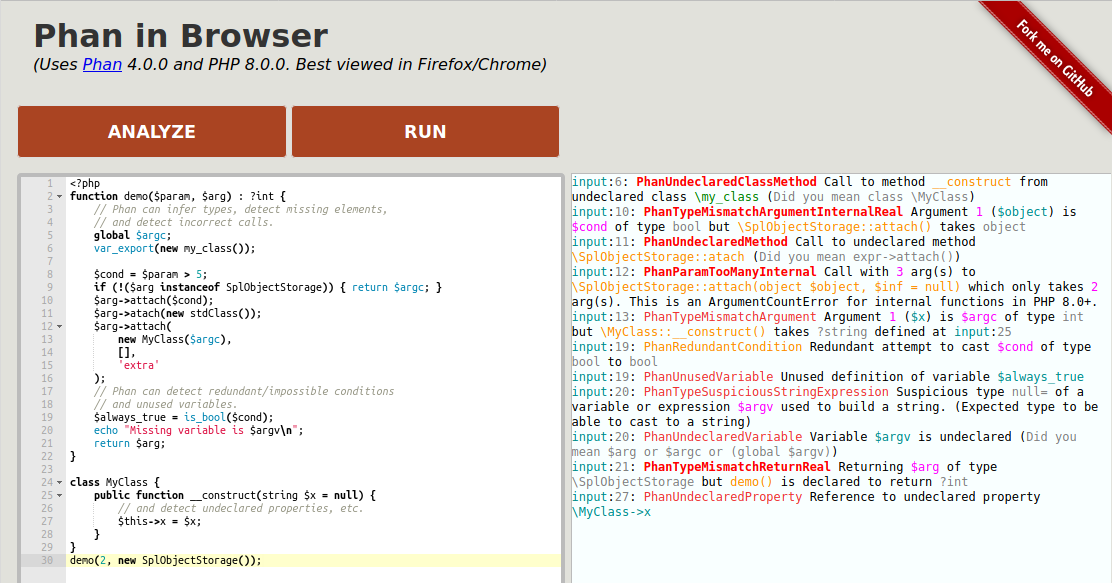
Online Demo
This requires an up to date version of Firefox/Chrome and at least 4 GB of free RAM. (this is a 15 MB download)
Top Related Projects
PHP Static Analysis Tool - discover bugs in your code without running it!
A PHP static analysis tool for finding errors and security vulnerabilities in PHP applications
:bug: A tool that can speed up linting of php files by running several lint processes at once.
⚗️ Adds code analysis to Laravel improving developer productivity and code quality.
Convert  designs to code with AI
designs to code with AI

Introducing Visual Copilot: A new AI model to turn Figma designs to high quality code using your components.
Try Visual Copilot