 silero-models
silero-models
Silero Models: pre-trained speech-to-text, text-to-speech and text-enhancement models made embarrassingly simple
Top Related Projects
Offline speech recognition API for Android, iOS, Raspberry Pi and servers with Python, Java, C# and Node
🐸💬 - a deep learning toolkit for Text-to-Speech, battle-tested in research and production
DeepSpeech is an open source embedded (offline, on-device) speech-to-text engine which can run in real time on devices ranging from a Raspberry Pi 4 to high power GPU servers.
End-to-End Speech Processing Toolkit
kaldi-asr/kaldi is the official location of the Kaldi project.
Facebook AI Research Sequence-to-Sequence Toolkit written in Python.
Quick Overview
Silero Models is an open-source project that provides pre-trained speech-to-text, text-to-speech, and voice activity detection models. It aims to make speech recognition and synthesis accessible and easy to use for developers and researchers, offering high-quality models that can be run efficiently on various devices.
Pros
- Easy to use and integrate into existing projects
- Supports multiple languages and accents
- Offers lightweight models suitable for edge devices and mobile applications
- Provides regular updates and improvements to model performance
Cons
- Limited customization options for specific use cases
- May not perform as well as some commercial solutions for certain languages
- Requires some technical knowledge to set up and use effectively
- Documentation could be more comprehensive for advanced usage scenarios
Code Examples
- Speech-to-Text (STT) example:
import torch
import zipfile
import torchaudio
from omegaconf import OmegaConf
# Load the model
model, decoder, utils = torch.hub.load(repo_or_dir='snakers4/silero-models',
model='silero_stt',
language='en')
# Transcribe audio
wav_path = 'path/to/audio/file.wav'
waveform, sample_rate = torchaudio.load(wav_path)
transcription = model(waveform)
print(transcription)
- Text-to-Speech (TTS) example:
import torch
# Load the model
model, _ = torch.hub.load(repo_or_dir='snakers4/silero-models',
model='silero_tts',
language='en',
speaker='en_0')
# Generate speech
text = "Hello, this is a test of text-to-speech synthesis."
audio = model.apply_tts(text=text,
speaker='en_0',
sample_rate=48000)
# Save the audio
torchaudio.save('output.wav', audio.unsqueeze(0), sample_rate=48000)
- Voice Activity Detection (VAD) example:
import torch
import torchaudio
# Load the model
model, utils = torch.hub.load(repo_or_dir='snakers4/silero-models',
model='silero_vad',
force_reload=True)
# Perform VAD on audio
wav_path = 'path/to/audio/file.wav'
waveform, sample_rate = torchaudio.load(wav_path)
vad_segments = utils.get_speech_timestamps(waveform, model, threshold=0.5)
print(vad_segments)
Getting Started
To get started with Silero Models:
-
Install the required dependencies:
pip install torch torchaudio omegaconf -
Load the desired model using
torch.hub.load()as shown in the code examples above. -
Process your audio or text data using the loaded model's functions.
-
For more detailed usage instructions and advanced features, refer to the project's GitHub repository and documentation.
Competitor Comparisons
Offline speech recognition API for Android, iOS, Raspberry Pi and servers with Python, Java, C# and Node
Pros of vosk-api
- Supports a wider range of languages and accents
- Offers offline speech recognition capabilities
- Provides a more flexible API for integration into various applications
Cons of vosk-api
- Generally slower processing speed compared to Silero models
- Requires more computational resources for operation
- Less focus on lightweight models for edge devices
Code Comparison
vosk-api:
from vosk import Model, KaldiRecognizer
import pyaudio
model = Model("model")
rec = KaldiRecognizer(model, 16000)
p = pyaudio.PyAudio()
stream = p.open(format=pyaudio.paInt16, channels=1, rate=16000, input=True, frames_per_buffer=8000)
stream.start_stream()
while True:
data = stream.read(4000)
if rec.AcceptWaveform(data):
print(rec.Result())
silero-models:
import torch
from silero import models
model, decoder, utils = torch.hub.load(repo_or_dir='snakers4/silero-models', model='silero_stt')
device = torch.device('cpu')
model = model.to(device)
wav_path = 'audio.wav'
transcription = model.transcribe(wav_path)
print(transcription)
Both repositories offer speech recognition capabilities, but they differ in their approach and use cases. vosk-api provides a more comprehensive solution for various languages and offline usage, while silero-models focuses on lightweight, efficient models suitable for edge devices and quick processing.
🐸💬 - a deep learning toolkit for Text-to-Speech, battle-tested in research and production
Pros of TTS
- More comprehensive and feature-rich, offering a wider range of TTS models and voice conversion capabilities
- Active development with frequent updates and a larger community
- Supports multiple languages and provides pre-trained models for various use cases
Cons of TTS
- Higher complexity and steeper learning curve compared to Silero Models
- Requires more computational resources and may have longer inference times
- Installation process can be more involved, especially for certain features
Code Comparison
TTS:
from TTS.api import TTS
tts = TTS(model_name="tts_models/en/ljspeech/tacotron2-DDC")
tts.tts_to_file(text="Hello world!", file_path="output.wav")
Silero Models:
import torch
model, _ = torch.hub.load(repo_or_dir='snakers4/silero-models', model='silero_tts')
audio = model.apply_tts("Hello world!", speaker='en_0', sample_rate=48000)
Both repositories offer powerful text-to-speech capabilities, but TTS provides a more extensive set of features and models at the cost of increased complexity. Silero Models, on the other hand, offers a simpler and more lightweight solution that may be easier to integrate for basic TTS needs.
DeepSpeech is an open source embedded (offline, on-device) speech-to-text engine which can run in real time on devices ranging from a Raspberry Pi 4 to high power GPU servers.
Pros of DeepSpeech
- More established project with a larger community and extensive documentation
- Supports multiple languages and accents out of the box
- Offers pre-trained models for immediate use
Cons of DeepSpeech
- Requires more computational resources and has a larger model size
- Can be more complex to set up and integrate into projects
- May have slower inference times compared to Silero Models
Code Comparison
DeepSpeech:
import deepspeech
model = deepspeech.Model('path/to/model.pbmm')
text = model.stt(audio)
Silero Models:
import torch
model, decoder, utils = torch.hub.load(repo_or_dir='snakers4/silero-models', model='silero_stt')
text = model(audio)
Both repositories provide speech-to-text functionality, but they differ in implementation and usage. DeepSpeech offers a more comprehensive solution with support for multiple languages, while Silero Models focuses on lightweight, efficient models. DeepSpeech may be better suited for large-scale projects with diverse language requirements, whereas Silero Models could be preferable for applications where speed and resource efficiency are crucial. The choice between the two depends on specific project needs, available computational resources, and desired features.
End-to-End Speech Processing Toolkit
Pros of ESPnet
- Comprehensive toolkit with support for various speech processing tasks (ASR, TTS, speech enhancement, etc.)
- Extensive documentation and active community support
- Flexible architecture allowing for easy customization and experimentation
Cons of ESPnet
- Steeper learning curve due to its extensive feature set
- Potentially higher computational requirements for training and inference
- More complex setup process compared to simpler alternatives
Code Comparison
ESPnet example (ASR training):
from espnet2.bin.asr_train import main
args = {
"output_dir": "exp/asr_train",
"max_epoch": 100,
"batch_size": 32,
"accum_grad": 2,
"use_amp": True
}
main(args)
Silero Models example (ASR inference):
import torch
from silero import models
model, decoder, utils = models.silero_stt(language='en', device='cpu')
audio_path = 'audio.wav'
transcription = model(audio_path)
The ESPnet code showcases its flexibility in training configuration, while Silero Models demonstrates simplicity in inference. ESPnet offers more control over the training process, whereas Silero Models provides a straightforward API for quick deployment.
kaldi-asr/kaldi is the official location of the Kaldi project.
Pros of Kaldi
- Comprehensive toolkit with extensive documentation and examples
- Highly flexible and customizable for various ASR tasks
- Large community support and active development
Cons of Kaldi
- Steeper learning curve and more complex setup
- Requires more computational resources for training and inference
- Less suitable for quick prototyping or small-scale projects
Code Comparison
Silero-models (Python):
import torch
model, decoder, utils = torch.hub.load(repo_or_dir='snakers4/silero-models', model='silero_stt')
wav_path = 'audio.wav'
transcription = model.transcribe(wav_path)
Kaldi (Shell script):
#!/bin/bash
. ./path.sh
compute-mfcc-feats --config=conf/mfcc.conf scp:data/test/wav.scp ark:- | \
apply-cmvn-sliding --norm-vars=false --center=true --cmn-window=300 ark:- ark:- | \
gmm-latgen-faster --max-active=7000 --beam=13.0 --lattice-beam=6.0 --acoustic-scale=0.083333 \
--allow-partial=true --word-symbol-table=exp/tri4b/graph/words.txt \
exp/tri4b/final.mdl exp/tri4b/graph/HCLG.fst ark:- ark:- | \
lattice-best-path --word-symbol-table=exp/tri4b/graph/words.txt ark:- ark,t:transcription.txt
Facebook AI Research Sequence-to-Sequence Toolkit written in Python.
Pros of fairseq
- Comprehensive toolkit for sequence modeling tasks
- Supports a wide range of architectures and tasks
- Extensive documentation and community support
Cons of fairseq
- Steeper learning curve due to complexity
- Requires more computational resources
- Less focused on specific speech-to-text tasks
Code Comparison
silero-models:
import torch
model, decoder, utils = torch.hub.load(repo_or_dir='snakers4/silero-models', model='silero_stt')
fairseq:
from fairseq.models.wav2vec import Wav2VecModel
model = Wav2VecModel.from_pretrained('/path/to/model')
Key Differences
- silero-models focuses on speech recognition, while fairseq covers a broader range of sequence modeling tasks
- silero-models offers simpler integration and usage, while fairseq provides more flexibility and customization options
- fairseq has a larger codebase and more dependencies, whereas silero-models is more lightweight and easier to deploy
Use Cases
- Choose silero-models for quick implementation of speech recognition tasks
- Opt for fairseq when working on complex sequence modeling projects or research requiring extensive customization
Convert  designs to code with AI
designs to code with AI

Introducing Visual Copilot: A new AI model to turn Figma designs to high quality code using your components.
Try Visual CopilotREADME

- Silero Models
Silero Models
Silero Models: pre-trained enterprise-grade STT / TTS models and benchmarks.
Enterprise-grade STT made refreshingly simple (seriously, see benchmarks). We provide quality comparable to Google's STT (and sometimes even better) and we are not Google.
As a bonus:
- No Kaldi;
- No compilation;
- No 20-step instructions;
Also we have published TTS models that satisfy the following criteria:
- One-line usage;
- A large library of voices;
- A fully end-to-end pipeline;
- Natural-sounding speech;
- No GPU or training required;
- Minimalism and lack of dependencies;
- Faster than real-time on one CPU thread (!!!);
- Support for 16kHz and 8kHz out of the box;
Also we have published a model for text repunctuation and recapitalization that:
- Inserts capital letters and basic punctuation marks, e.g., dots, commas, hyphens, question marks, exclamation points, and dashes (for Russian);
- Works for 4 languages (Russian, English, German, and Spanish) and can be extended;
- Domain-agnostic by design and not based on any hard-coded rules;
- Has non-trivial metrics and succeeds in the task of improving text readability;
Installation and Basics
You can basically use our models in 3 flavours:
- Via PyTorch Hub:
torch.hub.load(); - Via pip:
pip install sileroand thenimport silero; - Via caching the required models and utils manually and modifying if necessary;
Models are downloaded on demand both by pip and PyTorch Hub. If you need caching, do it manually or via invoking a necessary model once (it will be downloaded to a cache folder). Please see these docs for more information.
PyTorch Hub and pip package are based on the same code. All of the torch.hub.load examples can be used with the pip package via this basic change:
# before
torch.hub.load(repo_or_dir='snakers4/silero-models',
model='silero_stt', # or silero_tts or silero_te
**kwargs)
# after
from silero import silero_stt, silero_tts, silero_te
silero_stt(**kwargs)
Speech-To-Text
All of the provided models are listed in the models.yml file. Any metadata and newer versions will be added there.
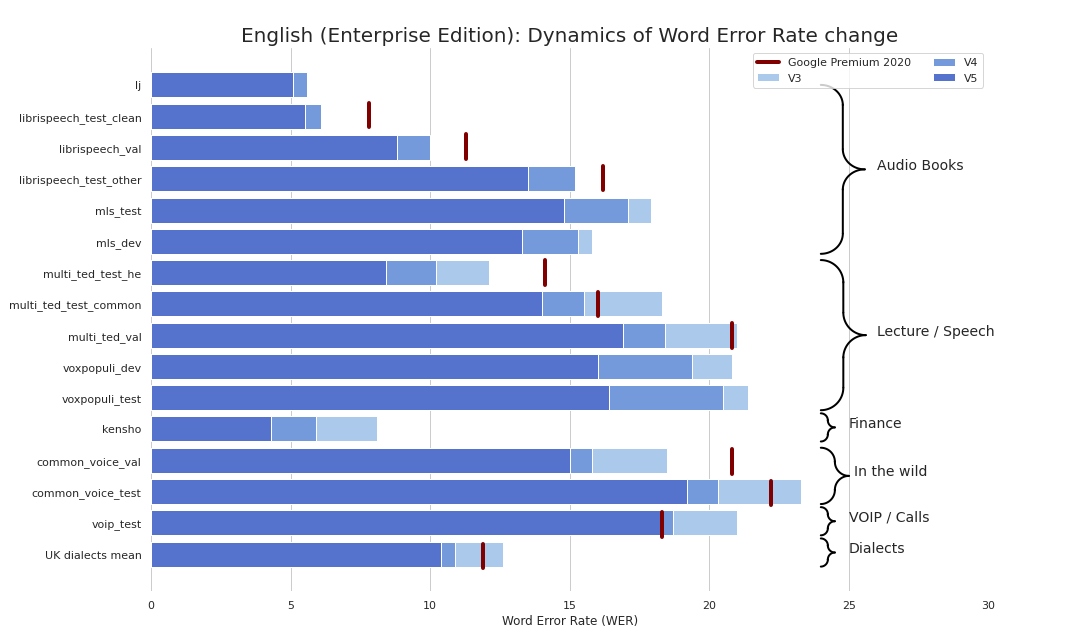
Currently we provide the following checkpoints:
| PyTorch | ONNX | Quantization | Quality | Colab | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
English (en_v6) | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | link | |
English (en_v5) | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | link | |
German (de_v4) | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :hourglass: | link | |
English (en_v3) | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | link | |
German (de_v3) | :heavy_check_mark: | :hourglass: | :hourglass: | link | |
German (de_v1) | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :hourglass: | link | |
Spanish (es_v1) | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :hourglass: | link | |
Ukrainian (ua_v3) | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | N/A |
Model flavours:
| jit | jit | jit | jit | jit_q | jit_q | onnx | onnx | onnx | onnx | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| xsmall | small | large | xlarge | xsmall | small | xsmall | small | large | xlarge | |
English en_v6 | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | |||||
English en_v5 | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | |||||
English en_v4_0 | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | ||||||||
English en_v3 | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | ||
German de_v4 | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | ||||||||
German de_v3 | :heavy_check_mark: | |||||||||
German de_v1 | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | ||||||||
Spanish es_v1 | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | ||||||||
Ukrainian ua_v3 | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: | :heavy_check_mark: |
Dependencies
- All examples:
torch, 1.8+ (used to clone the repo in TensorFlow and ONNX examples), breaking changes for versions older than 1.6torchaudio, latest version bound to PyTorch should just workomegaconf, latest should just work
- Additional dependencies for ONNX examples:
onnx, latest should just workonnxruntime, latest should just work
- Additional for TensorFlow examples:
tensorflow, latest should just worktensorflow_hub, latest should just work
Please see the provided Colab for details for each example below. All examples are maintained to work with the latest major packaged versions of the installed libraries.
PyTorch
import torch
import zipfile
import torchaudio
from glob import glob
device = torch.device('cpu') # gpu also works, but our models are fast enough for CPU
model, decoder, utils = torch.hub.load(repo_or_dir='snakers4/silero-models',
model='silero_stt',
language='en', # also available 'de', 'es'
device=device)
(read_batch, split_into_batches,
read_audio, prepare_model_input) = utils # see function signature for details
# download a single file in any format compatible with TorchAudio
torch.hub.download_url_to_file('https://opus-codec.org/static/examples/samples/speech_orig.wav',
dst ='speech_orig.wav', progress=True)
test_files = glob('speech_orig.wav')
batches = split_into_batches(test_files, batch_size=10)
input = prepare_model_input(read_batch(batches[0]),
device=device)
output = model(input)
for example in output:
print(decoder(example.cpu()))
ONNX
Our model will run anywhere that can import the ONNX model or that supports the ONNX runtime.
import onnx
import torch
import onnxruntime
from omegaconf import OmegaConf
language = 'en' # also available 'de', 'es'
# load provided utils
_, decoder, utils = torch.hub.load(repo_or_dir='snakers4/silero-models', model='silero_stt', language=language)
(read_batch, split_into_batches,
read_audio, prepare_model_input) = utils
# see available models
torch.hub.download_url_to_file('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/snakers4/silero-models/master/models.yml', 'models.yml')
models = OmegaConf.load('models.yml')
available_languages = list(models.stt_models.keys())
assert language in available_languages
# load the actual ONNX model
torch.hub.download_url_to_file(models.stt_models.en.latest.onnx, 'model.onnx', progress=True)
onnx_model = onnx.load('model.onnx')
onnx.checker.check_model(onnx_model)
ort_session = onnxruntime.InferenceSession('model.onnx')
# download a single file in any format compatible with TorchAudio
torch.hub.download_url_to_file('https://opus-codec.org/static/examples/samples/speech_orig.wav', dst ='speech_orig.wav', progress=True)
test_files = ['speech_orig.wav']
batches = split_into_batches(test_files, batch_size=10)
input = prepare_model_input(read_batch(batches[0]))
# actual ONNX inference and decoding
onnx_input = input.detach().cpu().numpy()
ort_inputs = {'input': onnx_input}
ort_outs = ort_session.run(None, ort_inputs)
decoded = decoder(torch.Tensor(ort_outs[0])[0])
print(decoded)
TensorFlow
SavedModel example
import os
import torch
import subprocess
import tensorflow as tf
import tensorflow_hub as tf_hub
from omegaconf import OmegaConf
language = 'en' # also available 'de', 'es'
# load provided utils using torch.hub for brevity
_, decoder, utils = torch.hub.load(repo_or_dir='snakers4/silero-models', model='silero_stt', language=language)
(read_batch, split_into_batches,
read_audio, prepare_model_input) = utils
# see available models
torch.hub.download_url_to_file('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/snakers4/silero-models/master/models.yml', 'models.yml')
models = OmegaConf.load('models.yml')
available_languages = list(models.stt_models.keys())
assert language in available_languages
# load the actual tf model
torch.hub.download_url_to_file(models.stt_models.en.latest.tf, 'tf_model.tar.gz')
subprocess.run('rm -rf tf_model && mkdir tf_model && tar xzfv tf_model.tar.gz -C tf_model', shell=True, check=True)
tf_model = tf.saved_model.load('tf_model')
# download a single file in any format compatible with TorchAudio
torch.hub.download_url_to_file('https://opus-codec.org/static/examples/samples/speech_orig.wav', dst ='speech_orig.wav', progress=True)
test_files = ['speech_orig.wav']
batches = split_into_batches(test_files, batch_size=10)
input = prepare_model_input(read_batch(batches[0]))
# tf inference
res = tf_model.signatures["serving_default"](tf.constant(input.numpy()))['output_0']
print(decoder(torch.Tensor(res.numpy())[0]))
Text-To-Speech
Models and Speakers
All of the provided models are listed in the models.yml file. Any metadata and newer versions will be added there.
V4
V4 models support SSML. Also see Colab examples for main SSML tag usage.
| ID | Speakers | Auto-stress | Language | SR | Colab |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
v4_ru | aidar, baya, kseniya, xenia, eugene, random | yes | ru (Russian) | 8000, 24000, 48000 | |
v4_cyrillic | b_ava, marat_tt, kalmyk_erdni... | no | cyrillic (Avar, Tatar, Kalmyk, ...) | 8000, 24000, 48000 | |
v4_ua | mykyta, random | no | ua (Ukrainian) | 8000, 24000, 48000 | |
v4_uz | dilnavoz | no | uz (Uzbek) | 8000, 24000, 48000 | |
v4_indic | hindi_male, hindi_female, ..., random | no | indic (Hindi, Telugu, ...) | 8000, 24000, 48000 |
V3
V3 models support SSML. Also see Colab examples for main SSML tag usage.
| ID | Speakers | Auto-stress | Language | SR | Colab |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
v3_en | en_0, en_1, ..., en_117, random | no | en (English) | 8000, 24000, 48000 | |
v3_en_indic | tamil_female, ..., assamese_male, random | no | en (English) | 8000, 24000, 48000 | |
v3_de | eva_k, ..., karlsson, random | no | de (German) | 8000, 24000, 48000 | |
v3_es | es_0, es_1, es_2, random | no | es (Spanish) | 8000, 24000, 48000 | |
v3_fr | fr_0, ..., fr_5, random | no | fr (French) | 8000, 24000, 48000 | |
v3_indic | hindi_male, hindi_female, ..., random | no | indic (Hindi, Telugu, ...) | 8000, 24000, 48000 |
Dependencies
Basic dependencies for Colab examples:
torch, 1.10+ for v3 models/ 2.0+ for v4 models;torchaudio, latest version bound to PyTorch should work (required only because models are hosted together with STT, not required for work);omegaconf, latest (can be removed as well, if you do not load all of the configs);
PyTorch
# V4
import torch
language = 'ru'
model_id = 'v4_ru'
sample_rate = 48000
speaker = 'xenia'
device = torch.device('cpu')
model, example_text = torch.hub.load(repo_or_dir='snakers4/silero-models',
model='silero_tts',
language=language,
speaker=model_id)
model.to(device) # gpu or cpu
audio = model.apply_tts(text=example_text,
speaker=speaker,
sample_rate=sample_rate)
Standalone Use
- Standalone usage only requires PyTorch 1.10+ and the Python Standard Library;
- Please see the detailed examples in Colab;
# V4
import os
import torch
device = torch.device('cpu')
torch.set_num_threads(4)
local_file = 'model.pt'
if not os.path.isfile(local_file):
torch.hub.download_url_to_file('https://models.silero.ai/models/tts/ru/v4_ru.pt',
local_file)
model = torch.package.PackageImporter(local_file).load_pickle("tts_models", "model")
model.to(device)
example_text = 'РнедÑаÑ
ÑÑндÑÑ Ð²ÑдÑÑ Ð² г+еÑÑаÑ
Ñ+ÑÑÑÑ Ð² вÑдÑа ÑдÑа кедÑов.'
sample_rate = 48000
speaker='baya'
audio_paths = model.save_wav(text=example_text,
speaker=speaker,
sample_rate=sample_rate)
SSML
Check out our TTS Wiki page.
Cyrillic languages
Supported tokenset:
!,-.:?iµöабвгдежзийклмнопÑÑÑÑÑÑ
ÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑÑѳÒÒÒÒÒÒ¡Ò£Ò¥Ò«Ò¯Ò±Ò³Ò·Ò»ÓÓÓÓÓÓÓÓÓ¥Ó§Ó©Ó±Ó³ÓµÓ¹
| Speaker_ID | Language | Gender |
|---|---|---|
| b_ava | Avar | F |
| b_bashkir | Bashkir | M |
| b_bulb | Bulgarian | M |
| b_bulc | Bulgarian | M |
| b_che | Chechen | M |
| b_cv | Chuvash | M |
| cv_ekaterina | Chuvash | F |
| b_myv | Erzya | M |
| b_kalmyk | Kalmyk | M |
| b_krc | Karachay-Balkar | M |
| kz_M1 | Kazakh | M |
| kz_M2 | Kazakh | M |
| kz_F3 | Kazakh | F |
| kz_F1 | Kazakh | F |
| kz_F2 | Kazakh | F |
| b_kjh | Khakas | F |
| b_kpv | Komi-Ziryan | M |
| b_lez | Lezghian | M |
| b_mhr | Mari | F |
| b_mrj | Mari High | M |
| b_nog | Nogai | F |
| b_oss | Ossetic | M |
| b_ru | Russian | M |
| b_tat | Tatar | M |
| marat_tt | Tatar | M |
| b_tyv | Tuvinian | M |
| b_udm | Udmurt | M |
| b_uzb | Uzbek | M |
| b_sah | Yakut | M |
| kalmyk_erdni | Kalmyk | M |
| kalmyk_delghir | Kalmyk | F |
Indic languages
Example
(!!!) All input sentences should be romanized to ISO format using aksharamukha. An example for hindi:
# V3
import torch
from aksharamukha import transliterate
# Loading model
model, example_text = torch.hub.load(repo_or_dir='snakers4/silero-models',
model='silero_tts',
language='indic',
speaker='v4_indic')
orig_text = "पà¥à¤°à¤¸à¤¿à¤¦à¥à¤¦ à¤à¤¬à¥à¤° à¤
धà¥à¤¯à¥à¤¤à¤¾, पà¥à¤°à¥à¤·à¥à¤¤à¥à¤¤à¤® à¤
à¤à¥à¤°à¤µà¤¾à¤² à¤à¤¾ यह शà¥à¤§ à¤à¤²à¥à¤, à¤à¤¸ रामानà¤à¤¦ à¤à¥ à¤à¥à¤ à¤à¤°à¤¤à¤¾ हà¥"
roman_text = transliterate.process('Devanagari', 'ISO', orig_text)
print(roman_text)
audio = model.apply_tts(roman_text,
speaker='hindi_male')
Supported languages
| Language | Speakers | Romanization function |
|---|---|---|
| hindi | hindi_female, hindi_male | transliterate.process('Devanagari', 'ISO', orig_text) |
| malayalam | malayalam_female, malayalam_male | transliterate.process('Malayalam', 'ISO', orig_text) |
| manipuri | manipuri_female | transliterate.process('Bengali', 'ISO', orig_text) |
| bengali | bengali_female, bengali_male | transliterate.process('Bengali', 'ISO', orig_text) |
| rajasthani | rajasthani_female, rajasthani_female | transliterate.process('Devanagari', 'ISO', orig_text) |
| tamil | tamil_female, tamil_male | transliterate.process('Tamil', 'ISO', orig_text, pre_options=['TamilTranscribe']) |
| telugu | telugu_female, telugu_male | transliterate.process('Telugu', 'ISO', orig_text) |
| gujarati | gujarati_female, gujarati_male | transliterate.process('Gujarati', 'ISO', orig_text) |
| kannada | kannada_female, kannada_male | transliterate.process('Kannada', 'ISO', orig_text) |
Text-Enhancement
| Languages | Quantization | Quality | Colab |
|---|---|---|---|
| 'en', 'de', 'ru', 'es' | :heavy_check_mark: | link |
Dependencies
Basic dependencies for Colab examples:
torch, 1.9+;pyyaml, but it's installed with torch itself
Standalone Use
- Standalone usage only requires PyTorch 1.9+ and the Python Standard Library;
- Please see the detailed examples in Colab;
import torch
model, example_texts, languages, punct, apply_te = torch.hub.load(repo_or_dir='snakers4/silero-models',
model='silero_te')
input_text = input('Enter input text\n')
apply_te(input_text, lan='en')
Denoise
Denoise models attempt to reduce background noise along with various artefacts such as reverb, clipping, high/lowpass filters etc., while trying to preserve and/or enhance speech. They also attempt to enhance audio quality and increase sampling rate of the input up to 48kHz.
Models
All of the provided models are listed in the models.yml file.
Dependencies
Basic dependencies for Colab examples:
torch, 2.0+;torchaudio, latest version bound to PyTorch should work;omegaconf, latest (can be removed as well, if you do not load all of the configs).
PyTorch
import torch
name = 'small_slow'
device = torch.device('cpu')
model, samples, utils = torch.hub.load(
repo_or_dir='snakers4/silero-models',
model='silero_denoise',
name=name,
device=device)
(read_audio, save_audio, denoise) = utils
i = 0
torch.hub.download_url_to_file(
samples[i],
dst=f'sample{i}.wav',
progress=True
)
audio_path = f'sample{i}.wav'
audio = read_audio(audio_path).to(device)
output = model(audio)
save_audio(f'result{i}.wav', output.squeeze(1).cpu())
i = 1
torch.hub.download_url_to_file(
samples[i],
dst=f'sample{i}.wav',
progress=True
)
output, sr = denoise(model, f'sample{i}.wav', f'result{i}.wav', device='cpu')
Standalone Use
import os
import torch
device = torch.device('cpu')
torch.set_num_threads(4)
local_file = 'model.pt'
if not os.path.isfile(local_file):
torch.hub.download_url_to_file('https://models.silero.ai/denoise_models/sns_latest.jit',
local_file)
model = torch.jit.load(local_file)
torch._C._jit_set_profiling_mode(False)
torch.set_grad_enabled(False)
model.to(device)
a = torch.rand((1, 48000))
a = a.to(device)
out = model(a)
FAQ
Wiki
Also check out our wiki.
Performance and Quality
Please refer to these wiki sections:
Adding new Languages
Please refer here.
Contact
Get in Touch
Try our models, create an issue, join our chat, email us, and read the latest news.
Commercial Inquiries
Please refer to our wiki and the Licensing and Tiers page for relevant information, and email us.
Citations
@misc{Silero Models,
author = {Silero Team},
title = {Silero Models: pre-trained enterprise-grade STT / TTS models and benchmarks},
year = {2021},
publisher = {GitHub},
journal = {GitHub repository},
howpublished = {\url{https://github.com/snakers4/silero-models}},
commit = {insert_some_commit_here},
email = {hello@silero.ai}
}
Further reading
English
-
STT:
-
TTS:
-
VAD:
-
Text Enhancement:
- We have published a model for text repunctuation and recapitalization for four languages - link
Chinese
- STT:
Russian
-
STT
- OpenAI ÑеÑили ÑаÑпознавание ÑеÑи! РазбиÑаемÑÑ Ñак ли ÑÑо ⦠- link
- ÐаÑи ÑеÑвиÑÑ Ð´Ð»Ñ Ð±ÐµÑплаÑного ÑаÑÐ¿Ð¾Ð·Ð½Ð°Ð²Ð°Ð½Ð¸Ñ ÑеÑи ÑÑали лÑÑÑе и Ñдобнее - link
- Telegram-Ð±Ð¾Ñ Silero беÑплаÑно пеÑÐµÐ²Ð¾Ð´Ð¸Ñ ÑеÑÑ Ð² ÑекÑÑ - link
- ÐеÑплаÑное ÑаÑпознавание ÑеÑи Ð´Ð»Ñ Ð²ÑÐµÑ Ð¶ÐµÐ»Ð°ÑÑÐ¸Ñ - link
- ÐоÑледние Ð¾Ð±Ð½Ð¾Ð²Ð»ÐµÐ½Ð¸Ñ Ð¼Ð¾Ð´ÐµÐ»ÐµÐ¹ ÑаÑÐ¿Ð¾Ð·Ð½Ð°Ð²Ð°Ð½Ð¸Ñ ÑеÑи из Silero Models - link
- Сжимаем ÑÑанÑÑоÑмеÑÑ: пÑоÑÑÑе, ÑнивеÑÑалÑнÑе и пÑикладнÑе ÑпоÑÐ¾Ð±Ñ cделаÑÑ Ð¸Ñ ÐºÐ¾Ð¼Ð¿Ð°ÐºÑнÑми и бÑÑÑÑÑми - link
- УлÑÑимаÑивное ÑÑавнение ÑиÑÑем ÑаÑÐ¿Ð¾Ð·Ð½Ð°Ð²Ð°Ð½Ð¸Ñ ÑеÑи: Ashmanov, Google, Sber, Silero, Tinkoff, Yandex - link
- ÐÑ Ð¾Ð¿Ñбликовали ÑовÑеменнÑе STT модели ÑÑавнимÑе по каÑеÑÑÐ²Ñ Ñ Google - link
- Ðонижаем баÑÑеÑÑ Ð½Ð° Ð²Ñ Ð¾Ð´ в ÑаÑпознавание ÑеÑи - link
- ÐгÑомнÑй оÑкÑÑÑÑй даÑаÑÐµÑ ÑÑÑÑкой ÑеÑи веÑÑÐ¸Ñ 1.0 - link
- ÐаÑколÑко ÐÑÑÑÑой Ðожно СделаÑÑ Ð¡Ð¸ÑÑÐµÐ¼Ñ STT? - link
- ÐаÑа ÑиÑÑема Speech-To-Text - link
- Speech-To-Text - link
-
TTS:
- ТепеÑÑ Ð½Ð°Ñ ÑинÑез Ñакже доÑÑÑпен в виде боÑа в ТелегÑаме - link
- ÐÐ¾Ð¶ÐµÑ Ð»Ð¸ ÑинÑез ÑеÑи обманÑÑÑ ÑиÑÑÐµÐ¼Ñ Ð±Ð¸Ð¾Ð¼ÐµÑÑиÑеÑкой иденÑиÑикаÑии? - link
- ТепеÑÑ Ð½Ð°Ñ ÑинÑез на 20 ÑзÑÐºÐ°Ñ - link
- ТепеÑÑ Ð½Ð°Ñ Ð¿ÑблиÑнÑй ÑинÑез в ÑÑпеÑ-вÑÑоком каÑеÑÑве, в 10 Ñаз бÑÑÑÑее и без деÑÑÐºÐ¸Ñ Ð±Ð¾Ð»ÑÑек - link
- СинÑезиÑÑем Ð³Ð¾Ð»Ð¾Ñ Ð±Ð°Ð±ÑÑки, дедÑÑки и Ðенина + новоÑÑи наÑего пÑблиÑного ÑинÑеза - link
- ÐÑ Ñделали Ð½Ð°Ñ Ð¿ÑблиÑнÑй ÑинÑез ÑеÑи еÑе лÑÑÑе - link
- ÐÑ ÐпÑбликовали ÐаÑеÑÑвеннÑй, ÐÑоÑÑой, ÐоÑÑÑпнÑй и ÐÑÑÑÑÑй СинÑез РеÑи - link
-
VAD:
- ÐÐ°Ñ Ð¿ÑблиÑнÑй деÑекÑÐ¾Ñ Ð³Ð¾Ð»Ð¾Ñа ÑÑал лÑÑÑе - link
- Ð ÑÑ Ð¸ÑполÑзÑеÑÑ VAD? ЧÑо ÑÑо Ñакое и заÑем он нÑжен - link
- Ðодели Ð´Ð»Ñ ÐеÑекÑии РеÑи, ЧиÑел и РаÑÐ¿Ð¾Ð·Ð½Ð°Ð²Ð°Ð½Ð¸Ñ Ð¯Ð·Ñков - link
- ÐÑ Ð¾Ð¿Ñбликовали ÑовÑеменнÑй Voice Activity Detector и не ÑолÑко -link
-
Text Enhancement:
- ÐоÑÑÑановление знаков пÑнкÑÑаÑии и заглавнÑÑ Ð±Ñкв â ÑепеÑÑ Ð¸ на длиннÑÑ ÑекÑÑÐ°Ñ - link
- ÐÑ Ð¾Ð¿Ñбликовали моделÑ, ÑаÑÑÑавлÑÑÑÑÑ Ð·Ð½Ð°ÐºÐ¸ пÑÐµÐ¿Ð¸Ð½Ð°Ð½Ð¸Ñ Ð¸ заглавнÑе бÑÐºÐ²Ñ Ð² ÑекÑÑе на ÑеÑÑÑÐµÑ ÑзÑÐºÐ°Ñ - link
Donations
Please use the "sponsor" button.
Top Related Projects
Offline speech recognition API for Android, iOS, Raspberry Pi and servers with Python, Java, C# and Node
🐸💬 - a deep learning toolkit for Text-to-Speech, battle-tested in research and production
DeepSpeech is an open source embedded (offline, on-device) speech-to-text engine which can run in real time on devices ranging from a Raspberry Pi 4 to high power GPU servers.
End-to-End Speech Processing Toolkit
kaldi-asr/kaldi is the official location of the Kaldi project.
Facebook AI Research Sequence-to-Sequence Toolkit written in Python.
Convert  designs to code with AI
designs to code with AI

Introducing Visual Copilot: A new AI model to turn Figma designs to high quality code using your components.
Try Visual Copilot


