Top Related Projects
Lean's LEDE source
An opensource OpenWrt variant for mainland China users.
Armbian Linux build framework generates custom Debian or Ubuntu image for x86, aarch64, riscv64 & armhf
Quick Overview
The stupidloud/nanopi-openwrt repository is a project that provides OpenWrt firmware builds for NanoPi R2S and R4S single-board computers. It includes automated builds using GitHub Actions and offers various pre-configured packages and optimizations for these specific devices.
Pros
- Regular automated builds ensure up-to-date firmware
- Tailored specifically for NanoPi R2S and R4S devices
- Includes a wide range of pre-configured packages
- Optimized for performance on these single-board computers
Cons
- Limited to specific NanoPi models (R2S and R4S)
- May not be suitable for users who prefer vanilla OpenWrt builds
- Potential for introduced bugs or incompatibilities due to customizations
- Requires some technical knowledge to flash and set up
Getting Started
- Visit the repository's releases page: https://github.com/stupidloud/nanopi-openwrt/releases
- Download the appropriate firmware for your NanoPi device (R2S or R4S)
- Flash the firmware to your device using the recommended method for your NanoPi model
- Boot your device and access the OpenWrt web interface at 192.168.1.1
- Configure your network settings and install additional packages as needed
Note: Always refer to the repository's README and documentation for the most up-to-date instructions and any specific requirements or considerations for your device.
Competitor Comparisons
Lean's LEDE source
Pros of lede
- More comprehensive and feature-rich, with a wider range of supported devices
- Larger community and more frequent updates
- Better documentation and user guides
Cons of lede
- Potentially more complex for beginners due to its extensive features
- May require more system resources due to its broader scope
Code comparison
lede:
./scripts/feeds update -a
./scripts/feeds install -a
make menuconfig
make -j$(nproc) V=s
nanopi-openwrt:
./scripts/feeds update -a
./scripts/feeds install -a
make menuconfig
make -j$(($(nproc) + 1)) V=s
The code snippets show similar build processes, with lede using $(nproc) for parallel compilation, while nanopi-openwrt uses $(($(nproc) + 1)), potentially utilizing one additional thread.
nanopi-openwrt is specifically tailored for NanoPi devices, offering a more focused and potentially optimized experience for these boards. It may be easier to set up and use for NanoPi owners due to its specialized nature.
lede, on the other hand, provides a more versatile platform supporting a wide range of devices and use cases. It offers more customization options and features, making it suitable for advanced users and diverse hardware configurations.
An opensource OpenWrt variant for mainland China users.
Pros of ImmortalWrt
- More comprehensive support for a wider range of devices and architectures
- Larger community and more frequent updates
- Enhanced security features and optimizations
Cons of ImmortalWrt
- Higher complexity and steeper learning curve for beginners
- Potentially more resource-intensive due to additional features
Code Comparison
NanoPi-OpenWrt:
./scripts/feeds update -a
./scripts/feeds install -a
make menuconfig
make -j1 V=s
ImmortalWrt:
./scripts/feeds update -a
./scripts/feeds install -a
make defconfig
make menuconfig
make -j$(nproc) V=s
The main difference in the build process is that ImmortalWrt includes an additional make defconfig step, which sets up a default configuration before customization. ImmortalWrt also utilizes all available CPU cores for compilation with $(nproc), potentially speeding up the build process on multi-core systems.
Both projects are based on OpenWrt, but ImmortalWrt offers a more feature-rich and actively maintained distribution. NanoPi-OpenWrt focuses specifically on NanoPi devices, while ImmortalWrt supports a broader range of hardware. Users should consider their specific needs and hardware compatibility when choosing between the two projects.
Armbian Linux build framework generates custom Debian or Ubuntu image for x86, aarch64, riscv64 & armhf
Pros of build
- Supports a wider range of ARM-based single-board computers and devices
- More active development with frequent updates and contributions
- Comprehensive documentation and community support
Cons of build
- Larger codebase and potentially more complex setup process
- May require more system resources due to its broader scope
Code Comparison
build:
./compile.sh \
BOARD=nanopi-r2s \
BRANCH=current \
RELEASE=bullseye \
BUILD_MINIMAL=yes \
BUILD_DESKTOP=no
nanopi-openwrt:
./scripts/build.sh \
-d nanopi-r2s \
-o openwrt \
-v snapshot
Summary
While build offers broader device support and more active development, nanopi-openwrt provides a more focused solution specifically for NanoPi devices running OpenWrt. The build project may require more resources and have a steeper learning curve, but it offers greater flexibility and community support. nanopi-openwrt, on the other hand, presents a simpler, more streamlined approach for users specifically interested in running OpenWrt on NanoPi hardware.
Convert  designs to code with AI
designs to code with AI

Introducing Visual Copilot: A new AI model to turn Figma designs to high quality code using your components.
Try Visual CopilotREADME
Nanopi R1S R2S R2C R4S X86 Openwrt åºä»¶
å·æºå·¥å
·
ä¸è½½å°å
æ´æ°è¯´æ
使ç¨æ示
åºä»¶ç¹æ§
å¨çº¿å级
1åéçæèªå·±æéåºä»¶
ä¸è½½å°åï¼
https://github.com/stupidloud/nanopi-openwrt/tags
(img.gzæ¡£ä¸éè¦è§£åï¼å¯ä»¥ç´æ¥ä½¿ç¨å·æºå·¥å
·å·å
¥)
使ç¨æ示ï¼
é»è®¤ç¨æ·åæ¯root, å¯ç æ¯passwordï¼å±åç½IP为192.168.2.1
ç§å¶å®åºä»¶æå
¥tfå¡å¹¶å¯å¨å®æï¼çµè端æ¾ç¤ºâç½ç»ï¼å·²è¿æ¥ï¼âä¹åï¼å¨æµè§å¨è¾å
¥ http://immortalwrt/ å¯ä»¥ç´æ¥æå¼è·¯ç±å¨åå°ï¼æ éä¿®æ¹æ¬å°è¿æ¥è®¾ç½®æè
æ¥çIPå°åã
å¦æç½ç»ç¶æä¸ç´æ¯æªè¯å«ï¼ä¸çµè¶
è¿5åéï¼ï¼è¯·ç´æ¥ææä¸æ¬¡çµæºéå¯è¯è¯ã
ç»ç«¯å å¨çº¿å级æ¹æ³ï¼
wget -qO- https://github.com/stupidloud/nanopi-openwrt/raw/master/scripts/autoupdate-bash.sh | bash
slimç
wget -qO- https://github.com/stupidloud/nanopi-openwrt/raw/master/scripts/autoupdate-bash.sh | ver=-slim bash
x86å®è£ çä¸æ¯sdaçæ åµä¸ä½¿ç¨
wget -qO- https://github.com/klever1988/nanopi-openwrt/raw/master/scripts/autoupdate-bash.sh | disk=sdb bash
(èæ¬ç±gary lauæä¾ï¼é常æè°¢ï¼)
åºä»¶ç¹æ§ï¼
- slimçåºä»¶åªæOpenWrtæ¬ä½ï¼ä½å ç½®äºâæ¬å°è½¯ä»¶æºâï¼å å«å¤§é¨å常ç¨æ件ï¼ä¸å欢åºä»¶é¢è£ ç¹ææ件ç人å¯ä»¥éæ©è¿ä¸ªçæ¬ï¼è¿å ¥åå°è½¯ä»¶å éè£ æéæ件
- éç¨ext4æ件系ç»ï¼å·å¡ä¹åå¯èªè¡ä½¿ç¨ååºå·¥å ·å¯¹sdå¡æ©å®¹æ ¹ååºè³æ大
- æ¯æusbæ 线ç½å¡ï¼RTL8821CUè¯çï¼ä¾å¦COMFAST 811ACï¼ï¼å¯ä»¥é©±å¨æ 线ç½å¡è¿è¡å¨5Gé¢æ®µ
- 使ç¨å¨çº¿å级æ¶ï¼æ ¹ååºä¼èªå¨æ©å®¹ï¼æ¹ä¾¿æè ¾
1åéçæèªå·±æéåºä»¶
å 为æ¬é¡¹ç®é¢ç¼è¯äºImage builderï¼çæåºä»¶ä»
é1-3åéï¼å¦ææå
´è¶£èªå®ä¹åºä»¶å¯ä»¥Forkæ¬é¡¹ç®ï¼ç¼è¾è®¾å¤å¯¹åºçconfig.seedæ件ï¼ä¾å¦r2s.config.seed, å»æ(æ´è¡å é¤)ä¸éè¦çluci app软件å
é
ç½®è¡ï¼æ·»å èªå·±æéç软件ï¼å¯ç¨è½¯ä»¶çå表å¯ä»¥å¨github actionsæ件è¾åºå¤è·åï¼ä¾å¦


å®æä¹åè¿å
¥Actionsï¼ç¹å»å·¦ä¾§Buildï¼ç¹å»å³ä¾§Run workflowè¾å
¥è®¾å¤åï¼r2s/r2c/r4s/r1s/r1s-h3/r1p/r1p-ltsï¼

åç¹å»Runå³å¯è·åèªå·±æéçåºä»¶
æ´æ°è¯´æï¼
https://github.com/stupidloud/nanopi-openwrt/blob/master/CHANGELOG.md
æ¬åºä»¶NATåºåæ§è½æµè¯ï¼
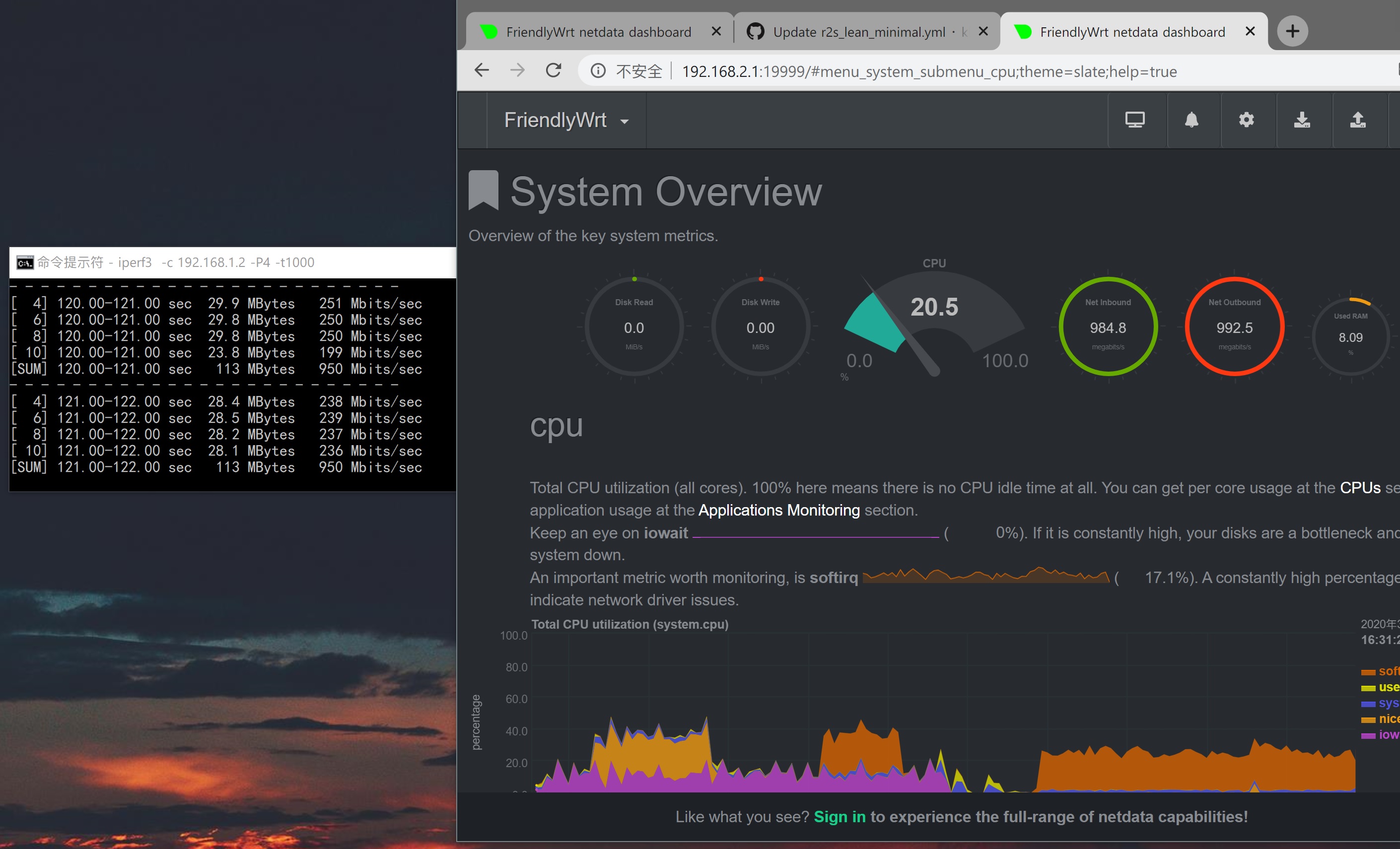
åºä»¶æºç ï¼
Top Related Projects
Lean's LEDE source
An opensource OpenWrt variant for mainland China users.
Armbian Linux build framework generates custom Debian or Ubuntu image for x86, aarch64, riscv64 & armhf
Convert  designs to code with AI
designs to code with AI

Introducing Visual Copilot: A new AI model to turn Figma designs to high quality code using your components.
Try Visual Copilot