 react-native-background-geolocation
react-native-background-geolocation
Sophisticated, battery-conscious background-geolocation with motion-detection
Top Related Projects
Background and foreground geolocation plugin for React Native. Tracks user when app is running in background.
React native geolocation service for iOS and android
Geolocation APIs for React Native
React Native Mapview component for iOS + Android
Quick Overview
React Native Background Geolocation is a comprehensive location tracking module for React Native applications. It offers sophisticated background location tracking with battery-conscious technology, supporting both iOS and Android platforms. The library provides a rich set of features for tracking user location, including geofencing, motion detection, and trip logging.
Pros
- Highly configurable with numerous options for fine-tuning location tracking behavior
- Battery-efficient implementation, minimizing power consumption
- Robust cross-platform support for both iOS and Android
- Extensive documentation and active community support
Cons
- Complex setup process, especially for iOS due to required permissions and capabilities
- Potential learning curve for developers new to background location tracking concepts
- Premium features require a paid license
- Large package size due to comprehensive feature set
Code Examples
- Basic setup and initialization:
import BackgroundGeolocation from "react-native-background-geolocation";
BackgroundGeolocation.ready({
desiredAccuracy: BackgroundGeolocation.DESIRED_ACCURACY_HIGH,
distanceFilter: 10,
stopOnTerminate: false,
startOnBoot: true,
}, (state) => {
console.log("BackgroundGeolocation is ready: ", state);
});
- Starting and stopping location tracking:
// Start tracking
BackgroundGeolocation.start();
// Stop tracking
BackgroundGeolocation.stop();
- Listening for location updates:
BackgroundGeolocation.onLocation(location => {
console.log("[Location] ", location);
}, error => {
console.log("[Location Error] ", error);
});
- Setting up a geofence:
BackgroundGeolocation.addGeofence({
identifier: "Home",
radius: 200,
latitude: 45.51921926,
longitude: -73.61678581,
notifyOnEntry: true,
notifyOnExit: true
});
Getting Started
-
Install the package:
npm install react-native-background-geolocation -
For iOS, add the following to your
Info.plist:<key>NSLocationAlwaysUsageDescription</key> <string>Location required in background</string> <key>NSLocationWhenInUseUsageDescription</key> <string>Location required when app is in use</string> -
For Android, add the following permissions to your
AndroidManifest.xml:<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION" /> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_BACKGROUND_LOCATION" /> -
Initialize and configure the plugin in your app as shown in the first code example above.
Competitor Comparisons
Background and foreground geolocation plugin for React Native. Tracks user when app is running in background.
Pros of react-native-background-geolocation (mauron85)
- Open-source and free to use without licensing restrictions
- Simpler setup and configuration process
- Lighter weight with fewer dependencies
Cons of react-native-background-geolocation (mauron85)
- Less frequent updates and maintenance
- Fewer advanced features compared to the transistorsoft version
- Limited documentation and community support
Code Comparison
react-native-background-geolocation (mauron85):
import BackgroundGeolocation from 'react-native-background-geolocation';
BackgroundGeolocation.configure({
desiredAccuracy: BackgroundGeolocation.HIGH_ACCURACY,
stationaryRadius: 50,
distanceFilter: 50,
notificationTitle: 'Background tracking',
notificationText: 'enabled',
debug: true,
startOnBoot: false,
stopOnTerminate: false,
locationProvider: BackgroundGeolocation.ACTIVITY_PROVIDER,
interval: 10000,
fastestInterval: 5000,
activitiesInterval: 10000,
});
react-native-background-geolocation (transistorsoft):
import BackgroundGeolocation from "react-native-background-geolocation";
BackgroundGeolocation.ready({
desiredAccuracy: BackgroundGeolocation.DESIRED_ACCURACY_HIGH,
distanceFilter: 10,
stopOnTerminate: false,
startOnBoot: true,
debug: true,
logLevel: BackgroundGeolocation.LOG_LEVEL_VERBOSE,
stopTimeout: 1,
url: 'http://yourserver.com/locations',
batchSync: false,
autoSync: true,
headers: {
"X-FOO": "bar"
},
params: {
"auth_token": "maybe_your_server_authenticates_via_token_YES?"
}
});
Both libraries offer similar core functionality for background geolocation in React Native applications. The mauron85 version is more straightforward and easier to set up, while the transistorsoft version provides more advanced features and configuration options.
React native geolocation service for iOS and android
Pros of react-native-geolocation-service
- Lightweight and focused solely on geolocation services
- Simpler setup and integration process
- Free and open-source without licensing restrictions
Cons of react-native-geolocation-service
- Limited background tracking capabilities
- Fewer advanced features like geofencing or motion detection
- Less comprehensive documentation and community support
Code Comparison
react-native-geolocation-service:
import Geolocation from 'react-native-geolocation-service';
Geolocation.getCurrentPosition(
(position) => {
console.log(position);
},
(error) => {
console.log(error.code, error.message);
},
{ enableHighAccuracy: true, timeout: 15000, maximumAge: 10000 }
);
react-native-background-geolocation:
import BackgroundGeolocation from "react-native-background-geolocation";
BackgroundGeolocation.ready({
desiredAccuracy: BackgroundGeolocation.DESIRED_ACCURACY_HIGH,
distanceFilter: 10,
stopOnTerminate: false,
startOnBoot: true,
}, (state) => {
console.log("- BackgroundGeolocation is ready: ", state);
});
The code comparison shows that react-native-geolocation-service offers a simpler API for basic geolocation tasks, while react-native-background-geolocation provides more advanced configuration options for persistent background tracking. The latter also includes features like automatic start on device boot, which is not available in the simpler library.
Geolocation APIs for React Native
Pros of react-native-geolocation
- Lightweight and focused solely on basic geolocation functionality
- Simpler setup and integration process
- Free and open-source without licensing restrictions
Cons of react-native-geolocation
- Lacks advanced background tracking capabilities
- Limited battery optimization features
- Fewer configuration options for fine-tuning location services
Code Comparison
react-native-geolocation:
import Geolocation from '@react-native-community/geolocation';
Geolocation.getCurrentPosition(
position => {
console.log(position);
},
error => console.log(error),
{ enableHighAccuracy: true, timeout: 20000, maximumAge: 1000 }
);
react-native-background-geolocation:
import BackgroundGeolocation from "react-native-background-geolocation";
BackgroundGeolocation.ready({
desiredAccuracy: BackgroundGeolocation.DESIRED_ACCURACY_HIGH,
distanceFilter: 10,
stopOnTerminate: false,
startOnBoot: true,
}, (state) => {
console.log("- BackgroundGeolocation is ready: ", state);
});
The code comparison shows that react-native-geolocation offers a simpler API for basic location tracking, while react-native-background-geolocation provides more advanced configuration options for continuous background tracking and power management. The latter offers more control over the geolocation process, making it suitable for apps requiring persistent location monitoring.
React Native Mapview component for iOS + Android
Pros of react-native-maps
- Focused on map rendering and interaction, providing a comprehensive set of map-related features
- Supports both iOS and Android platforms with a unified API
- Offers customizable map styles and markers
Cons of react-native-maps
- Limited to map-related functionality, lacking background location tracking capabilities
- May require additional libraries for advanced geolocation features
- Higher learning curve for complex map interactions
Code Comparison
react-native-maps:
import MapView, { Marker } from 'react-native-maps';
<MapView
initialRegion={{
latitude: 37.78825,
longitude: -122.4324,
latitudeDelta: 0.0922,
longitudeDelta: 0.0421,
}}
>
<Marker coordinate={{ latitude: 37.78825, longitude: -122.4324 }} />
</MapView>
react-native-background-geolocation:
import BackgroundGeolocation from 'react-native-background-geolocation';
BackgroundGeolocation.ready({
desiredAccuracy: BackgroundGeolocation.DESIRED_ACCURACY_HIGH,
distanceFilter: 10,
stopOnTerminate: false,
startOnBoot: true,
}, (state) => {
console.log('BackgroundGeolocation is ready: ', state);
});
The code examples highlight the different focus areas of each library. react-native-maps emphasizes map rendering and marker placement, while react-native-background-geolocation concentrates on configuring and managing background location tracking.
Convert  designs to code with AI
designs to code with AI

Introducing Visual Copilot: A new AI model to turn Figma designs to high quality code using your components.
Try Visual CopilotREADME
| Now with Expo support |
|---|
Background Geolocation for React Native · 

The most sophisticated background location-tracking & geofencing module with battery-conscious motion-detection intelligence for iOS and Android.
The plugin's Philosophy of Operation is to use motion-detection APIs (using accelerometer, gyroscope and magnetometer) to detect when the device is moving and stationary.
-
When the device is detected to be moving, the plugin will automatically start recording a location according to the configured
distanceFilter(meters). -
When the device is detected be stationary, the plugin will automatically turn off location-services to conserve energy.
Also available for Flutter, Cordova, NativeScript and pure native apps.
[!NOTE] The Android module requires purchasing a license. However, it will work for DEBUG builds. It will not work with RELEASE builds without purchasing a license. This plugin is supported full-time and field-tested daily since 2013.
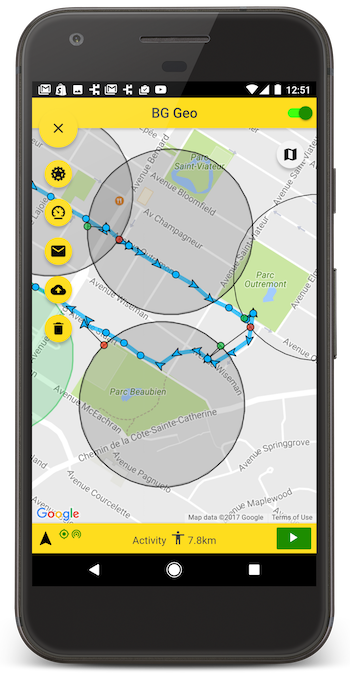
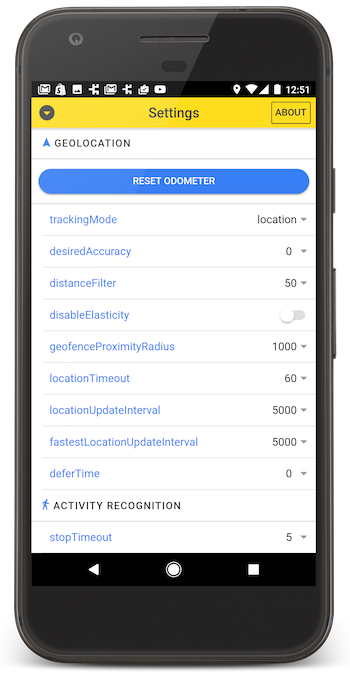
Contents
-
ð« Help!
-
:books: API Documentation
-
Installing the Plugin
-
Setup Guides
-
Configure your License
-
Using the plugin
-
Example
-
Debugging
-
Demo Application
-
Testing Server
-
Privacy Policy
:large_blue_diamond: Installing the Plugin
With Expo
npx expo install react-native-background-geolocation
With yarn
yarn add react-native-background-geolocation
With npm
$ npm install react-native-background-geolocation --save
:large_blue_diamond: Setup Guides
Expo
iOS
Android
:large_blue_diamond: Configure your license
-
Login to Customer Dashboard to generate an application key: www.transistorsoft.com/shop/customers

-
Add your license-key to
android/app/src/main/AndroidManifest.xml:
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.transistorsoft.backgroundgeolocation.react">
<application
android:name=".MainApplication"
android:allowBackup="true"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme">
<!-- react-native-background-geolocation licence -->
+ <meta-data android:name="com.transistorsoft.locationmanager.license" android:value="YOUR_LICENCE_KEY_HERE" />
.
.
.
</application>
</manifest>
:large_blue_diamond: Using the plugin
import BackgroundGeolocation from "react-native-background-geolocation";
Typescript API:
For those using Typescript (recommended), you can also import the interfaces:
import BackgroundGeolocation, {
State,
Config,
Location,
LocationError,
Geofence,
GeofenceEvent,
GeofencesChangeEvent,
HeartbeatEvent,
HttpEvent,
MotionActivityEvent,
MotionChangeEvent,
ProviderChangeEvent,
ConnectivityChangeEvent
} from "react-native-background-geolocation";
For more information, see this blog post
:large_blue_diamond: Example
There are three main steps to using BackgroundGeolocation
- Wire up event-listeners.
.ready(config)the plugin..start()the plugin.
[!WARNING] Do not execute any API method which will require accessing location-services until the
.ready(config)method resolves (Read its API docs), For example:
.getCurrentPosition.watchPosition.start
// NO! .ready() has not resolved.
BackgroundGeolocation.getCurrentPosition(options);
BackgroundGeolocation.start();
BackgroundGeolocation.ready(config).then((state) => {
// YES -- .ready() has now resolved.
BackgroundGeolocation.getCurrentPosition(options);
BackgroundGeolocation.start();
});
// NO! .ready() has not resolved.
BackgroundGeolocation.getCurrentPosition(options);
BackgroundGeolocation.start();
Example 1. — React Functional Component
Show Source
import React from 'react';
import {
Switch,
Text,
View,
} from 'react-native';
import BackgroundGeolocation, {
Location,
Subscription
} from "react-native-background-geolocation";
const HelloWorld = () => {
const [enabled, setEnabled] = React.useState(false);
const [location, setLocation] = React.useState('');
React.useEffect(() => {
/// 1. Subscribe to events.
const onLocation:Subscription = BackgroundGeolocation.onLocation((location) => {
console.log('[onLocation]', location);
setLocation(JSON.stringify(location, null, 2));
})
const onMotionChange:Subscription = BackgroundGeolocation.onMotionChange((event) => {
console.log('[onMotionChange]', event);
});
const onActivityChange:Subscription = BackgroundGeolocation.onActivityChange((event) => {
console.log('[onActivityChange]', event);
})
const onProviderChange:Subscription = BackgroundGeolocation.onProviderChange((event) => {
console.log('[onProviderChange]', event);
})
/// 2. ready the plugin.
BackgroundGeolocation.ready({
// Geolocation Config
desiredAccuracy: BackgroundGeolocation.DESIRED_ACCURACY_HIGH,
distanceFilter: 10,
// Activity Recognition
stopTimeout: 5,
// Application config
debug: true, // <-- enable this hear sounds for background-geolocation life-cycle.
logLevel: BackgroundGeolocation.LOG_LEVEL_VERBOSE,
stopOnTerminate: false, // <-- Allow the background-service to continue tracking when user closes the app.
startOnBoot: true, // <-- Auto start tracking when device is powered-up.
// HTTP / SQLite config
url: 'http://yourserver.com/locations',
batchSync: false, // <-- [Default: false] Set true to sync locations to server in a single HTTP request.
autoSync: true, // <-- [Default: true] Set true to sync each location to server as it arrives.
headers: { // <-- Optional HTTP headers
"X-FOO": "bar"
},
params: { // <-- Optional HTTP params
"auth_token": "maybe_your_server_authenticates_via_token_YES?"
}
}).then((state) => {
setEnabled(state.enabled)
console.log("- BackgroundGeolocation is configured and ready: ", state.enabled);
});
return () => {
// Remove BackgroundGeolocation event-subscribers when the View is removed or refreshed
// during development live-reload. Without this, event-listeners will accumulate with
// each refresh during live-reload.
onLocation.remove();
onMotionChange.remove();
onActivityChange.remove();
onProviderChange.remove();
}
}, []);
/// 3. start / stop BackgroundGeolocation
React.useEffect(() => {
if (enabled) {
BackgroundGeolocation.start();
} else {
BackgroundGeolocation.stop();
setLocation('');
}
}, [enabled]);
return (
<View style={{alignItems:'center'}}>
<Text>Click to enable BackgroundGeolocation</Text>
<Switch value={enabled} onValueChange={setEnabled} />
<Text style={{fontFamily:'monospace', fontSize:12}}>{location}</Text>
</View>
)
}
export default HelloWorld;
Example 2. — React Class Component
Show Source
import React from 'react';
import {
Switch,
Text,
View,
} from 'react-native';
import BackgroundGeolocation, {
Location,
Subscription
} from "react-native-background-geolocation";
export default class HelloWorld extends React.Component {
subscriptions:Subscription[] = [];
state:any = {};
constructor(props:any) {
super(props);
this.state = {
enabled: false,
location: ''
}
}
componentDidMount() {
/// 1. Subscribe to BackgroundGeolocation events.
this.subscriptions.push(BackgroundGeolocation.onLocation((location) => {
console.log('[onLocation]', location);
this.setState({location: JSON.stringify(location, null, 2)})
}, (error) => {
console.log('[onLocation] ERROR:', error);
}))
this.subscriptions.push(BackgroundGeolocation.onMotionChange((event) => {
console.log('[onMotionChange]', event);
}))
this.subscriptions.push(BackgroundGeolocation.onActivityChange((event) => {
console.log('[onActivityChange]', event);
}))
this.subscriptions.push(BackgroundGeolocation.onProviderChange((event) => {
console.log('[onProviderChange]', event);
}))
/// 2. ready the plugin.
BackgroundGeolocation.ready({
// Geolocation Config
desiredAccuracy: BackgroundGeolocation.DESIRED_ACCURACY_HIGH,
distanceFilter: 10,
// Activity Recognition
stopTimeout: 5,
// Application config
debug: true, // <-- enable this hear sounds for background-geolocation life-cycle.
logLevel: BackgroundGeolocation.LOG_LEVEL_VERBOSE,
stopOnTerminate: false, // <-- Allow the background-service to continue tracking when user closes the app.
startOnBoot: true, // <-- Auto start tracking when device is powered-up.
// HTTP / SQLite config
url: 'http://yourserver.com/locations',
batchSync: false, // <-- [Default: false] Set true to sync locations to server in a single HTTP request.
autoSync: true, // <-- [Default: true] Set true to sync each location to server as it arrives.
headers: { // <-- Optional HTTP headers
"X-FOO": "bar"
},
params: { // <-- Optional HTTP params
"auth_token": "maybe_your_server_authenticates_via_token_YES?"
}
}).then((state) => {
this.setState({enabled: state.enabled});
console.log("- BackgroundGeolocation is configured and ready: ", state.enabled);
})
}
/// When view is destroyed (or refreshed during development live-reload),
/// remove BackgroundGeolocation event subscriptions.
componentWillUnmount() {
this.subscriptions.forEach((subscription) => subscription.remove());
}
onToggleEnabled(value:boolean) {
console.log('[onToggleEnabled]', value);
this.setState({enabled: value})
if (value) {
BackgroundGeolocation.start();
} else {
this.setState({location: ''});
BackgroundGeolocation.stop();
}
}
render() {
return (
<View style={{alignItems:'center'}}>
<Text>Click to enable BackgroundGeolocation</Text>
<Switch value={this.state.enabled} onValueChange={this.onToggleEnabled.bind(this)} />
<Text style={{fontFamily:'monospace', fontSize:12}}>{this.state.location}</Text>
</View>
)
}
}
Promise API
The BackgroundGeolocation Javascript API supports Promises for nearly every method (the exceptions are #watchPosition and adding event-listeners via #onXXX method (eg: onLocation). For more information, see the API Documentation
BackgroundGeolocation.ready({
desiredAccuracy: BackgroundGeolocation.DESIRED_ACCURACY_HIGH,
distanceFilter: 50
}).then(state => {
console.log('- BackgroundGeolocation is ready: ', state);
}).catch(error => {
console.warn('- BackgroundGeolocation error: ', error);
});
// Or use await in an async function
try {
const state = await BackgroundGeolocation.ready({
desiredAccuracy: BackgroundGeolocation.DESIRED_ACCURACY_HIGH,
distanceFilter: 50
})
console.log('- BackgroundGeolocation is ready: ', state);
} catch (error) {
console.warn('- BackgroundGeolocation error: ', error);
}
:large_blue_diamond: Demo Application
A fully-featured Demo App is available in its own public repo. After first cloning that repo, follow the installation instructions in the README there. This demo-app includes a settings-screen allowing you to quickly experiment with all the different settings available for each platform.


:large_blue_diamond: Simple Testing Server
A simple Node-based web-application with SQLite database is available for field-testing and performance analysis. If you're familiar with Node, you can have this server up-and-running in about one minute.
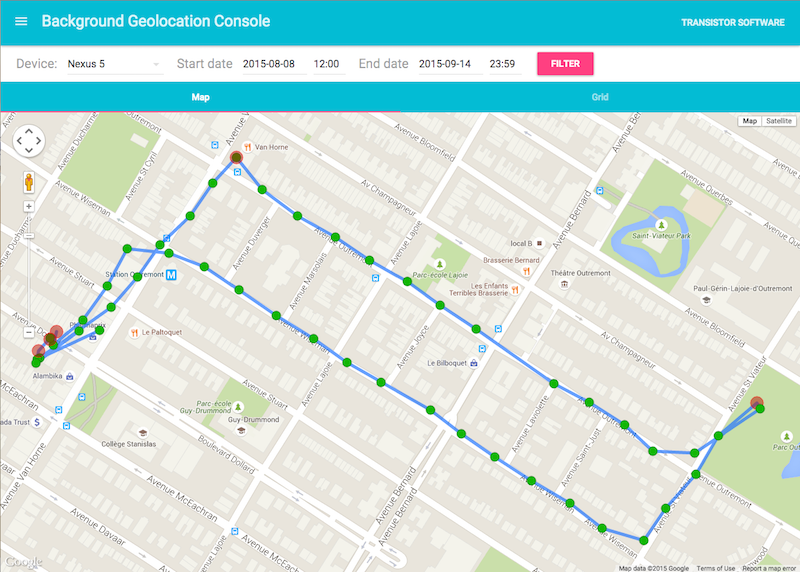
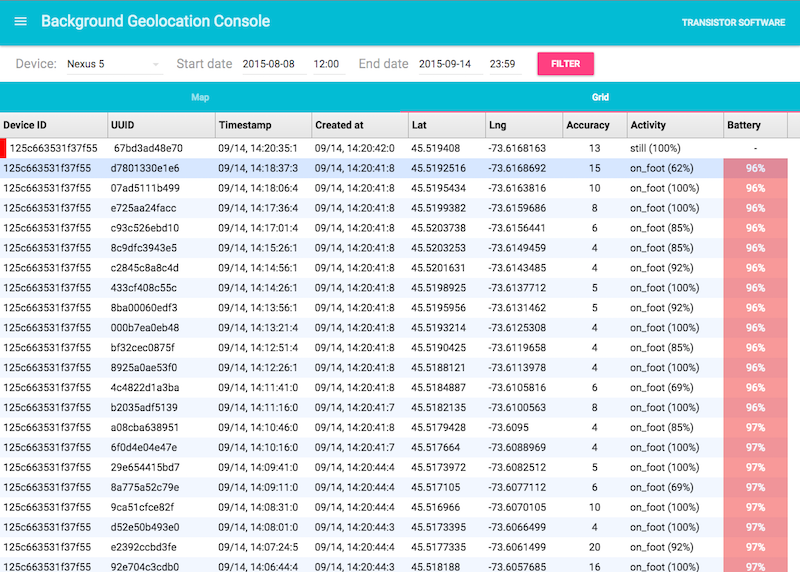
License
The MIT License (MIT)
Copyright (c) 2018 Chris Scott, Transistor Software
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
Top Related Projects
Background and foreground geolocation plugin for React Native. Tracks user when app is running in background.
React native geolocation service for iOS and android
Geolocation APIs for React Native
React Native Mapview component for iOS + Android
Convert  designs to code with AI
designs to code with AI

Introducing Visual Copilot: A new AI model to turn Figma designs to high quality code using your components.
Try Visual Copilot