 incubator-seata
incubator-seata
:fire: Seata is an easy-to-use, high-performance, open source distributed transaction solution.
Top Related Projects
:fire: Seata is an easy-to-use, high-performance, open source distributed transaction solution.
A distributed transaction framework, supports workflow, saga, tcc, xa, 2-phase message, outbox patterns, supports many languages.
ByteTCC is a distributed transaction manager based on the TCC(Try/Confirm/Cancel) mechanism. It’s compatible with the JTA specification. User guide: https://github.com/liuyangming/ByteTCC/wiki
tcc-transaction是TCC型事务java实现
Apache Seata(incubating) Samples for Java
SOFARPC is a high-performance, high-extensibility, production-level Java RPC framework.
Quick Overview
Apache Seata is an open-source distributed transaction solution that provides high performance and easy-to-use transaction services in microservices architecture. It aims to ensure data consistency across multiple databases and services without invasive transaction APIs.
Pros
- Supports multiple transaction modes (AT, TCC, SAGA, XA)
- High performance and low invasiveness
- Integrates well with popular microservices frameworks (Spring Cloud, Dubbo)
- Supports various databases and messaging systems
Cons
- Complexity in setup and configuration for large-scale systems
- Potential performance overhead in certain scenarios
- Limited support for non-Java ecosystems
- Requires careful consideration of transaction boundaries and isolation levels
Code Examples
- Configuring Seata in a Spring Boot application:
@Configuration
@EnableAutoDataSourceProxy
public class SeataAutoConfig {
@Bean
public GlobalTransactionScanner globalTransactionScanner() {
return new GlobalTransactionScanner("example-service", "example-tx-group");
}
}
- Using the @GlobalTransactional annotation for distributed transactions:
@GlobalTransactional
public void businessMethod() {
// Perform multiple database operations across services
serviceA.doSomething();
serviceB.doSomethingElse();
}
- Implementing a TCC (Try-Confirm-Cancel) transaction:
@LocalTCC
public class TCCServiceImpl implements TCCService {
@TwoPhaseBusinessAction(name = "tccAction", commitMethod = "confirm", rollbackMethod = "cancel")
public boolean try(BusinessActionContext actionContext, String param) {
// Try phase logic
}
public boolean confirm(BusinessActionContext actionContext) {
// Confirm phase logic
}
public boolean cancel(BusinessActionContext actionContext) {
// Cancel phase logic
}
}
Getting Started
- Add Seata dependency to your project:
<dependency>
<groupId>io.seata</groupId>
<artifactId>seata-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.5.2</version>
</dependency>
- Configure Seata in your application.yml:
seata:
tx-service-group: my_tx_group
service:
vgroup-mapping:
my_tx_group: default
registry:
type: nacos
nacos:
server-addr: localhost:8848
- Use @GlobalTransactional annotation on your business methods to enable distributed transactions.
Competitor Comparisons
:fire: Seata is an easy-to-use, high-performance, open source distributed transaction solution.
Pros of incubator-seata
- Active development and regular updates
- Comprehensive documentation and examples
- Strong community support and contributions
Cons of incubator-seata
- Learning curve for complex distributed transactions
- Potential performance overhead in certain scenarios
Code Comparison
Both repositories contain the same codebase, as they are mirrors of each other. Here's a sample from the GlobalTransactionScanner.java file:
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
if (disableGlobalTransaction) {
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Global transaction is disabled.");
}
return;
}
initClient();
}
This code snippet is identical in both repositories, demonstrating that they are the same project. The comparison between apache/incubator-seata and apache/incubator-seata> is not applicable, as they are likely mirrored repositories or duplicates of the same project.
In conclusion, there are no significant differences between these repositories, as they appear to be the same project. The pros and cons listed above apply to both, and the code comparison shows identical content.
A distributed transaction framework, supports workflow, saga, tcc, xa, 2-phase message, outbox patterns, supports many languages.
Pros of dtm
- Simpler architecture and easier to use, especially for microservices
- Supports multiple programming languages (Go, Java, Python, PHP)
- Offers both 2-phase commit and SAGA patterns for distributed transactions
Cons of dtm
- Less mature and smaller community compared to Seata
- Fewer features and integration options
- Limited documentation and examples for complex scenarios
Code Comparison
dtm (Go):
saga := dtmcli.NewSaga(DtmServer, gid).
Add(busi.Busi+"/TransOut", busi.Busi+"/TransOutCompensate", &req).
Add(busi.Busi+"/TransIn", busi.Busi+"/TransInCompensate", &req)
err := saga.Submit()
Seata (Java):
@GlobalTransactional
public void transfer(String fromAccount, String toAccount, double amount) {
accountService.debit(fromAccount, amount);
accountService.credit(toAccount, amount);
}
Both projects aim to solve distributed transaction management, but dtm focuses on simplicity and language-agnostic support, while Seata offers a more comprehensive solution with deeper integration into Java ecosystems. dtm's code example shows explicit transaction definition, while Seata uses annotations for global transactions.
ByteTCC is a distributed transaction manager based on the TCC(Try/Confirm/Cancel) mechanism. It’s compatible with the JTA specification. User guide: https://github.com/liuyangming/ByteTCC/wiki
Pros of ByteTCC
- Lightweight and easy to integrate with existing applications
- Supports multiple transaction modes (TCC, AT, XA)
- Flexible configuration options for different scenarios
Cons of ByteTCC
- Less active community and fewer contributors compared to Seata
- Limited documentation and examples available
- Fewer integrations with popular frameworks and databases
Code Comparison
ByteTCC:
@Compensable(confirmMethod = "confirmOrder", cancelMethod = "cancelOrder")
public void createOrder(Order order) {
// Business logic
}
Seata:
@GlobalTransactional
public void createOrder(Order order) {
// Business logic
}
ByteTCC requires explicit definition of confirm and cancel methods, while Seata uses a simpler annotation for global transactions. This reflects ByteTCC's more flexible but potentially more complex approach to transaction management.
Both projects aim to solve distributed transaction problems in microservices architectures, but Seata offers a more comprehensive solution with broader community support. ByteTCC provides a lightweight alternative with more granular control over transaction stages, which may be preferable for certain use cases or existing codebases.
tcc-transaction是TCC型事务java实现
Pros of tcc-transaction
- Lightweight and focused specifically on TCC (Try-Confirm-Cancel) pattern
- Simpler implementation for projects that only need TCC transactions
- Easier to understand and integrate for developers familiar with TCC concepts
Cons of tcc-transaction
- Limited scope compared to Seata's broader distributed transaction support
- Smaller community and less frequent updates
- Lacks some advanced features and integrations available in Seata
Code Comparison
tcc-transaction:
@Compensable(confirmMethod = "confirmMethod", cancelMethod = "cancelMethod")
public void tryMethod() {
// Try phase logic
}
Seata:
@GlobalTransactional
public void businessMethod() {
// Business logic with multiple resource operations
}
The tcc-transaction example shows a method annotated for TCC, while Seata's example demonstrates a global transaction annotation that can encompass various transaction modes, including TCC.
tcc-transaction is more focused on the TCC pattern, making it potentially easier to implement for projects specifically requiring TCC transactions. However, Seata offers a more comprehensive solution for distributed transactions, supporting multiple patterns and providing additional features and integrations. The choice between the two depends on the specific requirements of the project and the desired level of transaction management complexity.
Apache Seata(incubating) Samples for Java
Pros of incubator-seata-samples
- Provides practical examples and use cases for Seata implementation
- Offers a variety of sample projects covering different scenarios and frameworks
- Serves as a learning resource for developers new to Seata
Cons of incubator-seata-samples
- Limited to sample code, not suitable for production use
- May not always be up-to-date with the latest Seata features
- Smaller community and less frequent updates compared to the main Seata repository
Code Comparison
incubator-seata:
@GlobalTransactional
public void purchase(String userId, String commodityCode, int orderCount) {
Order order = orderService.create(userId, commodityCode, orderCount);
if (order == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("Create order failed");
}
}
incubator-seata-samples:
@GlobalTransactional(name = "purchase-tx", rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void purchase(String userId, String commodityCode, int orderCount) {
Order order = orderService.create(userId, commodityCode, orderCount);
if (order == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("Create order failed");
}
}
The sample code in incubator-seata-samples demonstrates a more specific use of the @GlobalTransactional annotation, including a named transaction and explicit rollback configuration. This provides a clearer example of how to implement Seata in real-world scenarios.
SOFARPC is a high-performance, high-extensibility, production-level Java RPC framework.
Pros of SOFA-RPC
- Lightweight and high-performance RPC framework
- Supports multiple protocols (Bolt, REST, Dubbo, gRPC)
- Extensive middleware integration (e.g., Spring Boot, Zookeeper)
Cons of SOFA-RPC
- Primarily focused on RPC, lacking distributed transaction support
- Less active community compared to Seata
- Limited documentation in English
Code Comparison
SOFA-RPC (Service Definition):
@SofaService
public interface HelloService {
String sayHello(String name);
}
Seata (Transaction Definition):
@GlobalTransactional
public void businessLogic() {
// Business logic with distributed transactions
}
Key Differences
- Seata is specifically designed for distributed transactions, while SOFA-RPC is a general-purpose RPC framework
- SOFA-RPC offers more flexibility in terms of communication protocols
- Seata provides a more comprehensive solution for managing distributed transactions across microservices
Use Cases
- SOFA-RPC: Ideal for building high-performance, multi-protocol microservices
- Seata: Best suited for applications requiring robust distributed transaction management
Community and Ecosystem
- Seata has a larger and more active community, with more frequent updates and contributions
- SOFA-RPC is part of the broader SOFA ecosystem, which includes other middleware components
Convert  designs to code with AI
designs to code with AI

Introducing Visual Copilot: A new AI model to turn Figma designs to high quality code using your components.
Try Visual CopilotREADME
Seata: Simple Extensible Autonomous Transaction Architecture
What is Seata?
A distributed transaction solution with high performance and ease of use for microservices architecture.
Distributed Transaction Problem in Microservices
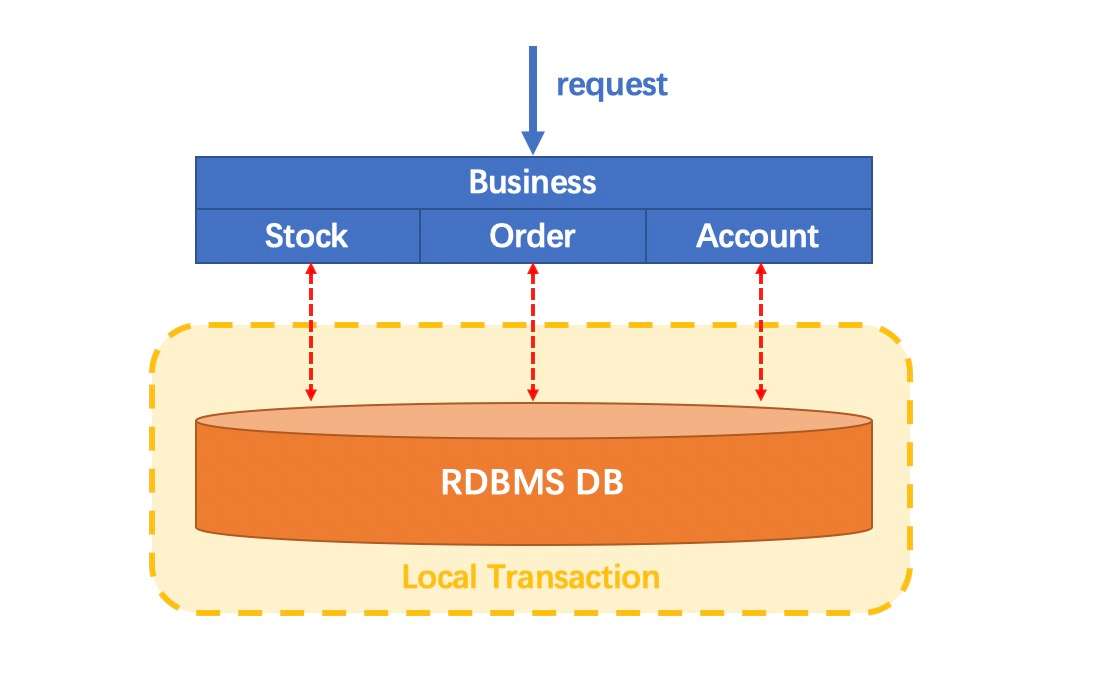
Let's imagine a traditional monolithic application. Its business is built up with 3 modules. They use a single local data source.
Naturally, data consistency will be guaranteed by the local transaction.
Things have changed in a microservices architecture. The 3 modules mentioned above are designed to be 3 services on top of 3 different data sources (Pattern: Database per service). Data consistency within every single service is naturally guaranteed by the local transaction.
But how about the whole business logic scope?

How Seata do?
Seata is just a solution to the problem mentioned above.
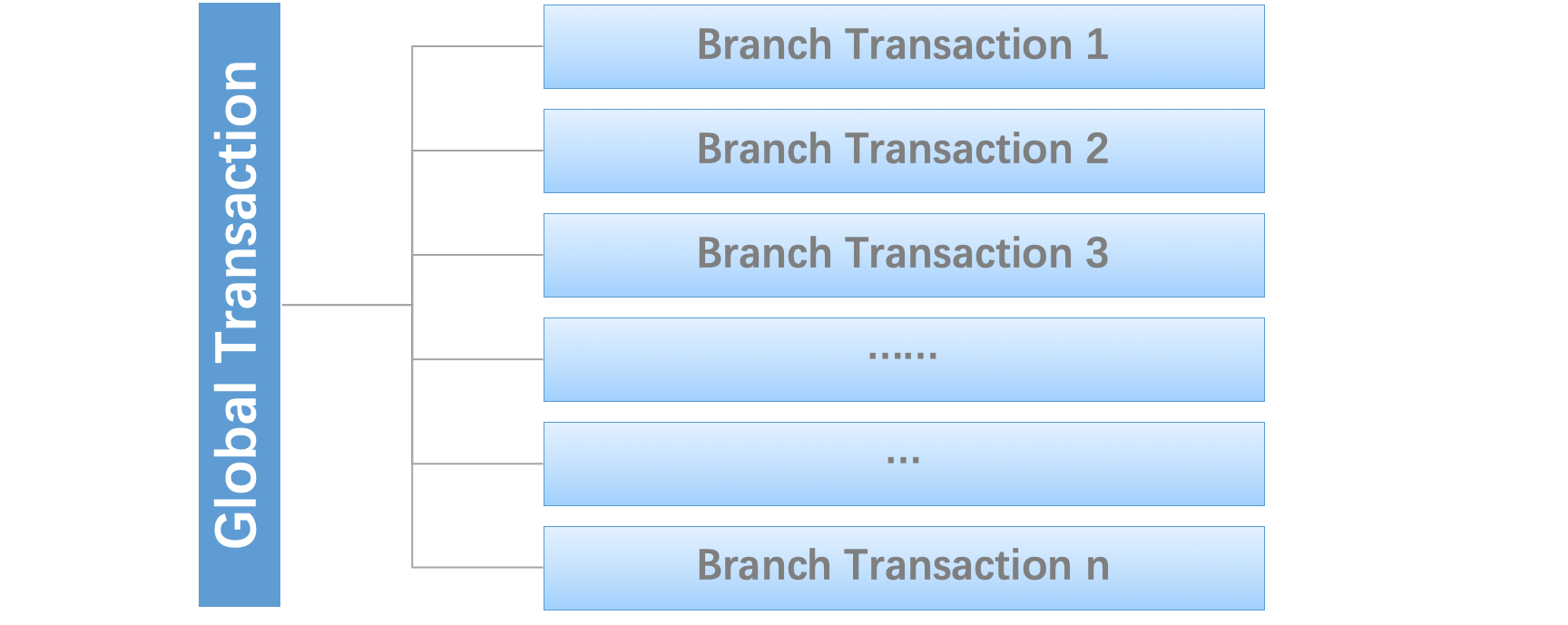
Firstly, how to define a Distributed Transaction?
We say, a Distributed Transaction is a Global Transaction which is made up with a batch of Branch Transaction, and normally Branch Transaction is just Local Transaction.
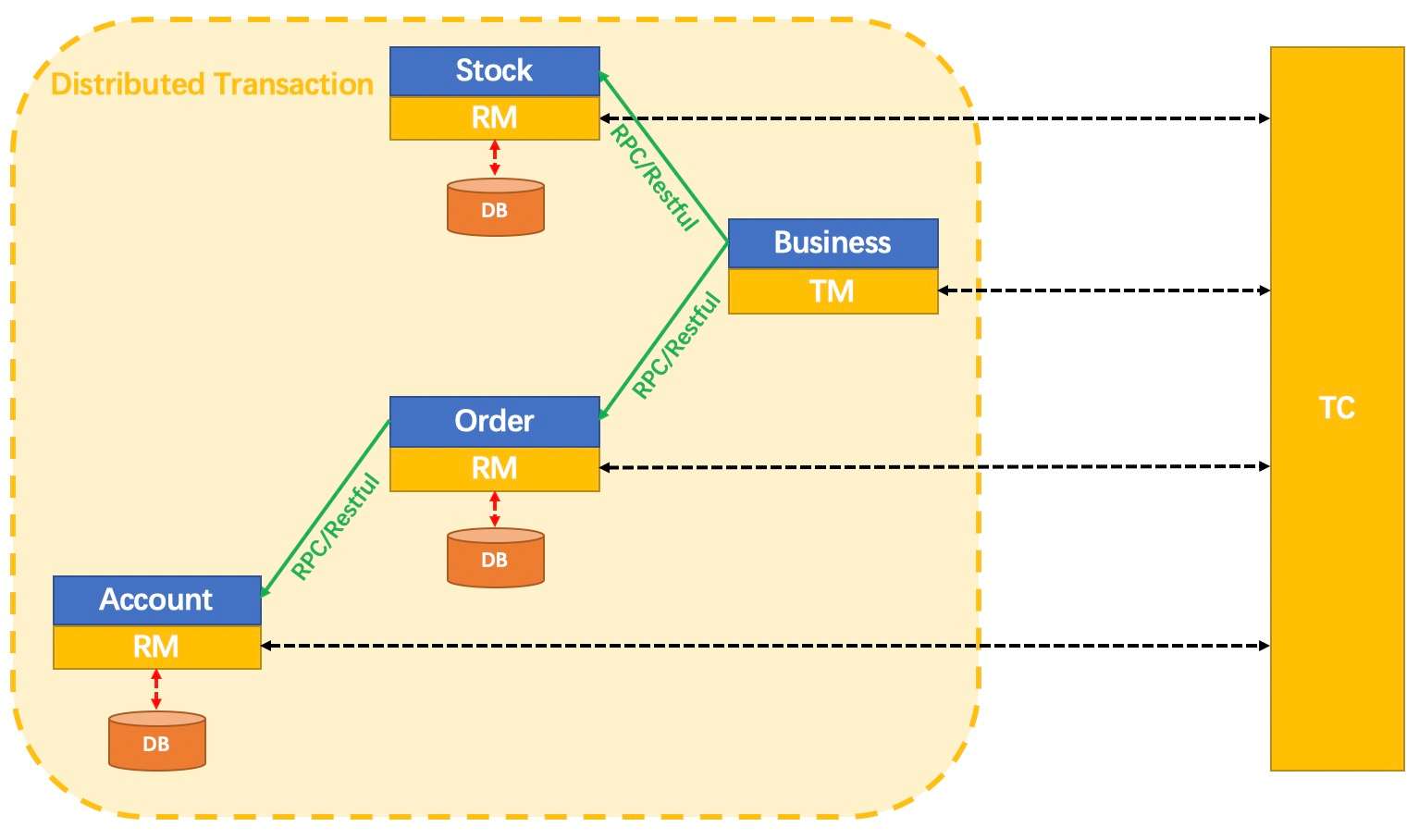
There are three roles in Seata Framework:
- Transaction Coordinator(TC): Maintain status of global and branch transactions, drive the global commit or rollback.
- Transaction Manager(TM): Define the scope of global transaction: begin a global transaction, commit or rollback a global transaction.
- Resource Manager(RM): Manage resources that branch transactions working on, talk to TC for registering branch transactions and reporting status of branch transactions, and drive the branch transaction commit or rollback.
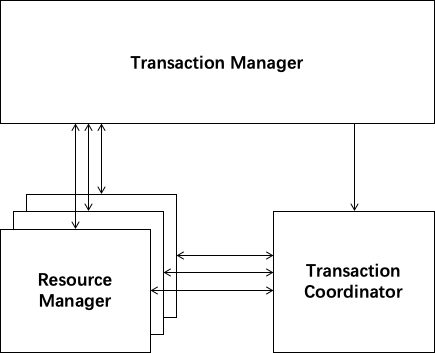
A typical lifecycle of Seata managed distributed transaction:
- TM asks TC to begin a new global transaction. TC generates an XID representing the global transaction.
- XID is propagated through microservices' invoke chain.
- RM registers local transaction as a branch of the corresponding global transaction of XID to TC.
- TM asks TC for committing or rollbacking the corresponding global transaction of XID.
- TC drives all branch transactions under the corresponding global transaction of XID to finish branch committing or rollbacking.
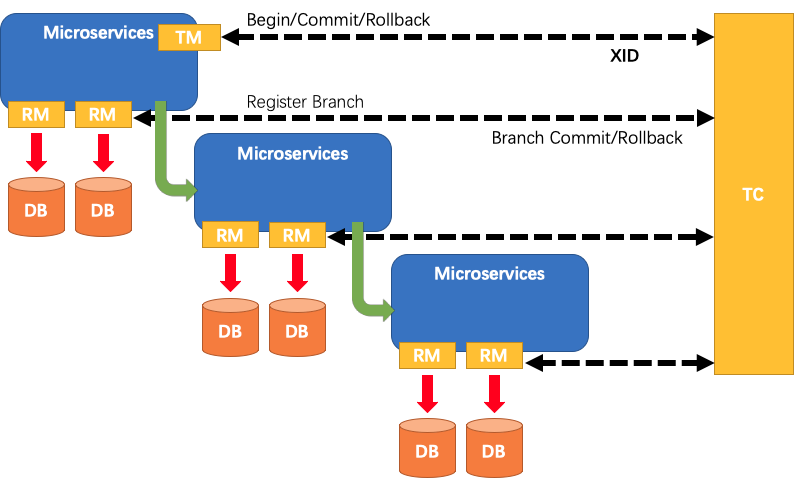
For more details about principle and design, please go to Seata wiki page.
History
Alibaba
- TXC: Taobao Transaction Constructor. Alibaba middleware team started this project since 2014 to meet the distributed transaction problems caused by application architecture change from monolithic to microservices.
- GTS: Global Transaction Service. TXC as an Aliyun middleware product with new name GTS was published since 2016.
- Fescar: we started the open source project Fescar based on TXC/GTS since 2019 to work closely with the community in the future.
Ant Financial
-
XTS: Extended Transaction Service. Ant Financial middleware team developed the distributed transaction middleware since 2007, which is widely used in Ant Financial and solves the problems of data consistency across databases and services.
-
DTX: Distributed Transaction Extended. Since 2013, XTS has been published on the Ant Financial Cloud, with the name of DTX .
Seata Community
- Seata :Simple Extensible Autonomous Transaction Architecture. Ant Financial joins Fescar, which make it to be a more neutral and open community for distributed transaction, and Fescar be renamed to Seata.
Maven dependency
Depending on the scenario, choose one of the two dependencies: org.apache.seata:seata-all or org.apache.seata:seata-spring-boot-starter.
<properties>
<seata.version>2.5.0</seata.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!--dependencies for non-SpringBoot application framework-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.seata</groupId>
<artifactId>seata-all</artifactId>
<version>${seata.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!--If your project base on `Spring Boot`, you can directly use the following dependencies-->
<!--Notice: `seata-spring-boot-starter` has already included `seata-all` dependency-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.seata</groupId>
<artifactId>seata-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>${seata.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Quick Start
Documentation
You can view the full documentation from Seata Official Website: Seata Website page.
Reporting bugs
Please follow the template for reporting any issues.
Security
Please do not use our public issue tracker but refer to our security policy
Contributing
Contributors are welcomed to join the Seata project. Please check CONTRIBUTING and CONTRIBUTING-CN about how to contribute to this project.
Contact
- Mailing list:
- dev@seata.apache.org , for dev/user discussion. subscribe, unsubscribe, archive
- Online chat:
| Dingtalk group | Wechat official account | QQ group | Wechat assistant |
|---|---|---|---|
 |  |  |  |
Seata ecosystem
- Seata Website - Seata official website
- Seata GoLang - Seata GoLang client
- Seata Samples - Samples for Seata Java
- Seata GoLang Samples - Samples for Seata GoLang
- Seata K8s - Seata integration with Kubernetes
- Seata CLI - CLI tool for Seata operations
Contributors
This project exists thanks to all the people who contribute. [Contributors].
License
Seata is under the Apache 2.0 license. See the LICENSE file for details.
Who is using
These are only part of the companies using Seata, for reference only. If you are using Seata, please add your company here to tell us your scenario to make Seata better.
Top Related Projects
:fire: Seata is an easy-to-use, high-performance, open source distributed transaction solution.
A distributed transaction framework, supports workflow, saga, tcc, xa, 2-phase message, outbox patterns, supports many languages.
ByteTCC is a distributed transaction manager based on the TCC(Try/Confirm/Cancel) mechanism. It’s compatible with the JTA specification. User guide: https://github.com/liuyangming/ByteTCC/wiki
tcc-transaction是TCC型事务java实现
Apache Seata(incubating) Samples for Java
SOFARPC is a high-performance, high-extensibility, production-level Java RPC framework.
Convert  designs to code with AI
designs to code with AI

Introducing Visual Copilot: A new AI model to turn Figma designs to high quality code using your components.
Try Visual Copilot
