 react-spreadsheet-grid
react-spreadsheet-grid
An Excel-like grid component for React with custom cell editors, performant scroll & resizable columns
Top Related Projects
JavaScript Data Grid / Data Table with a Spreadsheet Look & Feel. Works with React, Angular, and Vue. Supported by the Handsontable team ⚡
The best JavaScript Data Table for building Enterprise Applications. Supports React / Angular / Vue / Plain JavaScript.
Excel-like data grid (table) component for React
Feature-rich and customizable data grid React component
React-based drag'n'drop pivot table with Plotly.js charts
Quick Overview
React-spreadsheet-grid is a lightweight and customizable React component for creating spreadsheet-like grids. It provides a flexible and performant solution for displaying and editing tabular data in web applications, with features like scrolling, column resizing, and custom cell rendering.
Pros
- Highly customizable with support for custom cell renderers and editors
- Efficient rendering and scrolling for large datasets
- Easy integration with React applications
- Supports column resizing and row selection
Cons
- Limited built-in features compared to more comprehensive spreadsheet libraries
- Requires additional implementation for advanced features like filtering or sorting
- Documentation could be more extensive and provide more examples
- No built-in support for Excel-like formulas or complex calculations
Code Examples
- Basic usage of the SpreadsheetGrid component:
import React from 'react';
import { SpreadsheetGrid, Row, Column } from 'react-spreadsheet-grid';
const MyGrid = () => (
<SpreadsheetGrid
rows={[
{ id: 1, name: 'John', age: 30 },
{ id: 2, name: 'Jane', age: 25 },
]}
columns={[
{ key: 'name', title: 'Name', width: 200 },
{ key: 'age', title: 'Age', width: 100 },
]}
/>
);
- Using a custom cell renderer:
const CustomCell = ({ value }) => (
<div style={{ fontWeight: 'bold', color: 'blue' }}>{value}</div>
);
const MyGrid = () => (
<SpreadsheetGrid
rows={rows}
columns={[
{
key: 'name',
title: 'Name',
width: 200,
render: ({ value }) => <CustomCell value={value} />,
},
// ... other columns
]}
/>
);
- Implementing row selection:
const MyGrid = () => {
const [selectedRows, setSelectedRows] = useState([]);
return (
<SpreadsheetGrid
rows={rows}
columns={columns}
isRowSelectable={true}
selectedRows={selectedRows}
onRowsSelect={(newSelectedRows) => setSelectedRows(newSelectedRows)}
/>
);
};
Getting Started
To use react-spreadsheet-grid in your project:
-
Install the package:
npm install react-spreadsheet-grid -
Import and use the SpreadsheetGrid component in your React application:
import React from 'react'; import { SpreadsheetGrid } from 'react-spreadsheet-grid'; const MyComponent = () => ( <SpreadsheetGrid rows={yourDataArray} columns={[ { key: 'column1', title: 'Column 1', width: 200 }, { key: 'column2', title: 'Column 2', width: 150 }, ]} /> ); -
Customize the grid by adding props for features like row selection, column resizing, or custom cell rendering as needed.
Competitor Comparisons
JavaScript Data Grid / Data Table with a Spreadsheet Look & Feel. Works with React, Angular, and Vue. Supported by the Handsontable team ⚡
Pros of Handsontable
- More feature-rich with advanced functionalities like filtering, sorting, and validation
- Supports multiple frameworks (React, Angular, Vue) and vanilla JavaScript
- Extensive documentation and community support
Cons of Handsontable
- Larger bundle size due to its comprehensive feature set
- Steeper learning curve for basic implementations
- Commercial license required for some use cases
Code Comparison
react-spreadsheet-grid:
<SpreadsheetGrid
columns={columns}
rows={rows}
onCellChange={handleCellChange}
/>
Handsontable:
<HotTable
data={data}
colHeaders={true}
rowHeaders={true}
licenseKey="non-commercial-and-evaluation"
/>
Summary
Handsontable offers a more comprehensive solution with advanced features and multi-framework support, making it suitable for complex projects. However, it comes with a larger footprint and potential licensing costs. react-spreadsheet-grid provides a simpler, React-specific implementation that may be more suitable for lightweight projects or those requiring a smaller bundle size. The choice between the two depends on the specific project requirements, desired features, and development ecosystem.
The best JavaScript Data Table for building Enterprise Applications. Supports React / Angular / Vue / Plain JavaScript.
Pros of ag-grid
- More feature-rich with advanced functionality like filtering, sorting, and grouping
- Supports multiple frameworks (React, Angular, Vue) and vanilla JavaScript
- Extensive documentation and community support
Cons of ag-grid
- Steeper learning curve due to its complexity
- Larger bundle size, which may impact performance for simpler use cases
- Commercial license required for some advanced features
Code Comparison
react-spreadsheet-grid:
<SpreadsheetGrid
columns={columns}
rows={rows}
onCellChange={handleCellChange}
/>
ag-grid:
<AgGridReact
columnDefs={columnDefs}
rowData={rowData}
onCellValueChanged={handleCellValueChanged}
/>
Summary
ag-grid is a more comprehensive solution with advanced features and multi-framework support, making it suitable for complex data grid requirements. However, it comes with a steeper learning curve and potential licensing costs.
react-spreadsheet-grid is a simpler, React-specific solution that may be more suitable for basic spreadsheet-like functionality in React applications. It offers a more straightforward API but lacks some of the advanced features found in ag-grid.
The choice between the two depends on the specific project requirements, complexity, and whether additional features justify the learning curve and potential costs associated with ag-grid.
Excel-like data grid (table) component for React
Pros of react-datasheet
- More flexible cell rendering with custom components
- Built-in support for formulas and cell references
- Better handling of large datasets with virtualization
Cons of react-datasheet
- Less intuitive API for customizing cell behavior
- Limited built-in styling options
- Fewer options for column configuration
Code Comparison
react-spreadsheet-grid:
<SpreadsheetGrid
columns={columns}
rows={rows}
onCellChange={handleCellChange}
isColumnsResizable
/>
react-datasheet:
<ReactDataSheet
data={grid}
valueRenderer={(cell) => cell.value}
onCellsChanged={handleCellsChanged}
cellRenderer={CustomCell}
/>
Both libraries offer React components for creating spreadsheet-like grids, but they differ in their approach to customization and feature sets. react-spreadsheet-grid provides a more straightforward API for basic spreadsheet functionality, while react-datasheet offers more advanced features like formula support and custom cell rendering. The choice between the two depends on the specific requirements of your project, such as the need for complex calculations or highly customized cell appearance.
Feature-rich and customizable data grid React component
Pros of react-data-grid
- More feature-rich with built-in sorting, filtering, and cell editing
- Better performance for large datasets due to virtualization
- More active development and community support
Cons of react-data-grid
- Steeper learning curve due to more complex API
- Larger bundle size, which may impact load times
- Less flexibility for custom styling and layout
Code Comparison
react-data-grid:
import ReactDataGrid from 'react-data-grid';
const columns = [
{ key: 'id', name: 'ID' },
{ key: 'title', name: 'Title' }
];
const rows = [
{ id: 1, title: 'Example 1' },
{ id: 2, title: 'Example 2' }
];
function MyGrid() {
return <ReactDataGrid columns={columns} rows={rows} />;
}
react-spreadsheet-grid:
import { Grid } from 'react-spreadsheet-grid';
const columns = [
{ id: 'id', title: 'ID', value: (row) => row.id },
{ id: 'title', title: 'Title', value: (row) => row.title }
];
const rows = [
{ id: 1, title: 'Example 1' },
{ id: 2, title: 'Example 2' }
];
function MyGrid() {
return <Grid columns={columns} rows={rows} />;
}
Both libraries offer similar basic functionality, but react-data-grid provides more advanced features out of the box. react-spreadsheet-grid has a simpler API and may be easier to customize for specific use cases.
React-based drag'n'drop pivot table with Plotly.js charts
Pros of react-pivottable
- Advanced data analysis capabilities with pivot tables and charts
- Built-in drag-and-drop interface for easy data manipulation
- Supports various aggregation functions and chart types
Cons of react-pivottable
- Steeper learning curve due to more complex functionality
- May be overkill for simple spreadsheet-like data entry tasks
- Less customizable cell-level styling options
Code Comparison
react-pivottable:
import PivotTableUI from 'react-pivottable/PivotTableUI';
import 'react-pivottable/pivottable.css';
<PivotTableUI
data={data}
onChange={s => this.setState(s)}
{...this.state}
/>
react-spreadsheet-grid:
import { Grid } from 'react-spreadsheet-grid';
<Grid
columns={columns}
rows={rows}
getRowKey={row => row.id}
cellRenderer={cellProps => <Cell {...cellProps} />}
/>
react-pivottable is more suitable for complex data analysis and visualization, offering pivot table functionality and built-in charting. react-spreadsheet-grid is better for simpler spreadsheet-like interfaces with more control over individual cell rendering and styling. The choice depends on the specific requirements of your project, such as data complexity and desired user interaction.
Convert  designs to code with AI
designs to code with AI

Introducing Visual Copilot: A new AI model to turn Figma designs to high quality code using your components.
Try Visual CopilotREADME
React Spreadsheet Grid
An Excel-like grid component for React with custom cell editors, performant scroll & resizable columns
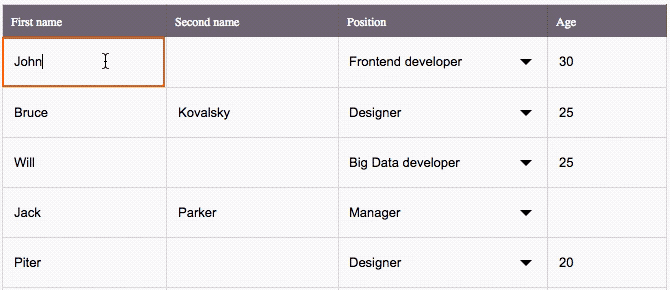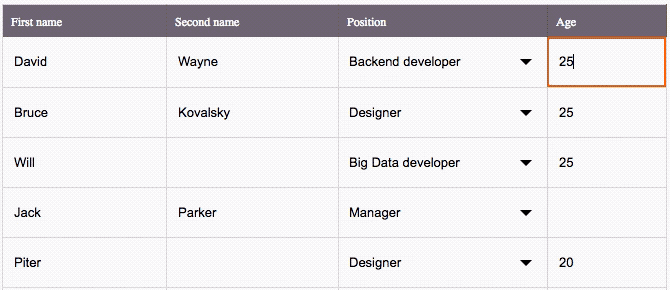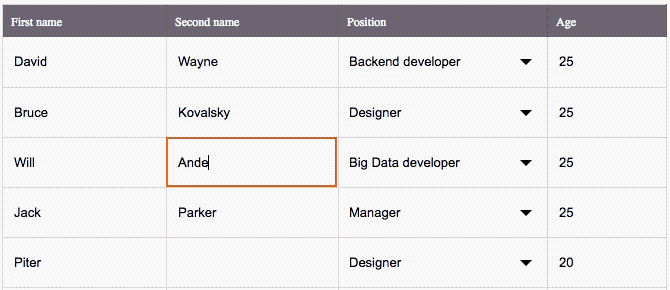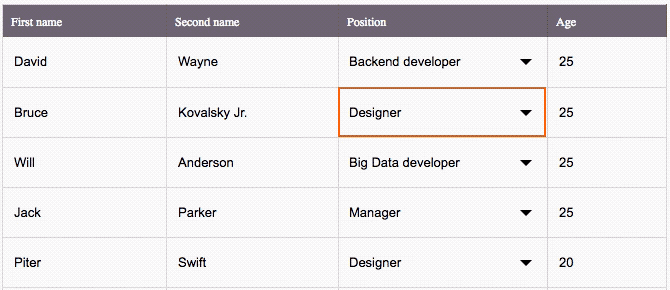
The key features
This is an Excel-like Spreadsheet Grid component that supports:
â Custom cell editors (use built-in Input and Select, or any other components) & header content
â Performant scroll for as many rows as you need
â Resizable columns
â Control by mouse & from keyboard
â Flexible setting of disabled cells
â Lazy loading support
â Customizable CSS styling
â Hooks compatible
â TypeScript compatible
Table of contents
- Live playground
- Installation
- A primitive example
- The pattern of regular usage
- Props
- Public methods
- Customizing cells & header content
- Performant scroll
- Resizable columns
- Control by mouse & from keyboard
- Lazy loading support
- Customizing CSS styles
Live playground
For examples of the grid in action, you can run the demo on your own computer:
- Clone this repository
npm installnpm run storybook- Visit http://localhost:6006/
Installation
This module is distributed via npm and should be installed as one of your project's dependencies:
npm install --save react-spreadsheet-grid
â ï¸ IMPORTANT! This package also depends on
react,react-domandprop-types. Please make sure you have those installed as well.
A primitive example
import React, { useState } from 'react'
import { Grid, Input, Select } from 'react-spreadsheet-grid'
const rows = [
{ id: 'user1', name: 'John Doe', positionId: 'position1' },
// and so on...
];
const MyAwesomeGrid = () => {
return (
<Grid
columns={[
{
title: () => 'Name',
value: (row, { focus }) => {
return (
<Input
value={row.name}
focus={focus}
/>
);
}
}, {
title: () => 'Position',
value: (row, { focus }) => {
return (
<Select
value={row.positionId}
isOpen={focus}
items={somePositions}
/>
);
}
}
]}
rows={rows}
getRowKey={row => row.id}
/>
)
}
The pattern of regular usage
Take a closer look at 2 main thing: a declaration of columns and work with the state of the parent component.
To get the correct behavior of the grid you should:
- Store rows and columns of the grid in the state of the parent component.
- Describe how the grid renders values of the cells.
- Have a callback that changes values of the rows in the state of the parent component.
Let's see how it works:
import { Grid, Input, Select } from 'react-spreadsheet-grid'
import AwesomeAutocomplete from 'awesome-autocomplete'
const rows = [
{ id: 'user1', name: 'John Doe', positionId: 'position1', managerId: 'manager1' },
// and so on...
];
const MyAwesomeGrid = () => {
// Rows are stored in the state.
const [rows, setRows] = useState(rows);
// A callback called every time a value changed.
// Every time it save a new value to the state.
const onFieldChange = (rowId, field) => (value) => {
// Find the row that is being changed
const row = rows.find({ id } => id === rowId);
// Change a value of a field
row[field] = value;
setRows([].concat(rows))
}
const initColumns = () => [
{
title: () => 'Name',
value: (row, { focus }) => {
// You can use the built-in Input.
return (
<Input
value={row.name}
focus={focus}
onChange={onFieldChange(row.id, 'name')}
/>
);
}
}, {
title: () => 'Position',
value: (row, { focus }) => {
// You can use the built-in Select.
return (
<Select
value={row.positionId}
isOpen={focus}
items={somePositions}
onChange={onFieldChange(row.id, 'positionId')}
/>
);
}
}, {
title: () => 'Manager',
value: (row, { active, focus }) => {
// You can use whatever component you want to change a value.
return (
<AwesomeAutocomplete
value={row.managerId}
active={active}
focus={focus}
onSelectItem={onFieldChange(row.id, 'managerId')}
/>
);
}
}
]
return (
<Grid
columns={initColumns()}
rows={rows}
isColumnsResizable
onColumnResize={onColumnResize}
getRowKey={row => row.id}
/>
)
}
Props
columns
arrayOf({
id: string / number,
title: string / func,
value: string / func(row, { active, focus, disabled }),
width: number,
getCellClassName: func(row)
})
defaults to
[]
required
This is the most important prop that defines columns of the table. Every item of the array is responsible for the corresponding column.
| key | Required | Mission |
|---|---|---|
id | yes | An identifier of a row. |
title | yes | This is what you want to put in the header of the column, it could be passed as a string or as a func returning a React element. |
value | yes | This is content of the cell. Works the same way as title, but func receives row and current state of the cell ({ active, focus, disabled }) as parameters, so you can create an output based on them. |
width | no | Pass this property if you want to initialize the width of a column. You can set width not for all the columns, then the rest of the table width would be distributed between the columns with unspecified width. Also, you can get width of the columns from onColumnResize callback to store somewhere and use for the next render to make columns stay the same width. |
getCellClassName | no | An additional class name getter for a row. |
rows
arrayOf(any)| defaults to[]
required
This is an array of rows for the table. Every row will be passed to a column.value func (if you use it).
getRowKey
func(row)
required
This is a func that must return unique key for a row based on this row in a parameter.
placeholder
string| defaults to"There are no rows"
Used as a placeholder text when the rows array is empty.
disabledCellChecker
func(row, columnId): bool
Use this func to define what cells are disabled in the table. It gets row and columnId (defined as column.id in a columns array) as parameters and identifiers of a cell. It should return boolean true / false. A disabled cell gets special CSS-class and styles. Also, you can define a column.value output based on the disabled state parameter.
onCellClick
func(row, columnId)
A click handler function for a cell. It gets row and columnId (defined as column.id in the columns array) as parameters and identifiers of a cell.
onActiveCellChanged
func({ x, y })
A callback called every time the active cell is changed. It gets { x, y } coordinates of the new active cell as parameters.
headerHeight
number| defaults to40
The height of the header of the table in pixels.
â ï¸ Define it as a prop, not in CSS styles to not broke the scroll of the table. â ï¸
rowHeight
number| defaults to48
The height of a row of the table in pixels.
â ï¸ Define it as a prop, not in CSS styles to not broke the scroll of the table. â ï¸
focusOnSingleClick
boolean
defaults to
false
By default, double clicking a cell sets the focus on the cell's input. Pass true if you want to set the focus on the cell's input upon single clicking it.
isColumnsResizable
bool| defaults tofalse
Switch this on if you want the table provides an opportunity to resize column width.
onColumnResize
func(widthValues: object)
A callback called every time the width of a column was resized. Gets widthValues object as a parameter. widthValues is a map of values of width for all the columns in percents (columnId - value).
isScrollable
boolean
defaults to
true
This defines should a grid has a scrollable container inside of a DOM-element where it was rendered, or not. When it turned on (by default), only visible rows are rendered and that improves performance. If you pass false, all the rows will be rendered at once (that is not a good way to handle with a big amount of them), but you will have opportunity to set up a scroll area where you want it to be and have other components (before or after the grid) included in this area.
onScroll
func(scrollPosition: number)
A callback called every time the position of the scroll of the grid was changed.
onScrollReachesBottom
func()
A callback called when the scroll of the grid reaches its bottom value. Usually, it could be used to implement the lazy loading feature in your grid (see the Lazy loading support section for details).
Public methods
Use public methods via a grid's ref:
const GridWrapper = () => {
const gridRef = React.createRef()
React.useEffect(() => {
gridRef.current.resetScroll()
})
return (
<Grid
ref={gridRef}
// other props
/>
)
}
resetScroll()
Call to reset the scroll to the top of the container.
focusCell({ x: number, y: number })
Call to make the cell with this x, y coordinates (starting from 0) active and focused.
Customizing cells & header content
You can customize content of titles and cells using title and value keys of elements of the columns property. Setting these components using row and { active, focus, disabled } parameters of the functions.
title could be a string or a func returning any React element.
value works the same way, but func receives current row and current state of the cell ({ active, focused, disabled }) as parameters, so you can create an output based on them.
For the basic usage, the library provide 2 default components that you can use out-of-the-box: Input and Select. Perhaps, they will be enough for you. However, you can use any other React components for that purpose: autocompletes, checkboxes, etc.
Built-in Input
Input prop types:
| Prop | Type | Mission |
|---|---|---|
value | string | The value of the input |
placeholder | string | Placeholder displaying when there is no value |
focus | bool | Should the input has focus or not |
selectTextOnFocus | bool | Should the input content be selected when focused or not |
onChange | func | Blur callback. Use it to catch a changed value |
Usage:
import { Grid, Input } from 'react-spreadsheet-grid'
<Grid
columns={[
{
id: 'name',
title: () => {
return <span>Name</span>
},
value: (row, { focus }) => {
return (
<Input
value={row.name}
focus={focus}
onChange={onFieldChange(row.id, 'name')}
/>
);
}
}
]}
/>
Built-in Select
Select prop types:
| Prop | Type | Mission |
|---|---|---|
items | arrayOf({ id: string / number, name: string }) | Items for select |
selectedId | string / number | Id of a selected item |
placeholder | string | Placeholder displaying when there is no selected item |
isOpen | bool | Should the select be open or not |
onChange | func | Change item callback. Use it to catch a changed value |
Usage:
import { Grid, Select } from 'react-spreadsheet-grid'
const positions = [{
id: 1,
name: 'Frontend developer'
}, {
id: 2,
name: 'Backend developer'
}];
<Grid
columns={[
{
id: 'position',
title: () => {
return <span>Position</span>
},
value: (row, { focus }) => {
return (
<Select
items={positions}
selectedId={row.positionId}
isOpen={focus}
onChange={onFieldChange(row.id, 'positionId')}
/>
);
}
}
]}
/>
Another component
Let's suggest you need to use an autocomplete as a content of a cell. This is how it could be done:
import { Grid } from 'react-spreadsheet-grid'
import AwesomeAutocomplete from 'awesome-autocomplete'
<Grid
columns={[
{
id: 'manager',
title: () => {
return <span>Manager</span>
},
value: (row, { focus, active }) => {
return (
<AwesomeAutocomplete
value={row.managerId}
active={active}
focus={focus}
onSelectItem={onFieldChange(row.id, 'managerId')}
/>
);
}
}
]}
/>
Performant scroll
A behavior of scroll depends on the isScrollable prop.
If isScrollable is false, the grid renders all the passed rows without a scroll. Probably, this would be useful for small amount of the rows.
If isScrollable is true, the height of the grid is equal to the height of its container, it has a scroll and renders only the rows that are visible. Therefore, you can pass to it as many rows as you want - it will work fine without any problems with rendering and scroll. This would be useful for big amount of the rows.
This is an example, how we could make a 500px height scrollable grid:
<div style={{ height: '500px' }}>
<Grid
isScrollable
/* other props */
/>
</div>
Resizable columns
react-spreadsheet-grid provides the opportunity to set initial width values for columns, to resize them from the UI and to react on these changes. Use relevant columnWidthValues, isColumnsResizable and onColumnResize properties for that purpose.
This is how it could be done:
import React, { useState } from 'react'
import { Grid } from 'react-spreadsheet-grid'
const ResizableGrid = () => {
// Put columns to the state to be able to store there their width values.
const [columns, setColumns] = useState(initColumns())
// Change columns width values in the state to not lose them.
const onColumnResize = (widthValues) => {
const newColumns = [].concat(columns)
Object.keys(widthValues).forEach((columnId) => {
newColumns[columnId].width = widthValues[columnId]
})
setColumns(newColumns)
}
return (
<Grid
columns={columns}
isColumnsResizable
onColumnResize={onColumnResize}
rows={/* some rows here */}
getRowKey={row => row.id}
/>
)
}
Control by mouse & from keyboard
react-spreadsheet-grid could be controlled by a mouse and from keyboard (just like Excel-table could). When a mouse is used, single click make a cell active, double click make a cell focused. When a keyboard used, â â â â move active cell, ENTER and TAB make a cell focused.
Customizing CSS styles
Right now, the easiest way to tweak react-spreadsheet-grid is to create another stylesheet to override the default styles. For example, you could create a file named react_spreadsheet_grid_overrides.css with the following contents:
.SpreadsheetGrid__cell_active {
box-shadow: inset 0 0 0 2px green;
}
This would override the color of borders for the table active cell.
â ï¸ The only exception, that you have to use headerHeight and rowHeight props to redefine height of the header and rows to not broke the scroll of the table.
Lazy loading support
react-spreadsheet-grid provides the opportunity to implement the lazy loading feature in your grid. Use the onScrollReachesBottom callback to handle a situation when the scroll position reaches its bottom. Load a new portion of the rows and put them in the state of a high-order component.
This is how it could be done:
import React, { useState } from 'react'
import { Grid } from 'react-spreadsheet-grid'
const LazyLoadingGrid = () => {
/* Init the state with the initial portion of the rows */
const [rows, setRows] = useState(initialRows);
const onScrollReachesBottom = () => {
loadNewPortionOfRows().then((newRows) => {
setRows(rows.concat(newRows));
});
}
const loadNewPortionOfRows = () => {
/* an ajax request here */
}
return (
<Grid
columns={/* some columns here */}
row={rows}
getRowKey={row => row.id}
onScrollReachesBottom={onScrollReachesBottom}
/>
)
}
Top Related Projects
JavaScript Data Grid / Data Table with a Spreadsheet Look & Feel. Works with React, Angular, and Vue. Supported by the Handsontable team ⚡
The best JavaScript Data Table for building Enterprise Applications. Supports React / Angular / Vue / Plain JavaScript.
Excel-like data grid (table) component for React
Feature-rich and customizable data grid React component
React-based drag'n'drop pivot table with Plotly.js charts
Convert  designs to code with AI
designs to code with AI

Introducing Visual Copilot: A new AI model to turn Figma designs to high quality code using your components.
Try Visual Copilot