Top Related Projects
Examples and server integrations for generating the Swagger API Specification, which enables easy access to your REST API
Automated JSON API documentation for API's built with Spring
OpenAPI Generator allows generation of API client libraries (SDK generation), server stubs, documentation and configuration automatically given an OpenAPI Spec (v2, v3)
The OpenAPI Specification Repository
📘 OpenAPI/Swagger-generated API Reference Documentation
Turn any OpenAPI2/3 and Postman Collection file into an API server with mocking, transformations and validations.
Quick Overview
Springdoc-openapi is a library that helps automate the generation of API documentation using spring boot and OpenAPI 3. It works by examining an application at runtime to infer API semantics based on spring configurations, class structure and various annotations.
Pros
- Seamless integration with Spring Boot applications
- Automatic generation of OpenAPI 3 documentation
- Supports both Swagger UI and OpenAPI UI for visualizing and interacting with the API
- Customizable through various configuration options and annotations
Cons
- May require additional setup for complex API structures
- Documentation generation can slightly increase application startup time
- Some advanced features may require manual configuration
- Learning curve for developers new to OpenAPI and Swagger concepts
Code Examples
- Basic configuration in a Spring Boot application:
@SpringBootApplication
@OpenAPIDefinition(info = @Info(title = "My API", version = "v1"))
public class MyApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MyApplication.class, args);
}
}
- Customizing operation documentation:
@RestController
public class MyController {
@Operation(summary = "Get a user by ID", description = "Returns a user object")
@ApiResponses(value = {
@ApiResponse(responseCode = "200", description = "Successful operation"),
@ApiResponse(responseCode = "404", description = "User not found")
})
@GetMapping("/users/{id}")
public User getUser(@PathVariable Long id) {
// Implementation
}
}
- Grouping APIs:
@RestController
@Tag(name = "User Management", description = "APIs for managing users")
public class UserController {
// Controller methods
}
Getting Started
To use springdoc-openapi in your Spring Boot project:
- Add the dependency to your
pom.xml:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springdoc</groupId>
<artifactId>springdoc-openapi-starter-webmvc-ui</artifactId>
<version>2.1.0</version>
</dependency>
-
Run your Spring Boot application. The OpenAPI documentation will be available at:
- Swagger UI:
http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html - OpenAPI JSON:
http://localhost:8080/v3/api-docs
- Swagger UI:
-
Customize the documentation using annotations on your controllers and models.
Competitor Comparisons
Examples and server integrations for generating the Swagger API Specification, which enables easy access to your REST API
Pros of swagger-core
- More mature and established project with a larger community
- Supports a wider range of Java frameworks beyond Spring
- Offers more customization options for advanced use cases
Cons of swagger-core
- Requires more manual configuration and setup
- Less seamless integration with Spring Boot applications
- May have a steeper learning curve for beginners
Code Comparison
swagger-core:
@Api(value = "users")
@Path("/users")
public class UserResource {
@GET
@ApiOperation(value = "Get user by ID")
public Response getUserById(@QueryParam("id") Long id) {
// Implementation
}
}
springdoc-openapi:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/users")
public class UserController {
@GetMapping
@Operation(summary = "Get user by ID")
public ResponseEntity<User> getUserById(@RequestParam Long id) {
// Implementation
}
}
Key Differences
-
Annotation usage: swagger-core uses
@Apiand@ApiOperation, while springdoc-openapi leverages Spring's existing annotations and adds@Operationfor additional OpenAPI information. -
Framework integration: springdoc-openapi is specifically designed for Spring Boot, offering tighter integration and easier setup, while swagger-core is more framework-agnostic.
-
Configuration: springdoc-openapi typically requires less configuration, as it automatically detects Spring components and generates OpenAPI documentation, whereas swagger-core often needs more manual setup.
-
Spring Boot compatibility: springdoc-openapi is built with Spring Boot in mind, making it a more natural fit for Spring Boot applications, while swagger-core may require additional adapters or configuration for optimal use with Spring Boot.
Automated JSON API documentation for API's built with Spring
Pros of springfox
- More mature project with a longer history and larger community
- Supports older versions of Spring Boot (2.x and earlier)
- Offers more customization options for advanced use cases
Cons of springfox
- No longer actively maintained (last release in 2020)
- Lacks support for OpenAPI 3.0 specification
- May have compatibility issues with newer Spring Boot versions (3.x+)
Code Comparison
springfox:
@Configuration
@EnableSwagger2
public class SwaggerConfig {
@Bean
public Docket api() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.any())
.paths(PathSelectors.any())
.build();
}
}
springdoc-openapi:
@Configuration
@OpenAPIDefinition(info = @Info(title = "My API", version = "v1"))
public class OpenApiConfig {
@Bean
public OpenAPI customOpenAPI() {
return new OpenAPI()
.components(new Components())
.info(new Info().title("My API").version("v1"));
}
}
Both libraries aim to generate OpenAPI documentation for Spring Boot applications, but springdoc-openapi is more up-to-date and aligned with modern Spring Boot versions and OpenAPI specifications.
OpenAPI Generator allows generation of API client libraries (SDK generation), server stubs, documentation and configuration automatically given an OpenAPI Spec (v2, v3)
Pros of openapi-generator
- Supports multiple programming languages and frameworks
- Generates both client and server code
- Offers a wide range of customization options
Cons of openapi-generator
- Steeper learning curve due to its extensive features
- May require more configuration for specific use cases
- Generated code might need manual adjustments
Code Comparison
springdoc-openapi:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class UserController {
@GetMapping("/users")
public List<User> getUsers() {
// Implementation
}
}
openapi-generator:
@javax.annotation.Generated(value = "org.openapitools.codegen.languages.JavaClientCodegen")
public class UserApi {
public ApiResponse<List<User>> getUsersWithHttpInfo() throws ApiException {
// Generated implementation
}
}
The springdoc-openapi example shows a simple Spring Boot controller, while the openapi-generator example demonstrates a generated API client. springdoc-openapi integrates seamlessly with existing Spring Boot applications, whereas openapi-generator creates standalone API clients and servers based on OpenAPI specifications.
The OpenAPI Specification Repository
Pros of OpenAPI-Specification
- Industry-standard specification for describing RESTful APIs
- Language-agnostic, allowing for broader adoption across different tech stacks
- Extensive ecosystem of tools and libraries for various use cases
Cons of OpenAPI-Specification
- Requires manual creation and maintenance of API documentation
- Less integration with specific frameworks or libraries
- May require additional tooling for code generation or validation
Code Comparison
OpenAPI-Specification (YAML):
openapi: 3.0.0
info:
title: Sample API
version: 1.0.0
paths:
/users:
get:
summary: List users
springdoc-openapi (Java):
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/users")
public class UserController {
@GetMapping
@Operation(summary = "List users")
public List<User> listUsers() {
// Implementation
}
}
SpringDoc OpenAPI automatically generates OpenAPI documentation from Spring Boot applications, while OpenAPI-Specification provides a standardized format for describing APIs across different platforms and languages. SpringDoc OpenAPI offers tighter integration with Spring Boot, reducing manual documentation efforts, whereas OpenAPI-Specification provides more flexibility and broader adoption across various technologies.
📘 OpenAPI/Swagger-generated API Reference Documentation
Pros of Redoc
- Focused on API documentation rendering with a sleek, customizable UI
- Supports multiple themes and responsive design out-of-the-box
- Lightweight and can be easily integrated into existing web applications
Cons of Redoc
- Limited to OpenAPI/Swagger specification rendering
- Requires manual integration with backend systems
- Less suitable for automatic API documentation generation from code
Code Comparison
Redoc usage:
<script src="https://cdn.redoc.ly/redoc/latest/bundles/redoc.standalone.js"></script>
<redoc spec-url="https://petstore.swagger.io/v2/swagger.json"></redoc>
Springdoc-openapi usage:
@Configuration
@OpenAPIDefinition(info = @Info(title = "My API", version = "v1"))
public class OpenApiConfig {
// Configuration code
}
Redoc focuses on rendering OpenAPI specifications, while Springdoc-openapi integrates with Spring Boot to automatically generate and expose API documentation. Springdoc-openapi offers more comprehensive features for Spring-based applications, including automatic generation of OpenAPI definitions from code. Redoc, on the other hand, excels in providing a polished, customizable documentation UI that can be easily embedded in various web applications.
Turn any OpenAPI2/3 and Postman Collection file into an API server with mocking, transformations and validations.
Pros of Prism
- Language-agnostic: Works with any API specification, not limited to Spring Boot applications
- Standalone mock server: Can be run independently without integrating into an existing application
- Supports multiple specification formats: OpenAPI, AsyncAPI, and JSON Schema
Cons of Prism
- Lacks automatic documentation generation for existing code
- Requires manual setup and configuration for each API endpoint
- Limited integration with existing frameworks and libraries
Code Comparison
Springdoc-openapi (Java):
@RestController
@Tag(name = "User API")
public class UserController {
@GetMapping("/users")
@Operation(summary = "Get all users")
public List<User> getAllUsers() {
// Implementation
}
}
Prism (Configuration file):
openapi: 3.0.0
paths:
/users:
get:
summary: Get all users
responses:
'200':
description: Successful response
content:
application/json:
schema:
type: array
items:
$ref: '#/components/schemas/User'
Springdoc-openapi automatically generates OpenAPI documentation from annotated code, while Prism requires manual configuration of API specifications. Springdoc-openapi is tightly integrated with Spring Boot, offering seamless documentation generation. Prism, on the other hand, provides a more flexible, language-agnostic approach for API mocking and testing across various platforms and frameworks.
Convert  designs to code with AI
designs to code with AI

Introducing Visual Copilot: A new AI model to turn Figma designs to high quality code using your components.
Try Visual CopilotREADME
IMPORTANT: springdoc-openapi v1.8.0 is the latest Open Source release supporting
Spring Boot 2.x and 1.x.
An extended support for springdoc-openapi v1 project is now available for organizations that need support beyond 2023.
For more details, feel free to reach out: sales@springdoc.org
springdoc-openapi is on Open Collective. If
you â¤ï¸ this project consider becoming a sponsor.
This project is sponsored by
Table of Contents
- Full documentation
- Introduction
- Getting Started
- Library for springdoc-openapi integration with spring-boot and swagger-ui
- Spring-boot with OpenAPI Demo applications.
- Integration of the library in a Spring Boot 3.x project without the swagger-ui:
- Error Handling for REST using @ControllerAdvice
- Adding API Information and Security documentation
- spring-webflux support with Annotated Controllers
- Acknowledgements
Full documentation
Introduction
The springdoc-openapi Java library helps automating the generation of API documentation using Spring Boot projects. springdoc-openapi works by examining an application at runtime to infer API semantics based on Spring configurations, class structure and various annotations.
The library automatically generates documentation in JSON/YAML and HTML formatted pages.
The generated documentation can be complemented using swagger-api annotations.
This library supports:
- OpenAPI 3
- Spring-boot v3 (Java 17 & Jakarta EE 9)
- JSR-303, specifically for @NotNull, @Min, @Max, and @Size.
- Swagger-ui
- OAuth 2
- GraalVM native images
The following video introduces the Library:
For spring-boot v3 support, make sure you use springdoc-openapi v2
This is a community-based project, not maintained by the Spring Framework Contributors ( Pivotal)
Getting Started
Library for springdoc-openapi integration with spring-boot and swagger-ui
- Automatically deploys swagger-ui to a Spring Boot 3.x application
- Documentation will be available in HTML format, using the official swagger-ui jars.
- The Swagger UI page should then be available at http://server:
port/context-path/swagger-ui.html and the OpenAPI description will be available at the
following url for json format: http://server:port/context-path/v3/api-docs
server: The server name or IPport: The server portcontext-path: The context path of the application
- Documentation can be available in yaml format as well, on the following path:
/v3/api-docs.yaml - Add the
springdoc-openapi-uilibrary to the list of your project dependencies (No additional configuration is needed):
Maven
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springdoc</groupId>
<artifactId>springdoc-openapi-starter-webmvc-ui</artifactId>
<version>last-release-version</version>
</dependency>
Gradle
implementation 'org.springdoc:springdoc-openapi-starter-webmvc-ui:latest'
- This step is optional: For custom path of the swagger documentation in HTML format, add a custom springdoc property, in your spring-boot configuration file:
# swagger-ui custom path
springdoc.swagger-ui.path=/swagger-ui.html
Spring-boot with OpenAPI Demo applications.
Source Code for Demo Applications.
Demo Spring Boot 3 Web MVC with OpenAPI 3.
Demo Spring Boot 3 WebFlux with OpenAPI 3.
Demo Spring Boot 3 WebFlux with Functional endpoints OpenAPI 3.
Demo Spring Boot 3 and Spring Cloud Function Web MVC.
Demo Spring Boot 3 and Spring Cloud Function WebFlux.
Demo Spring Boot 3 and Spring Cloud Gateway.
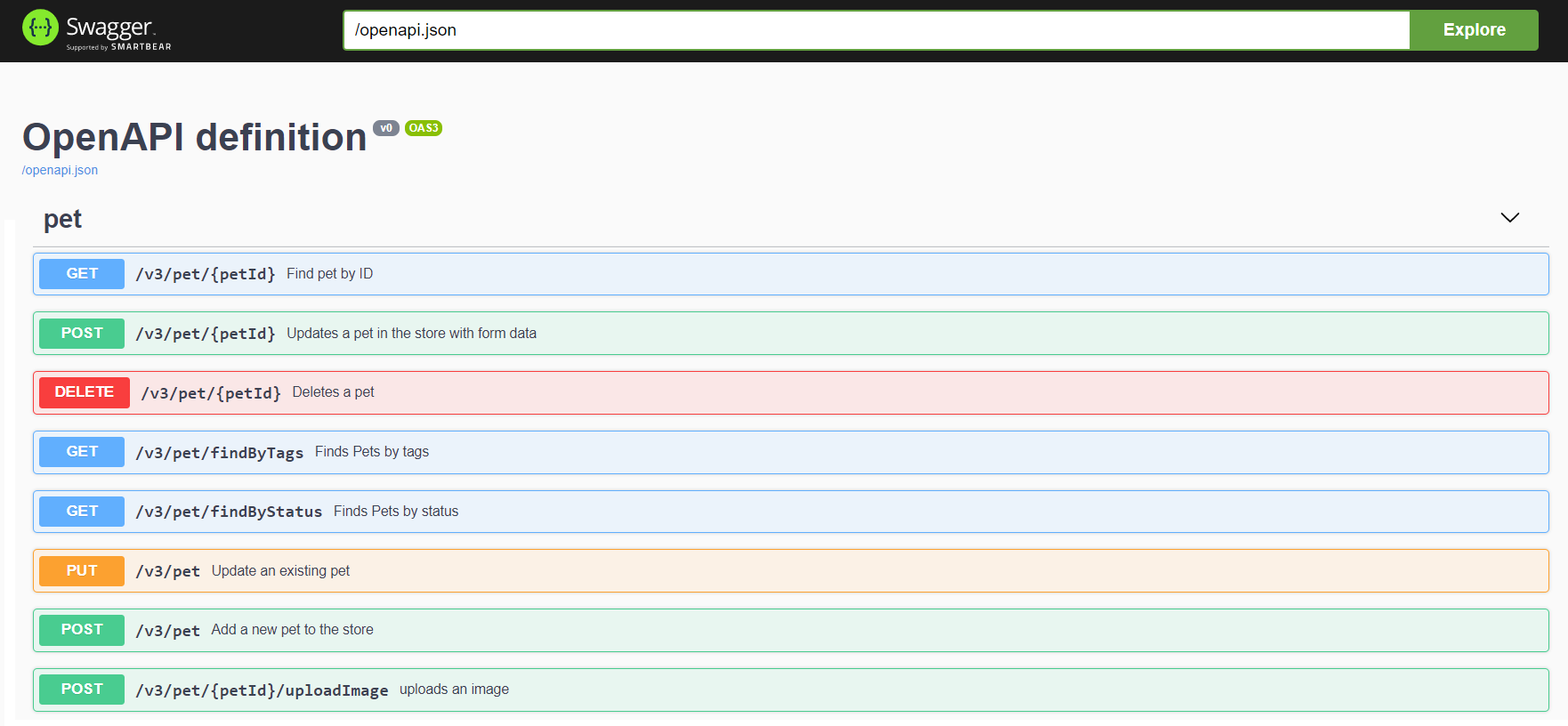
Integration of the library in a Spring Boot 3.x project without the swagger-ui:
- Documentation will be available at the following url for json format: http://server:
port/context-path/v3/api-docs
server: The server name or IPport: The server portcontext-path: The context path of the application
- Documentation will be available in yaml format as well, on the following
path :
/v3/api-docs.yaml - Add the library to the list of your project dependencies. (No additional configuration is needed)
Maven
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springdoc</groupId>
<artifactId>springdoc-openapi-starter-webmvc-api</artifactId>
<version>last-release-version</version>
</dependency>
Gradle
implementation 'org.springdoc:springdoc-openapi-starter-webmvc-ui:latest'
- This step is optional: For custom path of the OpenAPI documentation in Json format, add a custom springdoc property, in your spring-boot configuration file:
# /api-docs endpoint custom path
springdoc.api-docs.path=/api-docs
- This step is optional: If you want to disable
springdoc-openapiendpoints, add a custom springdoc property, in yourspring-bootconfiguration file:
# disable api-docs
springdoc.api-docs.enabled=false
Error Handling for REST using @ControllerAdvice
To generate documentation automatically, make sure all the methods declare the HTTP Code responses using the annotation: @ResponseStatus.
Adding API Information and Security documentation
The library uses spring-boot application auto-configured packages to scan for the
following annotations in spring beans: OpenAPIDefinition and Info.
These annotations declare, API Information: Title, version, licence, security, servers,
tags, security and externalDocs.
For better performance of documentation generation, declare @OpenAPIDefinition
and @SecurityScheme annotations within a Spring managed bean.
spring-webflux support with Annotated Controllers
- Documentation can be available in yaml format as well, on the following path : /v3/api-docs.yaml
- Add the library to the list of your project dependencies (No additional configuration is needed)
Maven
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springdoc</groupId>
<artifactId>springdoc-openapi-starter-webflux-ui</artifactId>
<version>last-release-version</version>
</dependency>
Gradle
implementation 'org.springdoc:springdoc-openapi-starter-webmvc-ui:latest'
- This step is optional: For custom path of the swagger documentation in HTML format, add a custom springdoc property, in your spring-boot configuration file:
# swagger-ui custom path
springdoc.swagger-ui.path=/swagger-ui.html
The springdoc-openapi libraries are hosted on maven central repository.
The artifacts can be viewed accessed at the following locations:
Releases:
Snapshots:
Acknowledgements
Contributors
springdoc-openapi is relevant and updated regularly due to the valuable contributions from its contributors.
Thanks you all for your support!
Additional Support
- Spring Team - Thanks for their support by sharing all relevant resources around Spring projects.
- JetBrains - Thanks a lot for supporting springdoc-openapi project.
Top Related Projects
Examples and server integrations for generating the Swagger API Specification, which enables easy access to your REST API
Automated JSON API documentation for API's built with Spring
OpenAPI Generator allows generation of API client libraries (SDK generation), server stubs, documentation and configuration automatically given an OpenAPI Spec (v2, v3)
The OpenAPI Specification Repository
📘 OpenAPI/Swagger-generated API Reference Documentation
Turn any OpenAPI2/3 and Postman Collection file into an API server with mocking, transformations and validations.
Convert  designs to code with AI
designs to code with AI

Introducing Visual Copilot: A new AI model to turn Figma designs to high quality code using your components.
Try Visual Copilot






