 react-notifications-component
react-notifications-component
Delightful and highly customisable React Component to notify your users
Top Related Projects
React notification made easy 🚀 !
Highly customizable notification snackbars (toasts) that can be stacked on top of each other
Smoking Hot React Notifications 🔥
A beautiful replacement for JavaScript's "alert"
Quick Overview
The react-notifications-component is a highly customizable and feature-rich notification library for React applications. It provides an easy-to-use API to display various types of notifications, including success, error, warning, and info messages, with a wide range of configuration options.
Pros
- Highly Customizable: The library offers a wide range of customization options, allowing developers to tailor the notifications to match the branding and design of their application.
- Flexible Positioning: Notifications can be positioned at different locations on the screen, including top, bottom, left, and right.
- Smooth Animations: The library provides smooth animations for the notifications, enhancing the overall user experience.
- Extensive Documentation: The project has detailed documentation, making it easy for developers to get started and understand the available features.
Cons
- Dependency on React: The library is specifically designed for React applications and may not be suitable for non-React projects.
- Limited Accessibility: The library may not have built-in accessibility features, which could be a concern for applications targeting users with disabilities.
- Potential Performance Issues: Depending on the number and frequency of notifications, the library may have a performance impact on the application.
- Limited Customization of Animations: While the library provides smooth animations, the customization options for these animations may be limited.
Code Examples
Here are a few code examples demonstrating the usage of the react-notifications-component library:
- Displaying a Success Notification:
import React from 'react';
import ReactNotification, { store } from 'react-notifications-component';
import 'react-notifications-component/dist/theme.css';
const MyComponent = () => {
const handleSuccess = () => {
store.addNotification({
title: 'Success!',
message: 'Your action was successful.',
type: 'success',
insert: 'top',
container: 'top-right',
animationIn: ['animate__animated', 'animate__fadeIn'],
animationOut: ['animate__animated', 'animate__fadeOut'],
dismiss: {
duration: 3000,
onScreen: true
}
});
};
return (
<div>
<button onClick={handleSuccess}>Show Success Notification</button>
<ReactNotification />
</div>
);
};
export default MyComponent;
- Displaying an Error Notification:
import React from 'react';
import ReactNotification, { store } from 'react-notifications-component';
import 'react-notifications-component/dist/theme.css';
const MyComponent = () => {
const handleError = () => {
store.addNotification({
title: 'Error!',
message: 'Something went wrong.',
type: 'danger',
insert: 'bottom',
container: 'bottom-left',
animationIn: ['animate__animated', 'animate__shakeX'],
animationOut: ['animate__animated', 'animate__fadeOut'],
dismiss: {
duration: 5000,
onScreen: true
}
});
};
return (
<div>
<button onClick={handleError}>Show Error Notification</button>
<ReactNotification />
</div>
);
};
export default MyComponent;
- Displaying a Warning Notification:
import React from 'react';
import ReactNotification, { store } from 'react-notifications-component';
import 'react-notifications-component/dist/theme.css';
const MyComponent = () => {
const handleWarning = () => {
store.addNotification({
title: 'Warning!',
message: 'This is a warning message.',
type: 'warning',
insert: 'top',
container: 'top-left',
animationIn: ['animate__animated', 'animate__bounceIn'],
animationOut: ['animate__animated', 'animate__fadeOut'],
dismiss: {
duration: 4000,
onScreen:
Competitor Comparisons
React notification made easy 🚀 !
Pros of react-toastify
- More popular and widely adopted, with a larger community and more frequent updates
- Offers a wider range of customization options and animation effects
- Supports mobile-friendly touch gestures for dismissing notifications
Cons of react-toastify
- Slightly larger bundle size compared to react-notifications-component
- May have a steeper learning curve due to its extensive API and configuration options
Code Comparison
react-toastify:
import { ToastContainer, toast } from 'react-toastify';
import 'react-toastify/dist/ReactToastify.css';
toast.success('Success message');
<ToastContainer />
react-notifications-component:
import { ReactNotifications, Store } from 'react-notifications-component';
import 'react-notifications-component/dist/theme.css';
Store.addNotification({
title: "Success",
message: "Success message",
type: "success"
});
<ReactNotifications />
Both libraries offer similar basic functionality for displaying notifications, but react-toastify provides a more concise API for common use cases. react-notifications-component requires slightly more setup code but offers a more explicit configuration approach.
While react-toastify is generally more feature-rich and popular, react-notifications-component may be preferred for simpler projects or when a smaller bundle size is crucial. The choice between the two depends on specific project requirements and developer preferences.
Highly customizable notification snackbars (toasts) that can be stacked on top of each other
Pros of notistack
- Seamless integration with Material-UI, providing a consistent look and feel
- Built-in support for snackbars, offering a more focused notification system
- Simpler API with less configuration required for basic usage
Cons of notistack
- Limited customization options compared to react-notifications-component
- Primarily designed for Material-UI, which may not suit all project styles
- Fewer animation options out of the box
Code Comparison
notistack:
import { useSnackbar } from 'notistack';
const { enqueueSnackbar } = useSnackbar();
enqueueSnackbar('This is a success message!', { variant: 'success' });
react-notifications-component:
import { store } from 'react-notifications-component';
store.addNotification({
title: "Success!",
message: "This is a success message!",
type: "success",
insert: "top",
container: "top-right",
animationIn: ["animate__animated", "animate__fadeIn"],
animationOut: ["animate__animated", "animate__fadeOut"],
});
The code comparison shows that notistack offers a more concise API for basic notifications, while react-notifications-component provides more detailed configuration options. notistack's approach is simpler and more straightforward, especially when working within a Material-UI ecosystem. However, react-notifications-component offers greater flexibility in terms of notification types, positioning, and animations, making it potentially more suitable for projects requiring extensive customization.
Smoking Hot React Notifications 🔥
Pros of react-hot-toast
- Lightweight and minimal bundle size
- Simple API with intuitive usage
- Built-in animations and smooth transitions
Cons of react-hot-toast
- Limited customization options compared to react-notifications-component
- Fewer notification types and layouts available
- Less control over individual notification behavior
Code Comparison
react-hot-toast:
import toast from 'react-hot-toast';
const notify = () => toast('Hello World!');
react-notifications-component:
import { store } from 'react-notifications-component';
const notify = () => {
store.addNotification({
title: "Hello World!",
type: "success",
insert: "top",
container: "top-right",
animationIn: ["animate__animated", "animate__fadeIn"],
animationOut: ["animate__animated", "animate__fadeOut"],
dismiss: { duration: 2000 }
});
};
react-hot-toast offers a more concise API for basic notifications, while react-notifications-component provides more detailed configuration options for advanced use cases. The choice between the two depends on the level of customization and complexity required for your project's notification system.
A beautiful replacement for JavaScript's "alert"
Pros of SweetAlert
- Simpler API and easier to use for basic alert scenarios
- Wider browser compatibility, including older versions
- Standalone library with no dependencies, suitable for non-React projects
Cons of SweetAlert
- Less customizable compared to react-notifications-component
- Limited to modal-style alerts, not suitable for toast notifications
- Not specifically designed for React, may require additional setup
Code Comparison
SweetAlert:
swal("Hello world!");
react-notifications-component:
<ReactNotifications />
store.addNotification({
title: "Hello world!",
message: "This is a notification",
type: "success",
container: "top-right",
dismiss: {
duration: 2000
}
});
Summary
SweetAlert is a simpler, more lightweight solution for basic alert scenarios, while react-notifications-component offers more flexibility and customization options specifically for React applications. SweetAlert is easier to implement for quick alerts, but react-notifications-component provides a wider range of notification types and positioning options. The choice between the two depends on the specific needs of your project, such as the desired level of customization, the development framework in use, and the types of notifications required.
Convert  designs to code with AI
designs to code with AI

Introducing Visual Copilot: A new AI model to turn Figma designs to high quality code using your components.
Try Visual CopilotREADME
react-notifications-component
A delightful, easy to use and highly configurable component to help you notify your users out of the box. No messy setup, just beautiful notifications!
Demo
https://teodosii.github.io/react-notifications-component/
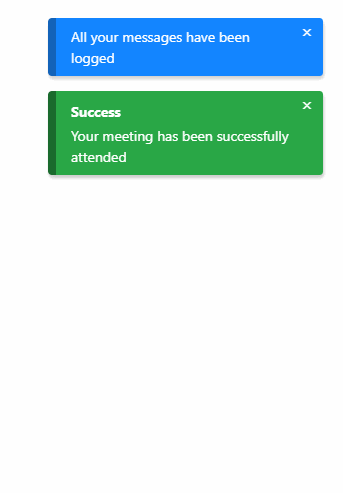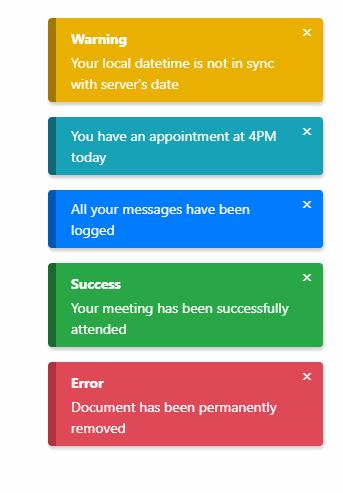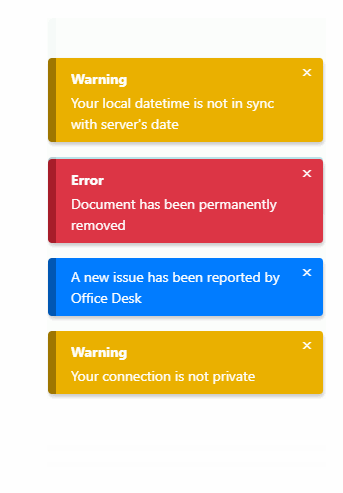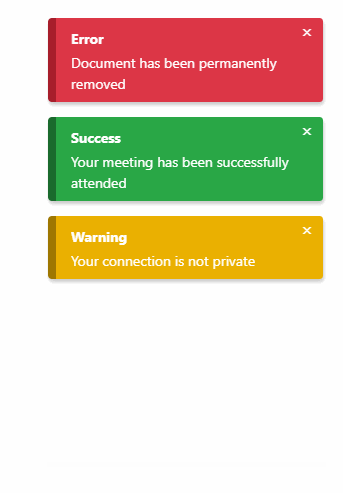
Features
- Touch support
- Responsive notifications
- Standard notification types
- Custom notification types
- Custom notification content
- Dismissable (touch, click, timeout)
- Customizable transitions
- Small library
Getting started
npm install react-notifications-component
Development
First build the library
npm run build:library:dev
then run the webpack server to see the app running
npm run start
Usage
Import react-notifications-component
import { ReactNotifications } from 'react-notifications-component'
Import the CSS theme
import 'react-notifications-component/dist/theme.css'
SASS
SASS files are located in react-notifications-component/dist/scss
Render react-notifications-component at the top of your application so that it does not conflict with other absolutely positioned DOM elements.
const App = () => {
return (
<div className="app-container">
<ReactNotifications />
<Application />
</div>
)
};
Import Store where needed - will be used to access addNotification and removeNotification API methods
import { Store } from 'react-notifications-component';
Then call addNotification and watch the magic happens
Store.addNotification({
title: "Wonderful!",
message: "teodosii@react-notifications-component",
type: "success",
insert: "top",
container: "top-right",
animationIn: ["animate__animated", "animate__fadeIn"],
animationOut: ["animate__animated", "animate__fadeOut"],
dismiss: {
duration: 5000,
onScreen: true
}
});
Voila!
Note: We rely on animate.css in this example as animate__fadeIn and animate__fadeOut are part of animate.css. We recommend using it as it's an excellent animation library, but you're not forced to. If you prefer you may also use your custom animations as long as they're valid CSS animations.
Note: animate.css latest version (v4) has breaking changes. It introduces animate__ prefix so that existing classes don't clash. If you still would like to use classes without prefix you can import animate.css/animate.compat.css
// preferred way to import (from `v4`). Uses `animate__` prefix.
import 'animate.css/animate.min.css';
// Alternate way to use classes without prefix like `animated fadeIn`
import 'animate.css/animate.compat.css'
In the examples, we will be using classes with animate__ prefix, which is the default behaviour of latest v4 version of animate.css.
For more info on how to use animate.css, please refer to animate.css docs
API
Store.addNotification(options)
Render a new notification. Method returns a unique id for the rendered notification. Supplied options are internally validated and an exception will be thrown if validation fails.
Store.removeNotification(id)
Manually remove a notification by id.
Examples
In the following examples for brevity some options will not be mentioned. Strictly focusing on the needed options to present each example. For reference, we will be using Object spread operator on a notification object to have non relevant fields included as well.
notification = {
title: "Wonderful!",
message: "Configurable",
type: "success",
insert: "top",
container: "top-right",
animationIn: ["animate__animated animate__fadeIn"], // `animate.css v4` classes
animationOut: ["animate__animated animate__fadeOut"] // `animate.css v4` classes
};
Notification container
You have in total 6 containers for desktop and 2 for mobile, if component is set to be responsive. List of containers:
top-lefttop-righttop-centercenterbottom-leftbottom-rightbottom-center
Store.addNotification({
...notification,
container: 'top-right'
})
Will position the notification in top right of the screen.
Notification type
List of types:
successdangerinfodefaultwarning
Store.addNotification({
...notification,
type: 'danger'
})
Will trigger a danger notification.
Animating
Store.addNotification({
...notification,
animationIn: ['animate__animated animate__fadeIn'], // `animate.css v4` classes
animationOut: ['animate__animated animate__fadeOut'] // `animate.css v4` classes
})
animationIn and animationOut rely on CSS classes that toggle animations. On github pages we rely on animate.css, we suggest you to import that package and use their animations as they have plenty.
Note: Failing to have animations set properly will lead to bugs in some causes, as react-notifications-component relies on onAnimationEnd event to know when an animation has finished.
Dismiss notification automatically after timeout expires
Store.addNotification({
...notification,
dismiss: {
duration: 2000
}
})
Dismiss notification automatically with the time left shown on UI
Store.addNotification({
...notification,
dismiss: {
duration: 2000,
onScreen: true
}
})
Subscribe to notification's removal
Easily subscribe to onRemoval by supplying callback as option to the notification object. Callback will get called after the removal animation finishes.
Store.addNotification({
...notification,
onRemoval: (id, removedBy) => {
...
}
})
Pause notification's timeout by hovering
Store.addNotification({
...notification,
dismiss: {
duration: 2000,
pauseOnHover: true
}
})
Change transition
Store.addNotification({
...notification,
slidingExit: {
duration: 800,
timingFunction: 'ease-out',
delay: 0
}
})
slidingEnter, touchRevert and touchSlidingExit can all be configured in the same way, with the mention that touchSlidingExit has 2 transitions nested.
Store.addNotification({
...notification,
touchSlidingExit: {
swipe: {
duration: 400,
timingFunction: 'ease-out',
delay: 0,
},
fade: {
duration: 400,
timingFunction: 'ease-out',
delay: 0
}
}
})
Props
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
isMobile |
Boolean |
Set whether you want component to be responsive or not. To be used together with breakpoint |
breakpoint |
Number |
Breakpoint for responsiveness - defaults to 768px |
types |
Array |
Custom types |
className |
string |
Classes assigned to the container |
id |
string |
Id of the container |
Options
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
id |
String |
Id of the notification. Supply option only if you prefer to have custom id, otherwise you should let the component handle generation for you. |
onRemoval |
Function |
Gets called on notification removal with id and removedBy arguments |
title |
String, React Node or Functional Component |
Title of the notification. Option is ignored if content is set, otherwise it is required. |
message |
String, React Node or Functional Component |
Message of the notification. Option is ignored if content is set, otherwise it is required. |
content |
Object |
Custom notification content, must be either Class Component, Functional Component or React element. If being supplied as functional or class component, id and notificationConfig will be supplied as prop. notificationConfig will return the parsed notification object as defined in the library. |
type |
String |
Type of the notification. Option is ignored if content is set, otherwise it is required. |
container |
String |
Container in which the notification will be displayed. Option is required. |
insert |
String |
Specify where to append notification into the container - top or bottom. Option defaults to top. |
dismiss |
Dismiss |
Specify how a notification should be dismissed. |
animationIn |
Array |
Array of CSS classes for animating the notification's entrance. |
animationOut |
Array |
Array of CSS classes for animating the notification's exit. |
slidingEnter |
Transition |
Transition to be used when sliding to show a notification. |
slidingExit |
Transition |
Transition to be used when sliding to remove a notification. |
touchRevert |
Transition |
Transition to be used when sliding back after an incomplete swipe. |
touchSlidingExit |
Transition |
Transition to be used when sliding on swipe. |
width |
Number |
Overwrite notification's width defined by CSS |
Transition
Transition is used each time you define a transition.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
duration |
Number |
Transition duration in ms. Its default value ranges from 300 to 600, depending on transition |
timingFunction |
String |
CSS timing function for the transition, defaults to linear |
delay |
Number |
Delay of the transition in ms, defaults to 0 |
Dismiss
Dismiss is used to describe how a notification should be dismissed.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
duration |
Number |
Time in milliseconds after notification gets dismissed. 0 will act as infinite duration. Defaults to 0 |
onScreen |
Boolean |
Show time left directly on the notification. Defaults to false |
pauseOnHover |
Boolean |
Hovering over notification will pause the dismiss timer. Defaults to false |
waitForAnimation |
Boolean |
When removing a notification by default we trigger the exit animation and the transition to height 0 at the same time. Setting this to true will wait for the exit animation to finish and then start the transition to height 0. Defaults to false |
click |
Boolean |
Enable dismissal by click, defaults to true |
touch |
Boolean |
Enable dismiss by touch move, defaults to true |
showIcon |
Boolean |
Show or hide the close icon, defaults to false. If set to true, it will respond to click interaction and will remove notification |
Migration from v1
- Ref usage has been deprecated. Import
Storefrom library and use it for adding and removing notifications touchSlidingBackhas been renamed totouchRevert- Default values for transitions have been slightly changed
dismissIconhas been removed. UseshowIconinstead. If you relly on customized close icon, then stick to custom content.dismisssupports now more optionscubicBezierhas been renamed totimingFunction- Validators are now no longer included in the prod build, they are only included in the dev build. If you inspect the npm package you will see that the component has 2 builds -
devandprod- and relies on ENV variable when importing.
License
MIT
Top Related Projects
React notification made easy 🚀 !
Highly customizable notification snackbars (toasts) that can be stacked on top of each other
Smoking Hot React Notifications 🔥
A beautiful replacement for JavaScript's "alert"
Convert  designs to code with AI
designs to code with AI

Introducing Visual Copilot: A new AI model to turn Figma designs to high quality code using your components.
Try Visual Copilot