 homebridge-raspbian-image
homebridge-raspbian-image
Official Homebridge Raspberry Pi Image based on Raspberry Pi OS Lite.
Top Related Projects
Homebridge Docker. HomeKit support for the impatient using Docker on x86_64, Raspberry Pi (ARM64). Includes ffmpeg + libfdk-aac.
HomeKit support for the impatient.
The Homebridge UI. Monitor, configure and backup Homebridge from a browser.
:house_with_garden: Open source home automation that puts local control and privacy first.
Quick Overview
Homebridge-raspbian-image is a project that provides a pre-configured Raspbian image with Homebridge pre-installed. This image allows users to quickly set up Homebridge on a Raspberry Pi, making it easier to integrate non-HomeKit devices into Apple's HomeKit ecosystem.
Pros
- Easy and quick setup for Homebridge on Raspberry Pi
- Pre-configured with essential plugins and settings
- Regular updates to keep the image current with the latest Homebridge version
- Includes a web-based interface for easy management
Cons
- Limited customization options compared to a manual Homebridge installation
- May include unnecessary plugins or configurations for some users
- Potential security concerns with pre-built images
- Requires re-flashing the SD card for major updates
Getting Started
- Download the latest image from the project's GitHub releases page.
- Flash the image to an SD card using a tool like Etcher or Raspberry Pi Imager.
- Insert the SD card into your Raspberry Pi and power it on.
- Connect to your Raspberry Pi's IP address in a web browser to access the Homebridge UI.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the setup and add your devices.
Note: This project is not a code library, so code examples are not applicable.
Competitor Comparisons
Homebridge Docker. HomeKit support for the impatient using Docker on x86_64, Raspberry Pi (ARM64). Includes ffmpeg + libfdk-aac.
Pros of docker-homebridge
- Easier to deploy across different platforms and architectures
- Provides better isolation and security for the Homebridge environment
- Simplifies updates and version management
Cons of docker-homebridge
- Requires more technical knowledge to set up and manage Docker
- May have slightly higher resource overhead due to containerization
- Potentially more complex networking configuration
Code Comparison
homebridge-raspbian-image:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y homebridge
sudo systemctl enable homebridge
sudo systemctl start homebridge
docker-homebridge:
docker pull oznu/homebridge:latest
docker run -d --net=host -v /path/to/config:/homebridge oznu/homebridge:latest
The homebridge-raspbian-image uses a traditional installation method with system packages and services, while docker-homebridge utilizes Docker containers for deployment. The Docker approach offers more flexibility and portability but may require additional setup steps.
Both repositories aim to simplify the installation and management of Homebridge, but they cater to different use cases and user preferences. The Raspbian image is more suitable for users who prefer a straightforward, pre-configured solution specifically for Raspberry Pi devices. On the other hand, the Docker version provides greater versatility and is ideal for users comfortable with containerization technology across various platforms.
HomeKit support for the impatient.
Pros of homebridge
- More flexible and customizable, as it can be installed on various platforms
- Allows for easier integration with existing systems and development workflows
- Provides a wider range of plugin options and compatibility
Cons of homebridge
- Requires more technical knowledge to set up and configure
- May need additional hardware or software dependencies depending on the installation environment
- Potentially less stable or consistent across different setups
Code comparison
homebridge:
const hap = require('hap-nodejs');
const Accessory = hap.Accessory;
const Service = hap.Service;
const Characteristic = hap.Characteristic;
// Create and publish accessories
homebridge-raspbian-image:
# No direct code comparison available
# The image comes pre-configured with Homebridge
# and necessary dependencies
Summary
Homebridge is a more versatile solution that can be installed on various platforms, offering greater customization and flexibility. It's ideal for users who want to integrate with existing systems or have specific requirements. However, it requires more technical expertise to set up and maintain.
Homebridge-raspbian-image, on the other hand, provides a pre-configured Raspberry Pi image with Homebridge already installed. This makes it easier for beginners to get started but may limit customization options and is specific to Raspberry Pi hardware.
The Homebridge UI. Monitor, configure and backup Homebridge from a browser.
Pros of homebridge-config-ui-x
- Provides a user-friendly web interface for managing Homebridge configurations
- Offers plugin management, including installation, updating, and removal
- Supports real-time log viewing and system information monitoring
Cons of homebridge-config-ui-x
- Requires separate installation and setup of Homebridge
- May have higher resource usage due to the web interface
- Potential security concerns if not properly configured
Code Comparison
homebridge-config-ui-x:
const hb = require('homebridge');
const ConfigUi = require('homebridge-config-ui-x');
hb.registerPlatform("homebridge-config-ui-x", "config", ConfigUi.Platform);
homebridge-raspbian-image:
#!/bin/bash
curl -sSfL https://repo.homebridge.io/install.sh | sudo bash -
The homebridge-config-ui-x code snippet shows how to register the platform with Homebridge, while the homebridge-raspbian-image code is a shell script for installing Homebridge on a Raspberry Pi.
homebridge-raspbian-image provides a pre-configured Raspberry Pi image with Homebridge and homebridge-config-ui-x already installed, making it easier for beginners to get started. However, it's limited to Raspberry Pi devices and may not offer as much flexibility for advanced users compared to homebridge-config-ui-x, which can be installed on various platforms and customized more extensively.
:house_with_garden: Open source home automation that puts local control and privacy first.
Pros of Home Assistant Core
- More comprehensive smart home platform with broader device support
- Highly customizable with a large ecosystem of integrations and add-ons
- Active community development and frequent updates
Cons of Home Assistant Core
- Steeper learning curve, especially for non-technical users
- Requires more system resources compared to Homebridge
- Setup and configuration can be more complex
Code Comparison
Homebridge (JavaScript):
this.api.registerPlatform("homebridge-example", "ExamplePlatform", ExamplePlatform);
class ExamplePlatform {
accessories(callback) {
// Add accessories here
}
}
Home Assistant Core (Python):
from homeassistant.components.light import LightEntity
class ExampleLight(LightEntity):
@property
def is_on(self):
return self._state
def turn_on(self, **kwargs):
self._state = True
Summary
Homebridge focuses on bridging non-HomeKit devices to Apple's HomeKit ecosystem, while Home Assistant Core is a more comprehensive smart home platform. Homebridge is generally easier to set up and use, especially for those already invested in HomeKit. Home Assistant Core offers more flexibility and customization options but may require more technical knowledge to configure and maintain.
Convert  designs to code with AI
designs to code with AI

Introducing Visual Copilot: A new AI model to turn Figma designs to high quality code using your components.
Try Visual CopilotREADME
Homebridge Raspberry Pi Image
This project provides a free Raspbian based Raspberry Pi image with Homebridge and Homebridge Config UI X pre-installed.
- Runs on RPI 2 or higher models supporting ARMv7 cpu's or greater ( Last version supporting RPI 1 and RPi Zero W was v1.2.4)
- Built on Raspbian Lite (no desktop)
- Simple WiFi Setup
- Includes
ffmpegpre-compiled with audio support (libfdk-aac) - Includes a user friendly, easy to use web based GUI to configure Homebridge and monitor your Raspberry Pi
- Visual configuration for over 400 plugins (no manual config.json editing required)
This image also provides a command called hb-config which helps you keep Node.js up-to-date, perform maintenance on your Homebridge server, and install additional optional software such as Pi Hole and deCONZ.
The Homebridge service is installed using the method described in the official Raspberry Pi Installation Guide on the Homebridge project wiki.
Download and Flash to SD Card
The Homebridge Raspberry Pi Image is completely free (no sign up required).
The easiest way to flash the Homebridge Raspberry Pi Image to your SD card is to use the Raspberry Pi Imager.

- Download and install the latest version of Raspberry Pi Imager.
- Open the Raspberry Pi Imager application.
- Click Choose Device
- Scroll down and select the No filtering option.
- Click Choose OS.
- Scroll down and select the Other specific purpose OS category.
- Select the Home assistants and home automation category.
- Select Homebridge, then choose your Homebridge image.
- 32bit - For all RPI Models (Not recommended, support will be ending Spring 2027 )
- 64bit - For RPI 3B, 3B+, 3A+, 4B, 400, 5, CM3, CM3+, CM4, CM4S, Zero 2 W (Recommended)
- Click Choose Storage and select your SD card.
- Click Next
- For Use OS Customisation, select No
- Click Write
Raspberry Pi Imager will now download and flash the latest version of the Homebridge Raspberry Pi Image to your SD card, this may take several minutes depending on the speed of your internet connection and SD card.
Advanced users:
If you wish to use another tool such as Etcher or dd to flash the Homebridge Raspberry Pi Image, you can manually download the image from our releases page:
Download Latest Version
First Boot / Network Setup
Now that you have flashed your SD card, you can insert it into your Raspberry Pi.
Before powering on your Raspberry Pi decide if you want to use Ethernet or WiFi to connect to your network.
Ethernet
:warning: An Ethernet connection is recommended as this provides the most simple and stable Homebridge setup.
If you have decided to connect your Raspberry Pi using ethernet, do so before you power on your device for the first time.
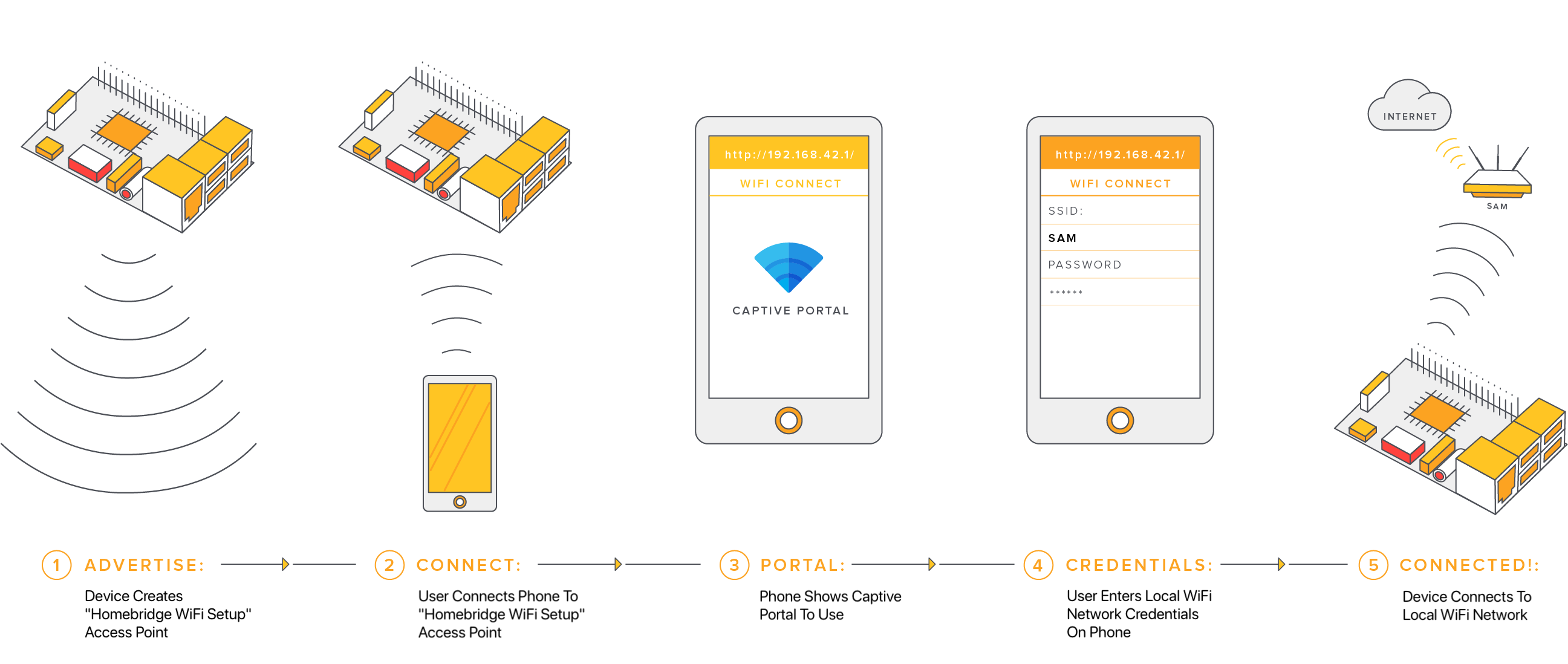
WiFi Setup
Follow these steps to connect your device to WiFi:
- Power on your device without an Ethernet cable attached.
- Wait 1-2 minutes
- Use your mobile phone to scan for new WiFi networks
- Connect to the hotspot named Homebridge WiFi Setup
- Wait a few moments until the captive portal opens, this portal will allow you to connect the Raspberry Pi to your local WiFi network.
If you enter your WiFi credentials incorrectly the Homebridge WiFi Setup hotspot will reappear allowing you to try again.
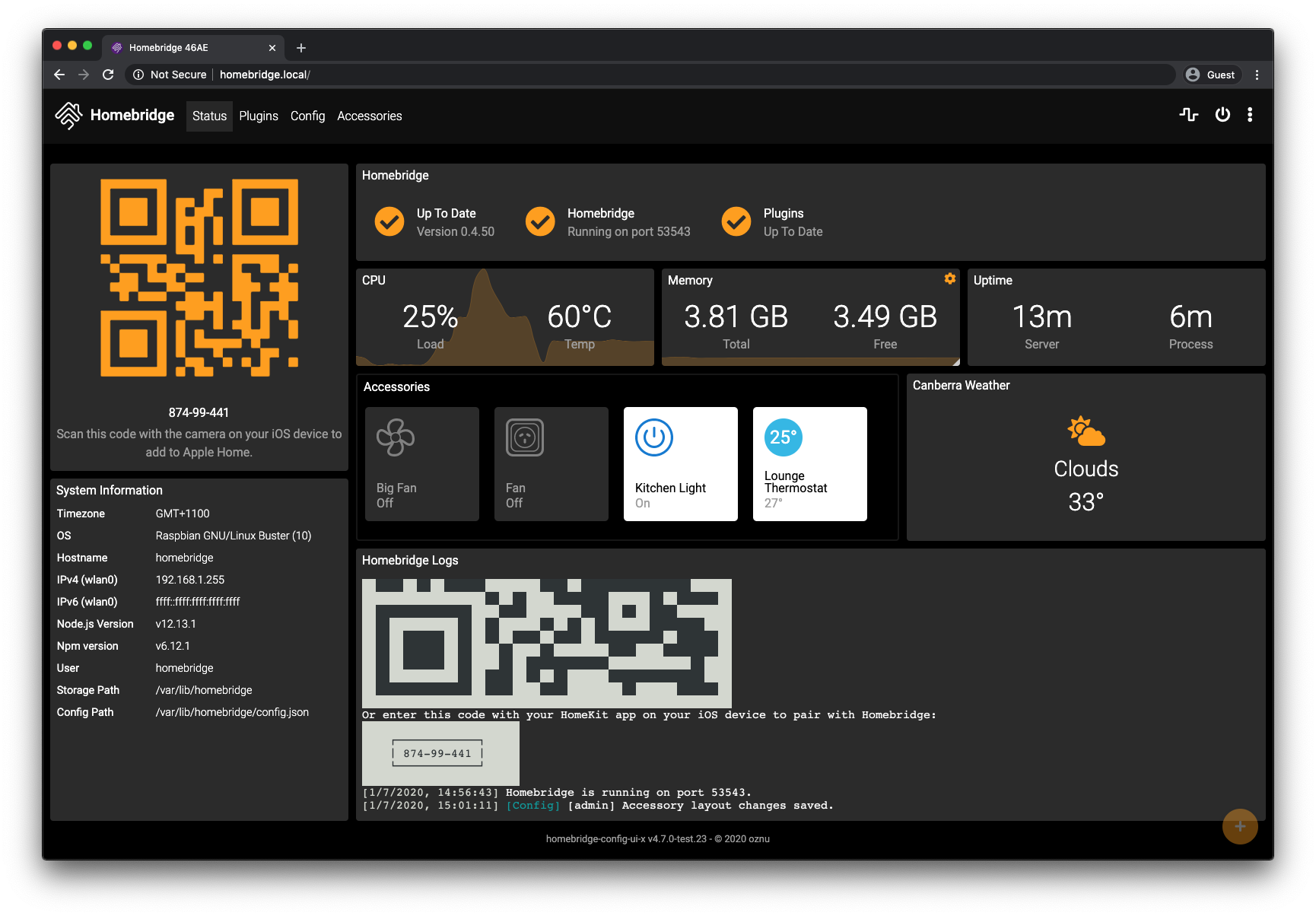
Managing Homebridge
The Homebridge UI web interface will allow you to install, remove and update plugins, and modify the Homebridge config.json and manage other aspects of your Homebridge service.
If you're using macOS or a mobile device, you should be able to access the UI via http://homebridge.local.
If you're using Windows, or http://homebridge.local does not work for you, you will need to find the IP address of your Raspberry Pi another way:
- Login to your router and find the "connected devices" or "dhcp clients" page to find the IP address that was assigned to the Raspberry Pi.
- Use an iPhone to access
http://homebridge.local, once you login using the default username and password (admin/admin) you can find the IP address under System Information. - Download the Fing app for iOS or Android to scan your network to find the IP address of your Raspberry Pi.
- As a last resort, if you plug a monitor into your Raspberry Pi, the IP address will be displayed on the attached screen once it has finished booting.
Once you've found your IP address, login to the web interface by going to http://<ip address of your server>.
Security and Privacy
- Privacy: The Homebridge Raspbian Image, as well as the Homebridge and Homebridge Config UI X software components, do not contain any analytics, call home, or similar features that would allow the project maintainers to track you or the usage of this image.
- Security: The Homebridge Raspbian Image is kept up-to-date with the latest official Raspbian builds. To find out more, or to report a security issue or vulnerability, please see the project's SECURITY policy.
- Transparency: The Homebridge Raspbian Image project is open source and each image is built using the public GitHub Action runners. The build logs for each release are publicly available on the project's GitHub Actions page and every release contains a SHA-256 checksum of the image you can use to verify the integrity of your download.
Community
The official Homebridge Discord server and Reddit community are where users can discuss Homebridge and ask for help.
Help
The Homebridge Raspberry Pi Image wiki contains more information and instructions on how to further customise your install:
https://github.com/homebridge/homebridge-raspbian-image/wiki
Top Related Projects
Homebridge Docker. HomeKit support for the impatient using Docker on x86_64, Raspberry Pi (ARM64). Includes ffmpeg + libfdk-aac.
HomeKit support for the impatient.
The Homebridge UI. Monitor, configure and backup Homebridge from a browser.
:house_with_garden: Open source home automation that puts local control and privacy first.
Convert  designs to code with AI
designs to code with AI

Introducing Visual Copilot: A new AI model to turn Figma designs to high quality code using your components.
Try Visual Copilot

