react-admin
react-admin
A frontend Framework for single-page applications on top of REST/GraphQL APIs, using TypeScript, React and Material Design
Top Related Projects
Material UI: Comprehensive React component library that implements Google's Material Design. Free forever.
An enterprise-class UI design language and React UI library
A React-based library for creating sleek presentations using JSX syntax that gives you the ability to live demo your code.
🚀 Strapi is the leading open-source headless CMS. It’s 100% JavaScript/TypeScript, fully customizable, and developer-first.
The flexible backend for all your projects 🐰 Turn your DB into a headless CMS, admin panels, or apps with a custom UI, instant APIs, auth & more.
The superpowered headless CMS for Node.js — built with GraphQL and React
Quick Overview
React-admin is a frontend framework for building data-driven applications running in the browser on top of REST/GraphQL APIs, using React and Material Design. It provides a set of reusable components and hooks that simplify the creation of admin interfaces, dashboards, and B2B applications.
Pros
- Rapid development of admin interfaces with pre-built components
- Highly customizable and extensible architecture
- Supports various data providers (REST, GraphQL, etc.)
- Strong TypeScript support and comprehensive documentation
Cons
- Learning curve can be steep for developers new to React or complex state management
- Performance can be an issue with large datasets if not optimized properly
- Some users report difficulties with complex custom layouts
- Limited built-in themes and styling options
Code Examples
- Creating a basic list view:
import { List, Datagrid, TextField, EmailField } from 'react-admin';
export const UserList = () => (
<List>
<Datagrid>
<TextField source="id" />
<TextField source="name" />
<EmailField source="email" />
</Datagrid>
</List>
);
- Implementing a custom action button:
import { Button } from '@mui/material';
import { useRecordContext, useNotify, useRedirect } from 'react-admin';
const ApproveButton = () => {
const record = useRecordContext();
const notify = useNotify();
const redirect = useRedirect();
const handleClick = () => {
// Custom logic here
notify('User approved');
redirect('/users');
};
return <Button onClick={handleClick}>Approve</Button>;
};
- Creating a custom input component:
import { useInput, TextInput } from 'react-admin';
const MyCustomInput = (props) => {
const { field, fieldState } = useInput(props);
return (
<TextInput
{...field}
label="My Custom Input"
error={fieldState.error?.message}
/>
);
};
Getting Started
To start a new react-admin project:
npx create-react-admin my-admin
cd my-admin
npm start
Basic setup in your App.js:
import { Admin, Resource } from 'react-admin';
import jsonServerProvider from 'ra-data-json-server';
import { UserList } from './users';
const dataProvider = jsonServerProvider('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com');
const App = () => (
<Admin dataProvider={dataProvider}>
<Resource name="users" list={UserList} />
</Admin>
);
export default App;
This sets up a basic admin interface with a list of users fetched from a JSON placeholder API.
Competitor Comparisons
Material UI: Comprehensive React component library that implements Google's Material Design. Free forever.
Pros of Material-UI
- More comprehensive UI component library with a wider range of components
- Highly customizable theming system for consistent design across applications
- Larger community and ecosystem, resulting in more third-party extensions and resources
Cons of Material-UI
- Steeper learning curve due to its extensive API and customization options
- Heavier bundle size, which may impact initial load times for smaller applications
- Less opinionated, requiring more setup and configuration for complex applications
Code Comparison
Material-UI example:
import { Button, TextField } from '@mui/material';
function LoginForm() {
return (
<form>
<TextField label="Username" variant="outlined" />
<Button variant="contained" color="primary">Login</Button>
</form>
);
}
React-Admin example:
import { TextInput, Button } from 'react-admin';
const LoginForm = () => (
<SimpleForm>
<TextInput source="username" />
<Button label="Login" />
</SimpleForm>
);
Summary
Material-UI offers a more extensive component library and customization options, making it suitable for a wide range of projects. React-Admin, on the other hand, provides a more focused solution for building admin interfaces with less setup required. The choice between the two depends on the specific needs of your project and the level of customization desired.
An enterprise-class UI design language and React UI library
Pros of Ant Design
- More comprehensive UI component library with a wider range of components
- Stronger focus on design aesthetics and customization options
- Larger community and ecosystem, leading to more third-party extensions and resources
Cons of Ant Design
- Steeper learning curve due to its extensive API and configuration options
- Less specialized for admin interfaces, requiring more setup for admin-specific features
- Potentially larger bundle size due to the comprehensive nature of the library
Code Comparison
Ant Design (Button component):
import { Button } from 'antd';
const MyComponent = () => (
<Button type="primary">Click me</Button>
);
React Admin (Button component):
import { Button } from 'react-admin';
const MyComponent = () => (
<Button label="Click me" />
);
While both libraries provide UI components, React Admin is specifically tailored for building admin interfaces, offering built-in features like data providers and authentication. Ant Design, on the other hand, is a more general-purpose UI library that can be used for various types of applications.
React Admin excels in rapid development of admin panels with its opinionated structure and pre-built components for common admin tasks. Ant Design offers more flexibility and a wider range of components but requires more setup for admin-specific functionality.
A React-based library for creating sleek presentations using JSX syntax that gives you the ability to live demo your code.
Pros of Spectacle
- Focused on creating presentations, offering a more specialized and streamlined experience
- Lightweight and easy to learn, with a simpler API and fewer dependencies
- Provides built-in themes and customizable styling options for quick and attractive presentations
Cons of Spectacle
- Limited to presentation creation, lacking the comprehensive admin panel functionality of React Admin
- Fewer built-in components and data management features compared to React Admin's extensive toolkit
- May require more custom development for complex data visualization or interactive elements
Code Comparison
React Admin example:
import { Admin, Resource, ListGuesser } from 'react-admin';
import { dataProvider } from './dataProvider';
const App = () => (
<Admin dataProvider={dataProvider}>
<Resource name="users" list={ListGuesser} />
</Admin>
);
Spectacle example:
import { Deck, Slide, Text } from 'spectacle';
const Presentation = () => (
<Deck>
<Slide>
<Text>Welcome to my presentation!</Text>
</Slide>
</Deck>
);
🚀 Strapi is the leading open-source headless CMS. It’s 100% JavaScript/TypeScript, fully customizable, and developer-first.
Pros of Strapi
- Provides a full-featured headless CMS with a built-in admin panel
- Offers a more comprehensive solution for content management and API creation
- Supports multiple databases out of the box (SQLite, PostgreSQL, MySQL, MongoDB)
Cons of Strapi
- Steeper learning curve due to its broader scope and functionality
- Less flexibility in customizing the admin interface compared to React Admin
- Requires more server resources to run as a standalone application
Code Comparison
Strapi (Content Type definition):
module.exports = {
attributes: {
title: {
type: 'string',
required: true,
},
content: {
type: 'richtext',
},
},
};
React Admin (Resource definition):
import { List, Datagrid, TextField, Edit, SimpleForm, TextInput } from 'react-admin';
export const PostList = (props) => (
<List {...props}>
<Datagrid>
<TextField source="title" />
<TextField source="content" />
</Datagrid>
</List>
);
While Strapi focuses on defining content types and generating APIs, React Admin is centered around creating admin interfaces for existing APIs. Strapi provides a more comprehensive backend solution, while React Admin offers greater flexibility in building custom admin UIs.
The flexible backend for all your projects 🐰 Turn your DB into a headless CMS, admin panels, or apps with a custom UI, instant APIs, auth & more.
Pros of Directus
- Offers a complete headless CMS solution with a built-in database and API
- Provides a user-friendly interface for non-technical users to manage content
- Supports real-time collaboration and data synchronization
Cons of Directus
- Less flexible for custom UI development compared to React Admin
- May have a steeper learning curve for developers familiar with React ecosystems
- Limited to specific database types (primarily SQL databases)
Code Comparison
React Admin:
import { Admin, Resource } from 'react-admin';
import { PostList, PostEdit, PostCreate } from './posts';
const App = () => (
<Admin dataProvider={...}>
<Resource name="posts" list={PostList} edit={PostEdit} create={PostCreate} />
</Admin>
);
Directus:
import { Directus } from '@directus/sdk';
const directus = new Directus('https://api.example.com');
async function getPosts() {
return await directus.items('posts').readByQuery({ limit: 5 });
}
Summary
React Admin is a flexible framework for building admin interfaces in React, while Directus is a complete headless CMS solution. React Admin offers more customization for developers, whereas Directus provides a more user-friendly interface for content management. The choice between them depends on project requirements and team expertise.
The superpowered headless CMS for Node.js — built with GraphQL and React
Pros of Keystone
- More flexible and customizable backend with GraphQL API
- Supports multiple database types (MongoDB, PostgreSQL)
- Built-in user authentication and access control
Cons of Keystone
- Steeper learning curve due to its more complex architecture
- Less out-of-the-box UI components compared to React Admin
- Requires more setup and configuration for basic functionality
Code Comparison
Keystone schema definition:
const { Text, Relationship } = require('@keystonejs/fields');
const ListSchema = {
fields: {
name: { type: Text },
author: { type: Relationship, ref: 'Author' },
},
};
React Admin resource definition:
import { List, Datagrid, TextField, ReferenceField } from 'react-admin';
export const PostList = props => (
<List {...props}>
<Datagrid>
<TextField source="name" />
<ReferenceField source="authorId" reference="authors">
<TextField source="name" />
</ReferenceField>
</Datagrid>
</List>
);
Both Keystone and React Admin offer powerful solutions for building admin interfaces, but they cater to different needs. Keystone provides a more comprehensive backend solution with greater flexibility, while React Admin focuses on rapid development of admin UIs with a simpler setup process. The choice between the two depends on project requirements, team expertise, and desired level of customization.
Convert  designs to code with AI
designs to code with AI

Introducing Visual Copilot: A new AI model to turn Figma designs to high quality code using your components.
Try Visual CopilotREADME
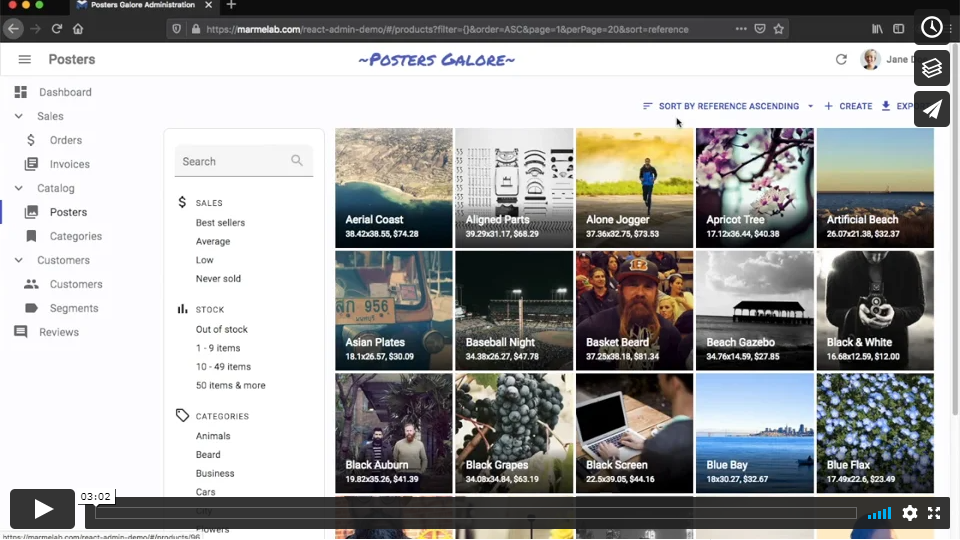
react-admin 

A frontend Framework for building single-page applications running in the browser on top of REST/GraphQL APIs, using TypeScript, React and Material Design. Open sourced and maintained by marmelab.
Home page - Documentation - Examples - Blog - Releases - Support
Features
-
ð Backend Agnostic: Connects to any API (REST or GraphQL, see the list of more than 45 adapters)
-
𧩠All The Building Blocks You Need: Provides hooks and components for authentication, routing, forms & validation, datagrid, search & filter, relationships, validation, roles & permissions, rich text editor, i18n, notifications, menus, theming, caching, etc.
-
𪡠High Quality: Accessibility, responsive, secure, fast, testable
-
ð» Great Developer Experience: Complete documentation, IDE autocompletion, type safety, storybook, demo apps with source code, modular architecture, declarative API
-
ð Great User Experience: Optimistic rendering, filter-as-you-type, undo, preferences, saved queries
-
ð Complete Customization: Replace any component with your own
-
âï¸ Opt-In Types: Develop either in TypeScript or JavaScript
-
ð¨âð©âð§âð¦ Powered by Material UI, react-hook-form, react-router, react-query, TypeScript and a few more
Installation
React-admin is available from npm. You can install it (and its required dependencies) using:
npm install react-admin
#or
yarn add react-admin
Documentation
- Read the Tutorial for a 30 minutes introduction
- Watch the YouTube video tutorials
- Head to the Documentation for a complete API reference
- Checkout the source code of the examples (e-commerce, CRM, blog, media player)
At a Glance
// in app.js
import * as React from "react";
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import { Admin, Resource } from 'react-admin';
import restProvider from 'ra-data-simple-rest';
import { PostList, PostEdit, PostCreate, PostIcon } from './posts';
ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root')!).render(
<Admin dataProvider={restProvider('http://localhost:3000')}>
<Resource name="posts" list={PostList} edit={PostEdit} create={PostCreate} icon={PostIcon} />
</Admin>
);
The <Resource> component defines CRUD pages (list, edit, and create) for an API endpoint (/posts). The page components use react-admin components to fetch and render data:
// in posts.js
import * as React from "react";
import { List, DataTable, Edit, Create, SimpleForm, DateField, EditButton, TextInput, DateInput, useRecordContext } from 'react-admin';
import BookIcon from '@mui/icons-material/Book';
export const PostIcon = BookIcon;
export const PostList = () => (
<List>
<DataTable>
<DataTable.Col source="id" />
<DataTable.Col source="title" />
<DataTable.Col source="published_at" field={DateField} />
<DataTable.Col source="average_note" />
<DataTable.Col source="views" />
<DataTable.Col>
<EditButton />
</DataTable.Col>
</DataTable>
</List>
);
const PostTitle = () => {
const record = useRecordContext();
return <span>Post {record ? `"${record.title}"` : ''}</span>;
};
export const PostEdit = () => (
<Edit title={<PostTitle />}>
<SimpleForm>
<TextInput disabled source="id" />
<TextInput source="title" />
<TextInput source="teaser" options={{ multiline: true }} />
<TextInput multiline source="body" />
<DateInput label="Publication date" source="published_at" />
<TextInput source="average_note" />
<TextInput disabled label="Nb views" source="views" />
</SimpleForm>
</Edit>
);
export const PostCreate = () => (
<Create title="Create a Post">
<SimpleForm>
<TextInput source="title" />
<TextInput source="teaser" options={{ multiline: true }} />
<TextInput multiline source="body" />
<TextInput label="Publication date" source="published_at" />
<TextInput source="average_note" />
</SimpleForm>
</Create>
);
Does It Work With My API?
Yes.
React-admin uses an adapter approach, with a concept called Data Providers. Existing providers can be used as a blueprint to design your API, or you can write your own Data Provider to query an existing API. Writing a custom Data Provider is a matter of hours.
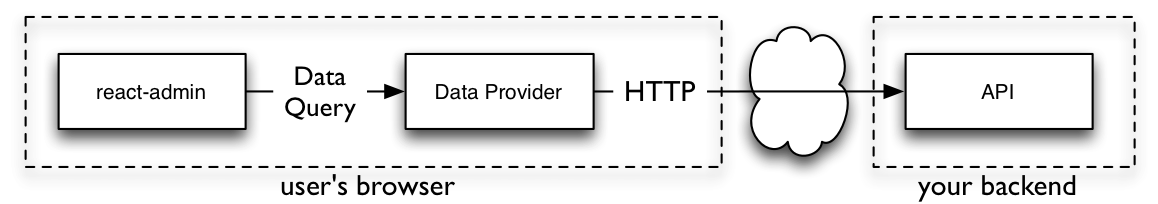
See the Data Providers documentation for details.
Batteries Included But Removable
React-admin is designed as a library of loosely coupled React components and hooks exposing reusable controller logic. It is very easy to replace any part of react-admin with your own, e.g. using a custom datagrid, GraphQL instead of REST, or Bootstrap instead of Material Design.
Examples
There are several examples inside the examples folder:
simple(StackBlitz): a simple blog with posts, comments and users that we use for our e2e tests.e-commerce: (demo, source) A fictional poster shop admin, serving as the official react-admin demo.CRM: (demo, source) A customer relationship management applicationhelpdesk: (demo, source) A ticketing application with realtime locks and notificationstutorial(Stackblitz): the application built while following the tutorial.
You can run those example applications by calling:
# At the react-admin project root
make install
# or
yarn install
# Run the simple application
make run-simple
# Run the tutorial application
make build
make run-tutorial
# Run the demo application
make build
make run-demo
And then browse to the URL displayed in your console.
Support
- Get commercial support from Marmelab via React-Admin Enterprise Edition
- Get community support via Discord and StackOverflow.
Versions In This Repository
-
master - commits that will be included in the next patch release
-
next - commits that will be included in the next major or minor release
Bugfix PRs that don't break BC should be made against master. All other PRs (new features, BC breaking bugfixes) should be made against next.
Contributing
If you want to give a hand: Thank you! There are many things you can do to help making react-admin better.
The easiest task is bug triaging. Check that new issues on GitHub follow the issue template and give a way to reproduce the issue. If not, comment on the issue to ask precisions. Then, try and reproduce the issue following the description. If you managed to reproduce the issue, add a comment to say it. Otherwise, add a comment to say that something is missing.
The second way to contribute is to answer support questions on StackOverflow. There are many beginner questions there, so even if you're not super experienced with react-admin, there is someone you can help there.
Pull requests for bug fixes are welcome on the GitHub repository. There is always a bunch of issues labeled "Good First Issue" in the bug trackerâstart with these.
If you want to add a feature, you can open a Pull request on the next branch. We don't accept all featuresâwe try to keep the react-admin code small and manageable. Try and see if your feature can't be built as an additional npm package. If you're in doubt, open a "Feature Request" issue to see if the core team would accept your feature before developing it.
For all Pull requests, you must follow the coding style of the existing files (based on prettier), and include unit tests and documentation. Be prepared for a thorough code review, and be patient for the mergeâthis is an open-source initiative.
Tip: Most of the commands used by the react-admin developers are automated in the makefile. Feel free to type make without argument to see a list of the available commands.
Setup
Clone this repository and run make install to grab the dependencies, then make build to compile the sources from TypeScript to JS.
Testing Your Changes In The Example Apps
When developing, most of the time we use the simple example to do visual check. It's the same application that we use in Stackblitz to reproduce errors (see https://stackblitz.com/github/marmelab/react-admin/tree/master/examples/simple). The source is located under examples/simple/. Call make run to launch that example on port 8080 (http://localhost:8080). This command includes a watch on the react-admin source, so any of the changes you make to the react-admin packages triggers a live update of the simple example in your browser.
However, the simple example is sometimes too limited. You can use the demo example (the source for https://marmelab.com/react-admin-demo/), which is more complete. The source is located under examples/demo/. Call make run-demo to launch the demo example with a REST dataProvider, or make run-graphql-demo to run it with a GraphQL dataProvider. Unfortunately, due to the fact that we use Create React App for this demo, these commands don't watch the changes made in the packages. You'll have to rebuild the react-admin packages after a change (using make build, or the more targeted make build-ra-core, make build-ra-ui-materialui, etc.) to see the effect in the demo app.
Both of these examples work without serverâthe API is simulated on the client-side.
Testing Your Changes In Your App
Using yarn link, you can have your project use a local checkout of the react-admin package instead of downloading from npm. This allows you to test react-admin changes in your app.
The following instructions are targeting yarn >= v3 in the client app.
# Go to the folder of your client app
$ cd /code/path/to/myapp/
# Use the latest version of yarn package manager
$ corepack enable && yarn set version stable
# Replace the npm-installed version with a symlink to your local version
$ yarn link /code/path/to/react-admin/packages/react-admin
# If you modified additional internal packages in the react-admin monorepo, e.g. ra-core, also make a link
$ yarn link /code/path/to/react-admin/packages/ra-core
# Build all of the react-admin package distribution
$ cd /code/path/to/react-admin/ && make build
# Return to your app and ensure all dependencies have resolved
$ cd /code/path/to/myapp/ && yarn install
# Start your app
$ yarn start
Tip: If you are still using yarn v1 as your package manager in your client app, we strongly recommend you to update as it is frozen and no longer maintained.
Automated Tests
Automated tests are also crucial in our development process. You can run all the tests (linting, unit and functional tests) by calling:
make test
Unit tests use jest, so you should be able to run a subset of tests, or run tests continuously on change, by passing options to
yarn jest
Besides, tests related to the modified files are run automatically at commit using a git pre-commit hook. This means you won't be able to commit your changes if they break the tests.
When working on the end-to-end tests, you can leverage cypress runner by starting the simple example yourself (make run-simple or yarn run-simple) and starting cypress in another terminal (make test-e2e-local or yarn test-e2e-local).
Coding Standards
If you have coding standards problems, you can fix them automatically using prettier by calling
make prettier
However, these commands are run automatically at each commit so you shouldn't have to worry about them.
Documentation
If you want to contribute to the documentation, install jekyll, then call
make doc
And then browse to http://localhost:4000/
License
React-admin is licensed under the MIT License, sponsored and supported by marmelab. It is free to use, even for commercial purpose.
If you want to give back, please talk about it, help newcomers, subscribe to the Enterprise Edition, or contribute code.
Top Related Projects
Material UI: Comprehensive React component library that implements Google's Material Design. Free forever.
An enterprise-class UI design language and React UI library
A React-based library for creating sleek presentations using JSX syntax that gives you the ability to live demo your code.
🚀 Strapi is the leading open-source headless CMS. It’s 100% JavaScript/TypeScript, fully customizable, and developer-first.
The flexible backend for all your projects 🐰 Turn your DB into a headless CMS, admin panels, or apps with a custom UI, instant APIs, auth & more.
The superpowered headless CMS for Node.js — built with GraphQL and React
Convert  designs to code with AI
designs to code with AI

Introducing Visual Copilot: A new AI model to turn Figma designs to high quality code using your components.
Try Visual Copilot