 FastAdapter
FastAdapter
The bullet proof, fast and easy to use adapter library, which minimizes developing time to a fraction...
Top Related Projects
General data-binding package for Jackson (2.x): works on streaming API (core) implementation(s)
An image loading and caching library for Android focused on smooth scrolling
A powerful image downloading and caching library for Android
Powerful and flexible library for loading, caching and displaying images on Android.
An Android Animation library which easily add itemanimator to RecyclerView items.
Epoxy is an Android library for building complex screens in a RecyclerView
Quick Overview
FastAdapter is a powerful and flexible RecyclerView adapter library for Android. It simplifies the process of creating and managing complex RecyclerViews by providing a modular approach to item management, drag & drop functionality, and expandable items.
Pros
- Easy to use and highly customizable
- Supports multiple view types and complex layouts
- Provides built-in features like filtering, sorting, and selection
- Excellent performance with minimal boilerplate code
Cons
- Learning curve for advanced features
- May be overkill for simple list implementations
- Limited documentation for some edge cases
- Dependency on other libraries for certain functionalities
Code Examples
- Creating a simple list adapter:
val fastAdapter = FastAdapter.with(itemAdapter)
recyclerView.adapter = fastAdapter
itemAdapter.add(SimpleItem("Item 1"))
itemAdapter.add(SimpleItem("Item 2"))
- Adding click listeners:
fastAdapter.onClickListener = { view, adapter, item, position ->
Toast.makeText(this, "Clicked on item $position", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
false
}
- Implementing drag and drop:
val touchCallback = SimpleDragCallback()
val touchHelper = ItemTouchHelper(touchCallback)
touchHelper.attachToRecyclerView(recyclerView)
fastAdapter.withOnTouchListener { v, event, position, fastAdapter, item ->
if (event.actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN) {
touchHelper.startDrag(recyclerView.findViewHolderForAdapterPosition(position)!!)
}
false
}
Getting Started
To use FastAdapter in your Android project, add the following dependencies to your build.gradle file:
dependencies {
implementation 'com.mikepenz:fastadapter:5.7.0'
implementation 'com.mikepenz:fastadapter-extensions-binding:5.7.0' // For view binding
implementation 'com.mikepenz:fastadapter-extensions-drag:5.7.0' // For drag & drop
implementation 'com.mikepenz:fastadapter-extensions-swipe:5.7.0' // For swipe actions
}
Then, create your item class extending AbstractItem, set up your RecyclerView, and create a FastAdapter instance:
class SimpleItem(val name: String) : AbstractItem<SimpleItem.ViewHolder>() {
override val layoutRes = R.layout.item_simple
override val type = R.id.fastadapter_sample_item
override fun getViewHolder(v: View) = ViewHolder(v)
class ViewHolder(view: View) : FastAdapter.ViewHolder<SimpleItem>(view) {
val name: TextView = view.findViewById(R.id.name)
override fun bindView(item: SimpleItem, payloads: List<Any>) {
name.text = item.name
}
override fun unbindView(item: SimpleItem) {
name.text = null
}
}
}
val itemAdapter = ItemAdapter<SimpleItem>()
val fastAdapter = FastAdapter.with(itemAdapter)
recyclerView.adapter = fastAdapter
Competitor Comparisons
General data-binding package for Jackson (2.x): works on streaming API (core) implementation(s)
Pros of jackson-databind
- More versatile for general JSON processing and data binding
- Supports a wide range of data formats beyond JSON (XML, YAML, etc.)
- Extensive customization options for complex data structures
Cons of jackson-databind
- Steeper learning curve due to its comprehensive feature set
- Can be overkill for simple JSON parsing tasks
- Potentially higher memory footprint for large datasets
Code Comparison
jackson-databind:
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
MyObject obj = mapper.readValue(jsonString, MyObject.class);
String json = mapper.writeValueAsString(obj);
FastAdapter:
FastAdapter<Item> fastAdapter = FastAdapter.with(items);
recyclerView.setAdapter(fastAdapter);
Summary
jackson-databind is a powerful library for JSON processing and data binding, offering extensive features and flexibility. It excels in complex scenarios involving various data formats and structures. However, its comprehensive nature can make it more challenging to learn and potentially less efficient for simpler tasks.
FastAdapter, on the other hand, is specifically designed for efficient RecyclerView adapters in Android development. It provides a streamlined approach to creating and managing list items, making it more suitable for UI-centric applications with less focus on data processing.
Choose jackson-databind for robust data handling and serialization needs, while FastAdapter is ideal for optimizing RecyclerView performance in Android apps.
An image loading and caching library for Android focused on smooth scrolling
Pros of Glide
- Specialized for image loading and caching, offering optimized performance for image-heavy applications
- Supports a wide range of image formats and sources, including GIFs and video thumbnails
- Extensive configuration options for image transformations and placeholders
Cons of Glide
- Limited to image handling, unlike FastAdapter's versatile item management for RecyclerViews
- Steeper learning curve due to its comprehensive API and configuration options
- Larger library size compared to FastAdapter's lightweight footprint
Code Comparison
FastAdapter (RecyclerView item binding):
class SimpleItem : AbstractItem<SimpleItem.ViewHolder>() {
override fun getLayoutRes(): Int = R.layout.simple_item
override fun getType(): Int = R.id.simple_item
override fun bindView(holder: ViewHolder, payloads: List<Any>) {
super.bindView(holder, payloads)
// Bind item data to views
}
}
Glide (Image loading):
Glide.with(context)
.load(imageUrl)
.placeholder(R.drawable.placeholder)
.error(R.drawable.error)
.into(imageView)
While FastAdapter focuses on efficient RecyclerView item management, Glide specializes in image loading and caching. FastAdapter offers more flexibility for various item types, whereas Glide excels in handling images from different sources with extensive customization options.
A powerful image downloading and caching library for Android
Pros of Picasso
- Specialized for image loading and caching
- Automatic memory and disk caching
- Supports image transformations and placeholders
Cons of Picasso
- Limited to image handling, not a general-purpose adapter
- Less flexibility for complex RecyclerView layouts
- No built-in support for item animations or drag-and-drop
Code Comparison
FastAdapter (RecyclerView setup):
val fastAdapter = FastAdapter.with(itemAdapter)
recyclerView.adapter = fastAdapter
Picasso (Image loading):
Picasso.get()
.load("https://example.com/image.jpg")
.into(imageView)
Key Differences
- FastAdapter is a versatile adapter for RecyclerView, while Picasso focuses on image loading and caching
- FastAdapter provides more control over item layouts and interactions
- Picasso simplifies image handling with built-in caching and transformations
Use Cases
- Use FastAdapter for complex RecyclerView implementations with diverse item types
- Choose Picasso for efficient image loading and caching in various Android views
Community and Support
- Both projects have active communities and regular updates
- FastAdapter offers more extensive documentation for advanced RecyclerView usage
- Picasso has widespread adoption and integration with many Android libraries
Powerful and flexible library for loading, caching and displaying images on Android.
Pros of Android-Universal-Image-Loader
- Extensive configuration options for image loading and caching
- Supports a wide range of image sources (network, file system, assets, etc.)
- Highly customizable with various display options and animations
Cons of Android-Universal-Image-Loader
- No longer actively maintained, last updated in 2016
- May not be optimized for modern Android development practices
- Lacks some features present in newer image loading libraries
Code Comparison
Android-Universal-Image-Loader:
ImageLoader imageLoader = ImageLoader.getInstance();
imageLoader.displayImage(imageUri, imageView, options);
FastAdapter:
FastAdapter<ImageItem> fastAdapter = new FastAdapter<>();
recyclerView.setAdapter(fastAdapter);
fastAdapter.add(new ImageItem().withImage(imageUri));
While Android-Universal-Image-Loader focuses on image loading and caching, FastAdapter is a more general-purpose adapter library for RecyclerViews. Android-Universal-Image-Loader provides more specific image handling capabilities, but FastAdapter offers a broader range of features for creating and managing list items in Android applications.
FastAdapter is actively maintained and integrates well with modern Android development practices, making it a more suitable choice for new projects. However, Android-Universal-Image-Loader may still be useful in legacy projects or situations where its specific image handling features are required.
An Android Animation library which easily add itemanimator to RecyclerView items.
Pros of recyclerview-animators
- Focuses specifically on animations for RecyclerView items
- Provides a wide range of pre-built animations out of the box
- Lightweight and easy to implement for simple animation needs
Cons of recyclerview-animators
- Limited to animations only, doesn't provide additional RecyclerView functionality
- May require more custom code for complex item management scenarios
- Less actively maintained compared to FastAdapter
Code Comparison
recyclerview-animators:
val animator = SlideInLeftAnimator()
recyclerView.itemAnimator = animator
FastAdapter:
val fastAdapter = FastAdapter.with(itemAdapter)
recyclerView.adapter = fastAdapter
fastAdapter.withSelectable(true)
fastAdapter.withMultiSelect(true)
Summary
recyclerview-animators is a specialized library for adding animations to RecyclerView items, offering a variety of pre-built animations. It's lightweight and easy to implement for basic animation needs. However, it's limited to animations and may require additional code for complex item management.
FastAdapter, on the other hand, is a more comprehensive solution for RecyclerView management. It provides a wider range of features beyond animations, including item selection, filtering, and drag-and-drop functionality. FastAdapter is more suitable for complex RecyclerView implementations but may have a steeper learning curve for simple use cases.
Choose recyclerview-animators for quick and easy animations, or FastAdapter for a more robust RecyclerView management solution.
Epoxy is an Android library for building complex screens in a RecyclerView
Pros of Epoxy
- More powerful and flexible for complex RecyclerView layouts
- Built-in support for data binding and view binding
- Automatic diffing and efficient updates
Cons of Epoxy
- Steeper learning curve due to its complexity
- Requires more boilerplate code for simple use cases
- Heavier dependency compared to FastAdapter
Code Comparison
FastAdapter:
val fastAdapter = FastAdapter.with(itemAdapter)
recyclerView.adapter = fastAdapter
itemAdapter.add(SimpleItem("Item 1"))
Epoxy:
class Controller : EpoxyController() {
override fun buildModels() {
simpleItem {
id("item1")
title("Item 1")
}
}
}
recyclerView.setController(controller)
Summary
FastAdapter is simpler and more lightweight, making it ideal for straightforward RecyclerView implementations. Epoxy, on the other hand, offers more advanced features and flexibility, making it better suited for complex, data-driven layouts. The choice between the two depends on the specific requirements of your project and the level of complexity you need to handle in your RecyclerViews.
Convert  designs to code with AI
designs to code with AI

Introducing Visual Copilot: A new AI model to turn Figma designs to high quality code using your components.
Try Visual CopilotREADME
FastAdapter
The FastAdapter is here to simplify creating adapters for RecyclerViews. Don't worry about the adapter anymore. Just write the logic for how your view/item should look like, and you are done. It's blazing fast, minimizing the code you need to write, and is easy to extend.
What's included ð • Setup ð ï¸ • Migration Guide 𧬠• Used by • Sample App
What's included ð
- Core module 100% in Kotlin
- Click / Long-Click listeners
- Selection / Multi-Selection (MultiselectSample, CheckBoxSample, RadioButtonSample)
- Expandable items (ExpandableSample, IconGridSample ,AdvancedSample)
- Write less code, get better results
- Highly optimized code
- Simple Drag & Drop (SimpleItemListSample)
- Headers (StickyHeaderSample, AdvancedSample)
- Footers
- Filter (SimpleItemListSample)
- Includes suggestions from the Android Team
- Easily extensible
- Endless Scroll (EndlessScrollSample)
- "Leave-Behind"-Pattern (SwipeListSample)
- Split item view and model (ModelItem, MultiTypeModelItem)
- Chain other Adapters (SimpleItemListSample, StickyHeaderSample)
- Comes with useful Helpers
- ActionModeHelper (MultiselectSample)
- UndoHelper (MultiselectSample)
- FastScroller (external lib) (SimpleItemListSample)
- Paging (via Jetpack paging lib) (PagedActivity)
- More to come...
Preview
Screenshots ð
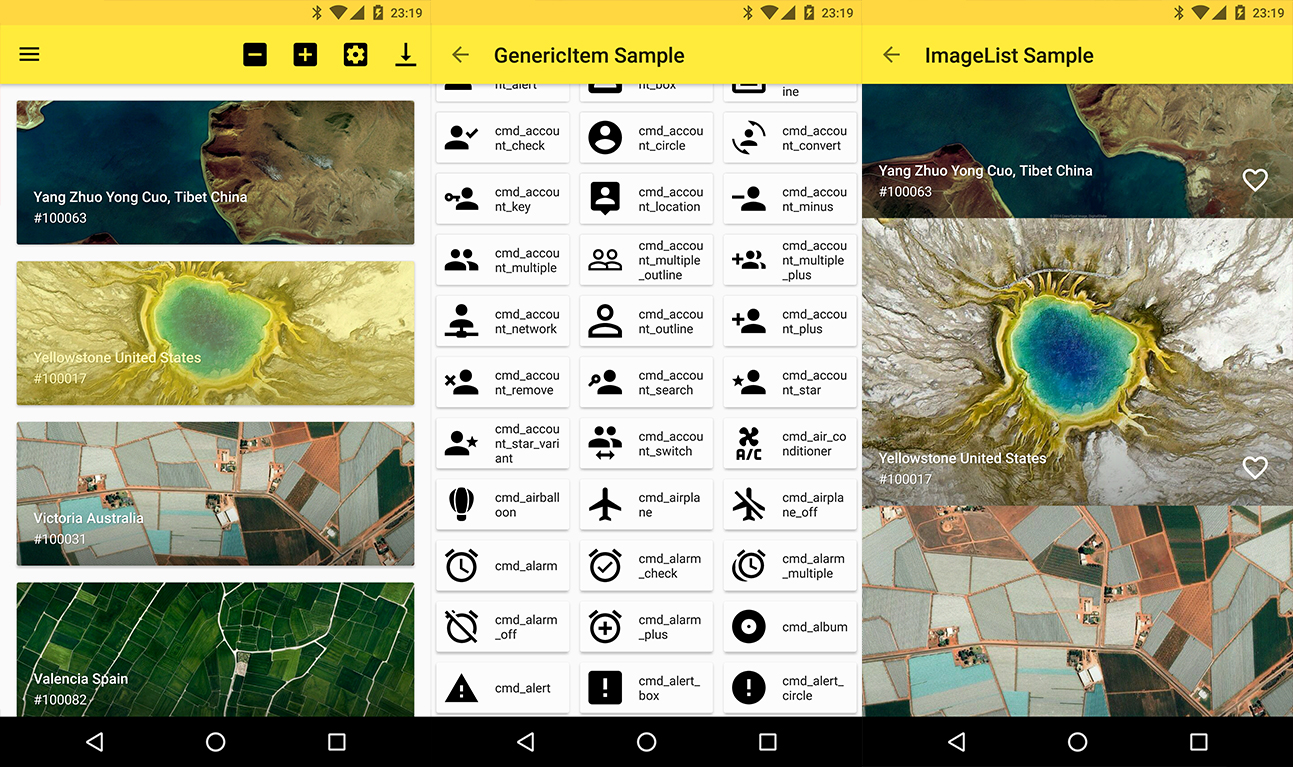
Setup
Latest releases ð
Provide the gradle dependency
The library is split up into core, commons, and extensions. The core functions are included in the following dependency.
implementation "com.mikepenz:fastadapter:${latestFastAdapterRelease}"
implementation "androidx.appcompat:appcompat:${androidX}"
implementation "androidx.recyclerview:recyclerview:${androidX}"
Expandable support is included and can be added via this
implementation "com.mikepenz:fastadapter-extensions-expandable:${latestFastAdapterRelease}"
Many helper classes are included in the following dependency.
implementation "com.mikepenz:fastadapter-extensions-binding:${latestFastAdapterRelease}" // view binding helpers
implementation "com.mikepenz:fastadapter-extensions-diff:${latestFastAdapterRelease}" // diff util helpers
implementation "com.mikepenz:fastadapter-extensions-drag:${latestFastAdapterRelease}" // drag support
implementation "com.mikepenz:fastadapter-extensions-paged:${latestFastAdapterRelease}" // paging support
implementation "com.mikepenz:fastadapter-extensions-scroll:${latestFastAdapterRelease}" // scroll helpers
implementation "com.mikepenz:fastadapter-extensions-swipe:${latestFastAdapterRelease}" // swipe support
implementation "com.mikepenz:fastadapter-extensions-ui:${latestFastAdapterRelease}" // pre-defined ui components
implementation "com.mikepenz:fastadapter-extensions-utils:${latestFastAdapterRelease}" // needs the `expandable`, `drag` and `scroll` extension.
// required for the ui components and the utils
implementation "com.google.android.material:material:${androidX}"
How to use
1. Implement your item
1a. Implement your item as usual (the easy way)
Just create a class which extends the AbstractItem as shown below. Implement the methods, and your item is ready.
open class SimpleItem : AbstractItem<SimpleItem.ViewHolder>() {
var name: String? = null
var description: String? = null
/** defines the type defining this item. must be unique. preferably an id */
override val type: Int
get() = R.id.fastadapter_sample_item_id
/** defines the layout which will be used for this item in the list */
override val layoutRes: Int
get() = R.layout.sample_item
override fun getViewHolder(v: View): ViewHolder {
return ViewHolder(v)
}
class ViewHolder(view: View) : FastAdapter.ViewHolder<SimpleItem>(view) {
var name: TextView = view.findViewById(R.id.material_drawer_name)
var description: TextView = view.findViewById(R.id.material_drawer_description)
override fun bindView(item: SimpleItem, payloads: List<Any>) {
name.text = item.name
description.text = item.name
}
override fun unbindView(item: SimpleItem) {
name.text = null
description.text = null
}
}
}
1b. Implement item with ViewBinding (the easiest way)
class BindingIconItem : AbstractBindingItem<IconItemBinding>() {
var name: String? = null
override val type: Int
get() = R.id.fastadapter_icon_item_id
override fun bindView(binding: IconItemBinding, payloads: List<Any>) {
binding.name.text = name
}
override fun createBinding(inflater: LayoutInflater, parent: ViewGroup?): IconItemBinding {
return IconItemBinding.inflate(inflater, parent, false)
}
}
Use the binding extension dependency in your application for this.
2. Set the Adapter to the RecyclerView
//create the ItemAdapter holding your Items
val itemAdapter = ItemAdapter<SimpleItem>()
//create the managing FastAdapter, by passing in the itemAdapter
val fastAdapter = FastAdapter.with(itemAdapter)
//set our adapters to the RecyclerView
recyclerView.setAdapter(fastAdapter)
//set the items to your ItemAdapter
itemAdapter.add(ITEMS)
3. Extensions
By default the FastAdapter only provides basic functionality, which comes with the abstraction of items as Item and Model.
And the general functionality of adding/removing/modifying elements. To enable selections, or expandables the provided extensions need to be activated.
3.1. SelectExtension
// Gets (or creates and attaches if not yet existing) the extension from the given `FastAdapter`
val selectExtension = fastAdapter.getSelectExtension()
// configure as needed
selectExtension.isSelectable = true
selectExtension.multiSelect = true
selectExtension.selectOnLongClick = false
// see the API of this class for more options.
3.2. ExpandableExtension
This requires the
fastadapter-extensions-expandableextension.
// Gets (or creates and attaches if not yet existing) the extension.
val expandableExtension = fastAdapter.getExpandableExtension()
// configure as needed
expandableExtension.isOnlyOneExpandedItem = true
For further details scroll down to the ExpandableItems (under advanced usage) section.
3. Click listener
fastAdapter.onClickListener = { view, adapter, item, position ->
// Handle click here
false
}
4. Click listeners for views inside your item
// just add an `EventHook` to your `FastAdapter` by implementing either a `ClickEventHook`, `LongClickEventHook`, `TouchEventHook`, `CustomEventHook`
fastAdapter.addEventHook(object : ClickEventHook<SimpleImageItem>() {
override fun onBind(viewHolder: RecyclerView.ViewHolder): View? {
//return the views on which you want to bind this event
return if (viewHolder is SimpleImageItem.ViewHolder) {
viewHolder.viewWhichReactsOnClick
} else {
null
}
}
override fun onClick(v: View, position: Int, fastAdapter: FastAdapter<SimpleImageItem>, item: SimpleImageItem) {
//react on the click event
}
})
5. Filter
// Call this in onQueryTextSubmit() & onQueryTextChange() when using SearchView
itemAdapter.filter("yourSearchTerm")
itemAdapter.itemFilter.filterPredicate = { item: SimpleItem, constraint: CharSequence? ->
item.name?.text.toString().contains(constraint.toString(), ignoreCase = true)
}
filter() should return true for items to be retained and false for items to be removed.
6. Drag and drop
This requires the
fastadapter-extensions-dragextension.
First, attach ItemTouchHelper to RecyclerView.
val dragCallback = SimpleDragCallback()
val touchHelper = ItemTouchHelper(dragCallback)
touchHelper.attachToRecyclerView(recyclerView)
Implement ItemTouchCallback interface in your Activity, and override the itemTouchOnMove() method.
override fun itemTouchOnMove(oldPosition: Int, newPosition: Int): Boolean {
DragDropUtil.onMove(fastItemAdapter.itemAdapter, oldPosition, newPosition) // change position
return true
}
7. Using different ViewHolders (like HeaderView)
Start by initializing your adapters:
// Header is a model class for your header
val headerAdapter = ItemAdapter<Header>()
Initialize a Model FastAdapter:
val itemAdapter = GenericItemAdapter()
Finally, set the adapter:
val fastAdapter: GenericFastAdapter = FastAdapter.with(headerAdapter, itemAdapter) //the order defines in which order the items will show up
// alternative the super type of both item adapters can be used. e.g.:
recyclerView.setAdapter(fastAdapter)
8. Infinite (endless) scrolling
Create a FooterAdapter. We need this to display a loading ProgressBar at the end of our list. (Don't forget to pass it into FastAdapter.with(..))
val footerAdapter = ItemAdapter<ProgressItem>()
Keep in mind that ProgressItem is provided by FastAdapterâs extensions.
recyclerView.addOnScrollListener(object : EndlessRecyclerOnScrollListener(footerAdapter) {
override fun onLoadMore(currentPage: Int) {
footerAdapter.clear()
footerAdapter.add(ProgressItem())
// Load your items here and add it to FastAdapter
itemAdapter.add(NEWITEMS)
}
})
For the complete tutorial and more features such as multi-select and CAB check out the sample app.
Advanced Usage
Proguard
- As of v2.5.0 there are no more known requirements to use the
FastAdapterwith Proguard
ExpandableItems
The FastAdapter comes with support for expandable items. After adding the dependency set up the Expandable extension via:
val expandableExtension = fastAdapter.getExpandableExtension()
Expandable items have to implement the IExpandable interface, and the sub items the ISubItem interface. This allows better support.
The sample app provides sample implementations of those. (Those in the sample are kept Model which allows them to be used with different parent / subitems)
As of the way how SubItems and their state are handled it is highly recommended to use the identifier based StateManagement. Just add withPositionBasedStateManagement(false) to your FastAdapter setup.
A simple item just needs to extend from the AbstractExpandableItem and provide the ViewHolder as type.
open class SimpleSubExpandableItem : AbstractExpandableItem<SimpleSubExpandableItem.ViewHolder>() {
/**
* BASIC ITEM IMPLEMENTATION
*/
}
// See the SimpleSubExpandableItem.kt of the sample application for more details.
Articles
- RecyclerView Adapter made easy (FastAdapter v2.x)
Used by
Mike Penz:
- AboutLibraries https://github.com/mikepenz/AboutLibraries
- Android-Iconics https://github.com/mikepenz/Android-Iconics
- ItemAnimators https://github.com/mikepenz/ItemAnimators
- MaterialDrawer https://github.com/mikepenz/MaterialDrawer
Developed By
-
Mike Penz
-
Fabian Terhorst
Contributors
This free, open source software was also made possible by a group of volunteers that put many hours of hard work into it. See the CONTRIBUTORS.md file for details.
Special mentions
A special thanks to the very active contributors who added many improvements to this library.
License
Copyright 2021 Mike Penz
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.
Top Related Projects
General data-binding package for Jackson (2.x): works on streaming API (core) implementation(s)
An image loading and caching library for Android focused on smooth scrolling
A powerful image downloading and caching library for Android
Powerful and flexible library for loading, caching and displaying images on Android.
An Android Animation library which easily add itemanimator to RecyclerView items.
Epoxy is an Android library for building complex screens in a RecyclerView
Convert  designs to code with AI
designs to code with AI

Introducing Visual Copilot: A new AI model to turn Figma designs to high quality code using your components.
Try Visual Copilot